Technology
Designing a better cement clinker
Published
9 years agoon
By
admin
Panyam Cements from Andhra Pradesh has implemented a non-linear model to formulate a better clinker composition. Sreekanth Sajjala recounts the results obtained with non-linear modelling.
Designing a better or a different clinker is a time-consuming effort. Right from the raw mix, the coal and the operating parameters of the kiln have to be changed. Often, this can impact the sta-ble running of the kiln which becomes very expensive in terms of fuel consumption and sub-optimal production.
Assessing a new clinker is also not instant, it takes 28 days for all the strengths to be measured. This means that all in all, it takes about two-three months to design and evaluate a new clinker composition. There currently are no accurate prediction methods as the formation of clinker and the link between its material properties and chemical composition are not linear. Machine learning is a field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. Computers are not programmed but are expected to identify patterns and thereby build a model which can generate repeatable results.
These patterns need not be linear or direct, which means that machine learning methods are ex-tremely well suited in the prediction of cement properties.
Our Scenario
Our clinker had excellent 28-day strengths (680-700) and relatively lower 1-day strengths (140-160); this meant that our customers were disappointed by our PSC where the addition of GGBS (a material with a low heat of hydration) further lowered the 1-day strengths. This meant that we couldn’t mix more than 45 per cent GGBS in PSC though up to 60 per cent was allowed. We needed a clinker which would have higher initial strengths and quickly, as the opportunity cost was quite high. We, in the R&D division, turned to non-linear modeling to design the chemical composition of a clinker that would have up to 50 per cent higher initial strengths.
The most important thing in non-linear modeling was the availability of reliable data and a lot of it. Though our lab maintained immaculate records of both chemical and physical aspects of clinker, they were all in physical form. We digitised over 18 months’ worth of clinker data. Over 500 records were used as the training set. The surface area and percentage of gypsum were not taken into account, as all the lab samples were ground evenly and had the same amount of gyp-sum.
The Method
A neural network with four hidden layers was used with a hyperbolic tangent activation func-tion. Neural networks are computer systems modeled on the human brain and nervous system. They are used mainly for non-linear modeling and computer vision. Each node is assigned a weight with which the incoming input matrix is multiplied by. These weights are assigned during training where back propagation and other training methods are used with the training set. The model is then validated on a smaller separate dataset called the testing set.
The results
When the directional output was plotted with the various variables, the optimal composition was realised for higher initial strengths. We were able to formulate a viable clinker with over 50 per cent higher 1-day strength and 10 per cent lower 28-day strength. The next step was to design a model which could predict the kiln’s output chemical composition on the basis of the raw meal chemical composition, coal consumption and the operating parameters. We believe this could help us match the raw mix and coal more optimally and help us preserve coal and high grade limestone. One thing non-linear modeling can do which linear modeling cannot do, is factor in the indirect impact of trace compounds like MgO. Non-linear models, by observing correlations, can link trace elects to the indirect effects like their function in the formation of major com-pounds. This model has helped us increase how much GGBS we add in our PSC and has contributed to great cost savings through clinker conservation.
About the author
Sreekanth Sajjala is a part of the R&D team at Panyam Cements, Andhra Pradesh. He is one of the main contributors to the model Panyam has developed to predict the strength of clinker on the basis of its chemical composition.
You may like
-


