Concrete
Strategic Capacity Enhancement
Published
2 years agoon
By
admin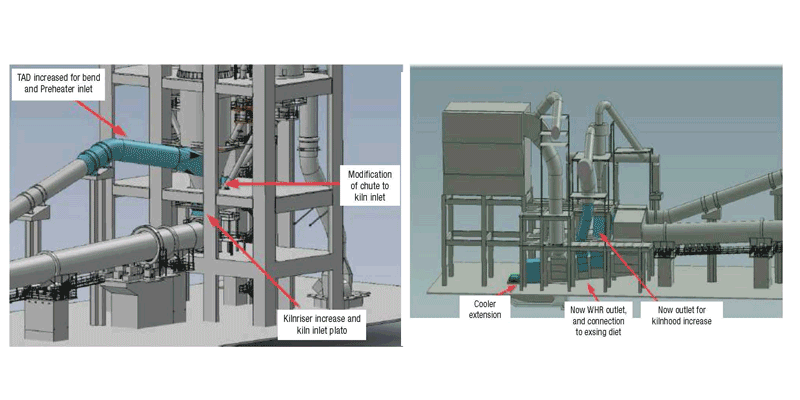
Amarkant Pandey, Deputy General Manager (Process), Prism Johnson (Cement Division), Satna, presents a case study on capacity enhancement of clinker production in an existing kiln.
This case study outlines the strategic initiatives taken to enhance production capacity of Prism Johnson (Unit-2) from 8000 TPD to 9100 TPD. This would help the company to expand its market share, develop new products and fortify our position in the cement industry.
With a consistent increase in regional demand and a positive market outlook, it was imperative for Prism Johnson’s Unit-2 to augment its production capacity from 8000 TPD to 9100 TPD in FY 2020-21. This enhancement aligned with