Low-Carbon Future: Reimagining Cement
-


Qlar’s New Bucket Elevator Sets a New Standard
-


Adani’s Strategic Emergence in India’s Cement Landscape
-


Cementing Circularity: From Waste to Value
-


ECS/ProcessExpert v9.1 (PXP) increases productivity at GCC Chihuahua
-


AFR can provide economic and environmental benefits

Ponnusamy Sampathkumar, Consultant – Process Optimisation and Training, discusses the role of skilled operators as the decisive link between advanced additives, digital control and world-class mill performance.
The industry always tries to reduce the number of operators in the Centre Control Room. (CCR) Though the concept was succeeded to certain extent, still we need a skilled person in the CCR.
In an era where artificial intelligence (AI) grinding aids, performance enhancers, and digital optimisation tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated, it’s tempting to believe that chemistry alone can solve the challenges of mill efficiency. Yet plants that consistently outperform their peers share one common trait: highly skilled operators who understand the mill as a living system, not just a machine.
Additives can improve flowability, reduce agglomeration, and enhance separator efficiency, but they cannot replace the nuanced judgement that comes from experience. Grinding is a dynamic process influenced by raw material variability, moisture, liner wear, ball charge distribution, ventilation, and separator loading. No additive can fully compensate for poor control of these fundamentals.
Operators see what additives cannot
When I joined the cement industry in 1981, not much modernisation was available then. Mostly the equipment was run from the local panel. Once I was visiting the cement mills section. The cement mills were water sprayed over the shell to reduce the temperature to avoid the gypsum disintegration.
The operator stopped the feeding for one of the mills. When I asked the reason, he replied that mill was getting jammed, and he added that he could understand the mill condition by its sound. I also learned that and it was useful throughout my career. In another plant I saw the ‘Electronic Ear,’ which checked the sound of the mill and the signal was looped with feed control!
Whatever modernisation we achieve, it is from the human factor that the development starts.
Additives respond to conditions; operators interpret them.
A skilled operator can detect subtle shifts, like a change in mill sound, a slight variation in circulating load, or a drift in separator cut point. It’s long before instrumentation flags a problem. These micro-observations often prevent major efficiency losses.
Additives work best when the process is stable
I would like to share one real time incident. The mill was running on auto mode looped with the mill outlet bucket elevator kilowatt. (KW)There was a decrease in the KW, and the mill feed was increased by the auto control (PID). After a while, the operator stopped both the feed and the mill. He asked the local operator to check the airslide between mill outlet and the elevator. They found the airslide was jammed and no material flow to the elevator!
The operator deduced the abnormality by his experience by seeing the conditions and the rate of increase of the feed by the auto control.
It’s always the human factor that adds value to the optimisation.
Grinding aids are multipliers,
not magicians.
They deliver maximum benefit only when:
• Mill ventilation is correct
• Ball charge is balanced
• Feed moisture is controlled
• Separator speed and loading are improved
• Blaine targets are realistic
Without these fundamentals, even advanced additives may become costly investments. The operator is responsible for ensuring process stability, whether using a ball mill or a vertical mill. After ensuring the system is stable, the operator observes it briefly before transitioning to automatic control. If there is any anomaly in the system the operator at once takes control of the system, stabilises and bring back to auto control.
Skilled operators adapt in real time
It will be interesting to note that the operators who operate from local panel start to operate from DCS also. They have the experience and the ability to adapt the changes. Operator checks each parameter deeply. Any meagre change in the parameters is also visible to him.
Raw materials change. Weather changes. Wear patterns change.
A skilled operator adjusts:
• Feed rate
• Water injection
• Separator speed
• Grinding pressure (in VRMs)
• Mill load distribution.
These adjustments require intuition built from years of experience, something no additive can replicate.
Human insight prevents over reliance on additives
Plants sometimes increase additive dosage to mask deeper issues like:
• Poor clinker quality
• Inadequate drying capacity
• Incorrect ball gradation
• High residue due to worn separator internals.
A knowledgeable operator finds root causes instead of chasing temporary chemical fixes.
The real optimisation sweet spot is reached when:
• Operators understand how additives interact with their specific mill.
• Additive suppliers collaborate with plant teams.
• Process data is interpreted by humans who know the mill’s behaviour.
This constructive collaboration consistently delivers:
• Lower kWh/t
• Higher throughput
• Better product consistency
• Optimum standard deviation.
Advanced additives are powerful tools, but they are not substitutes for human ability. Grinding optimisation is ultimately a human driven discipline, where skilled operators make the difference between average performance and world class efficiency. Additives enhance the process but operators
control it.
About the author:
Ponnusamy Sampathkumar, Consultant – Process Optimisation and Training, is a seasoned cement process consultant with 43+ years of global experience in plant operations, process optimisation, refractory management, safety systems and training multicultural teams across international cement plants.
Concrete
Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation
Published
3 weeks agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Professor Procyon Mukherjee discusses how as the cement industry accelerates its shift towards digitalisation, data-driven technologies are becoming the mainstay of sustainability and control across the value chain.
The cement industry, long perceived as traditional and resistant to change, is undergoing a profound transformation driven by digital technologies. As global infrastructure demand grows alongside increasing pressure to decarbonise and improve productivity, cement manufacturers are adopting data-centric tools to enhance performance across the value chain. Nowhere is this shift more impactful than in grinding, which is the energy-intensive final stage of cement production, and in the materials that make grinding more efficient: grinding media and grinding aids.
The imperative for digitalisation
Cement production accounts for roughly 7 per cent to 8 per cent of global CO2 emissions, largely due to the energy intensity of clinker production and grinding processes. Digital solutions, such as AI-driven process controls and digital twins, are helping plants improve stability, cut fuel use and reduce emissions while maintaining consistent product quality. In one deployment alongside ABB’s process controls at a Heidelberg plant in Czechia, AI tools cut fuel use by 4 per cent and emissions by 2 per cent, while also improving operational stability.
Digitalisation in cement manufacturing encompasses a suite of technologies, broadly termed as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), AI and machine learning, predictive analytics, cloud-based platforms, advanced process control and digital twins, each playing a role in optimising various stages of production from quarrying to despatch.
Grinding: The crucible of efficiency and cost
Of all the stages in cement production, grinding is among the most energy-intensive, historically consuming large amounts of electricity and representing a significant portion of plant operating costs. As a result, optimising grinding operations has become central to digital transformation strategies.
Modern digital systems are transforming grinding mills from mechanical workhorses into intelligent, interconnected assets. Sensors throughout the mill measure parameters such as mill load, vibration, mill speed, particle size distribution, and power consumption. This real-time data, fed into machine learning and advanced process control (APC) systems, can dynamically adjust operating conditions to maintain optimal throughput and energy usage.
For example, advanced grinding systems now predict inefficient conditions, such as impending mill overload, by continuously analysing acoustic and vibration signatures. The system can then proactively adjust clinker feed rates and grinding media distribution to sustain optimal conditions, reducing energy consumption and improving consistency.
Digital twins: Seeing grinding in the virtual world
One of the most transformative digital tools applied in cement grinding is the digital twin, which a real-time virtual replica of physical equipment and processes. By integrating sensor data and
process models, digital twins enable engineers to simulate process variations and run ‘what-if’
scenarios without disrupting actual production. These simulations support decisions on variables such as grinding media charge, mill speed and classifier settings, allowing optimisation of energy use and product fineness.
Digital twins have been used to optimise kilns and grinding circuits in plants worldwide, reducing unplanned downtime and allowing predictive maintenance to extend the life of expensive grinding assets.
Grinding media and grinding aids in a digital era
While digital technologies improve control and prediction, materials science innovations in grinding media and grinding aids have become equally crucial for achieving performance gains.
Grinding media, which comprise the balls or cylinders inside mills, directly influence the efficiency of clinker comminution. Traditionally composed of high-chrome cast iron or forged steel, grinding media account for nearly a quarter of global grinding media consumption by application, with efficiency improvements translating directly to lower energy intensity.
Recent advancements include ceramic and hybrid media that combine hardness and toughness to reduce wear and energy losses. For example, manufacturers such as Sanxin New Materials in China and Tosoh Corporation in Japan have developed sub-nano and zirconia media with exceptional wear resistance. Other innovations include smart media embedded with sensors to monitor wear, temperature, and impact forces in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and optimal media replacement scheduling. These digitally-enabled media solutions can increase grinding efficiency by as much as 15 per cent.
Complementing grinding media are grinding aids, which are chemical additives that improve mill throughput and reduce energy consumption by altering the surface properties of particles, trapping air, and preventing re-agglomeration. Technology leaders like SIKA AG and GCP Applied Technologies have invested in tailored grinding aids compatible with AI-driven dosing platforms that automatically adjust additive concentrations based on real-time mill conditions. Trials in South America reported throughput improvements nearing 19 per cent when integrating such digital assistive dosing with process control systems.
The integration of grinding media data and digital dosing of grinding aids moves the mill closer to a self-optimising system, where AI not only predicts media wear or energy losses but prescribes optimal interventions through automated dosing and operational adjustments.
Global case studies in digital adoption
Several cement companies around the world exemplify digital transformation in practice.
Heidelberg Materials has deployed digital twin technologies across global plants, achieving up to 15 per cent increases in production efficiency and 20 per cent reductions in energy consumption by leveraging real-time analytics and predictive algorithms.
Holcim’s Siggenthal plant in Switzerland piloted AI controllers that autonomously adjusted kiln operations, boosting throughput while reducing specific energy consumption and emissions.
Cemex, through its AI and predictive maintenance initiatives, improved kiln availability and reduced maintenance costs by predicting failures before they occurred. Global efforts also include AI process optimisation initiatives to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
Challenges and the road ahead
Despite these advances, digitalisation in cement grinding faces challenges. Legacy equipment may lack sensor readiness, requiring retrofits and edge-cloud connectivity upgrades. Data governance and integration across plants and systems remains a barrier for many mid-tier producers. Yet, digital transformation statistics show momentum: more than half of cement companies have implemented IoT sensors for equipment monitoring, and digital twin adoption is growing rapidly as part of broader Industry 4.0 strategies.
Furthermore, as digital systems mature, they increasingly support sustainability goals: reduced energy use, optimised media consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions. By embedding intelligence into grinding circuits and material inputs like grinding aids, cement manufacturers can strike a balance between efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
Digitalisation is not merely an add-on to cement manufacturing. It is reshaping the competitive and sustainability landscape of an industry often perceived as inertia-bound. With grinding representing a nexus of energy intensity and cost, digital technologies from sensor networks and predictive analytics to digital twins offer new levers of control. When paired with innovations in grinding media and grinding aids, particularly those with embedded digital capabilities, plants can achieve unprecedented gains in efficiency, predictability and performance.
For global cement producers aiming to reduce costs and carbon footprints simultaneously, the future belongs to those who harness digital intelligence not just to monitor operations, but to optimise and evolve them continuously.
About the author:
Professor Procyon Mukherjee, ex-CPO Lafarge-Holcim India, ex-President Hindalco, ex-VP Supply Chain Novelis Europe, has been an industry leader in logistics, procurement, operations and supply chain management. His career spans 38 years starting from Philips, Alcan Inc (Indian Aluminum Company), Hindalco, Novelis and Holcim. He authored the book, ‘The Search for Value in Supply Chains’. He serves now as Visiting Professor in SP Jain Global, SIOM and as the Adjunct Professor at SBUP. He advises leading Global Firms including Consulting firms on SCM and Industrial Leadership and is a subject matter expert in aluminum and cement. An Alumnus of IIM Calcutta and Jadavpur University, he has completed the LH Senior Leadership Programme at IVEY Academy at Western University, Canada.
Concrete
Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing
Published
3 weeks agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Dr Y Chandri Naidu, Chief Technology Officer, Nextcem Consulting highlights how digital technologies are enabling Indian cement plants to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and transition toward sustainable, low-carbon manufacturing.
Cement manufacturing is inherently resource- and energy-intensive due to high-temperature clinkerisation and extensive material handling and grinding operations. In India, where cement demand continues to grow in line with infrastructure development, producers must balance capacity expansion with sustainability commitments. Energy costs constitute a major share of operating expenditure, while process-related carbon dioxide emissions from limestone calcination remain unavoidable.
Traditional optimisation approaches, which are largely dependent on operator experience, static control logic and offline laboratory analysis, have reached their practical limits. This is especially evident when higher levels of alternative fuel and raw materials (AFR) are introduced or when raw material variability increases.
Digital technologies provide a systematic pathway to manage this complexity by enabling
real-time monitoring, predictive optimisation and integrated decision-making across cement manufacturing operations.
Digital cement manufacturing is enabled through a layered architecture integrating operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT). At the base are plant instrumentation, analysers, and automation systems, which generate continuous process data. This data is contextualised and analysed using advanced analytics and AI platforms, enabling predictive and prescriptive insights for operators and management.
Digital optimisation of energy efficiency
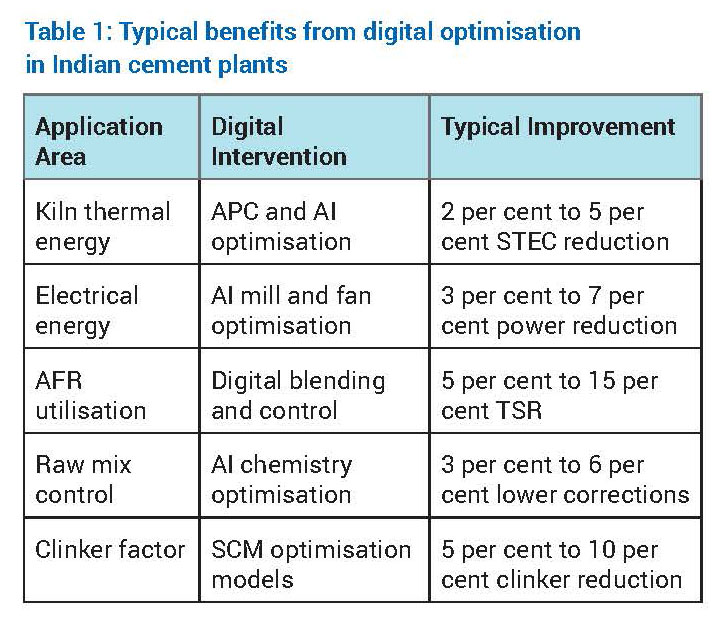
- Thermal energy optimisation
The kiln and calciner system accounts for approximately 60 per cent to 65 per cent of total energy consumption in an integrated cement plant. Digital optimisation focuses on reducing specific thermal energy consumption (STEC) while maintaining clinker quality and operational stability.
Advanced Process Control (APC) stabilises critical parameters such as burning zone temperature, oxygen concentration, kiln feed rate and calciner residence time. By minimising process variability, APC reduces the need for conservative over-firing. Artificial intelligence further enhances optimisation by learning nonlinear relationships between raw mix chemistry, AFR characteristics, flame dynamics and heat consumption.
Digital twins of kiln systems allow engineers to simulate operational scenarios such as increased AFR substitution, altered burner momentum or changes in raw mix burnability without operational risk. Indian cement plants adopting these solutions typically report STEC reductions in the range of 2 per cent to 5 per cent. - Electrical energy optimisation
Electrical energy consumption in cement plants is dominated by grinding systems, fans and material transport equipment. Machine learning–based optimisation continuously adjusts mill parameters such as separator speed, grinding pressure and feed rate to minimise specific power consumption while maintaining product fineness.
Predictive maintenance analytics identify inefficiencies caused by wear, fouling or imbalance in fans and motors. Plants implementing plant-wide electrical energy optimisation typically achieve
3 per cent to 7 per cent reduction in specific power consumption, contributing to both cost savings and indirect CO2 reduction.
Digital enablement of AFR
AFR challenges in the Indian context: Indian cement plants increasingly utilise biomass, refuse-derived fuel (RDF), plastic waste and industrial by-products. However, variability in calorific value, moisture, particle size, chlorine and sulphur content introduces combustion instability, build-up formation and emission risks.
Digital AFR management: Digital platforms integrate real-time AFR quality data from online analysers with historical kiln performance data. Machine learning models predict combustion behaviour, flame stability and emission trends for different AFR combinations. Based on these predictions, fuel feed distribution, primary and secondary air ratios, and burner momentum are dynamically adjusted to ensure stable kiln operation. Digitally enabled AFR management in cement plants will result in increased thermal substitution rates by 5-15 percentage points, reduced fossil fuel dependency, and improved kiln stability.
Digital resource and raw material optimisation
Raw mix control: Raw material variability directly affects kiln operation and clinker quality. AI-driven raw mix optimisation systems continuously adjust feed proportions to maintain target chemical parameters such as Lime Saturation Factor (LSF), Silica Modulus (SM), and Alumina Modulus (AM). This reduces corrective material usage and improves kiln thermal efficiency.
Clinker factor reduction: Reducing clinker factor through supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) such as fly ash, slag and calcined clay is a key decarbonisation lever. Digital models simulate blended cement performance, enabling optimisation of SCM proportions while maintaining strength and durability requirements.
Challenges and strategies for digital adoption
Key challenges in Indian cement plants include data quality limitations due to legacy instrumentation, resistance to algorithm-based decision-making, integration complexity across multiple OEM systems, and site-specific variability in raw materials and fuels.
Successful digital transformation requires strengthening the data foundation, prioritising high-impact use cases such as kiln APC and energy optimisation, adopting a human-in-the-loop approach, and deploying modular, scalable digital platforms with cybersecurity by design.
Future Outlook
Future digital cement plants will evolve toward autonomous optimisation, real-time carbon intensity tracking, and integration with emerging decarbonisation technologies such as carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS). Digital platforms will also support ESG reporting and regulatory compliance.
Digital pathways offer a practical and scalable solution for sustainable cement manufacturing in India. By optimising energy consumption, enabling higher AFR substitution and improving resource efficiency, digital technologies deliver measurable environmental and economic benefits. With appropriate data infrastructure, organisational alignment and phased implementation, digital transformation will remain central to the Indian cement industry’s low-carbon transition.
About the author:
Dr Y Chandri Naidu is a cement industry professional with 30+ years of experience in process optimisation, quality control and quality assistance, energy conservation and sustainable manufacturing, across leading organisations including NCB, Ramco, Prism, Ultratech, HIL, NCL and Vedanta. He is known for guiding teams, developing innovative plant solutions and promoting environmentally responsible cement production. He is also passionate about mentoring professionals and advancing durable, resource efficient technologies for future of construction materials.

NDMC Rolls Out Intensive Sanitation Drive Across Lutyens Delhi

UltraTech Appoints Jayant Dua As MD-Designate For 2027

Merlin Prime Spaces Acquires 13,185 Sq M Land Parcel In Pune

Adani Cement and Naredco Partner to Promote Sustainable Construction

Operational Excellence Redefined!

NDMC Rolls Out Intensive Sanitation Drive Across Lutyens Delhi

UltraTech Appoints Jayant Dua As MD-Designate For 2027

Merlin Prime Spaces Acquires 13,185 Sq M Land Parcel In Pune

Adani Cement and Naredco Partner to Promote Sustainable Construction












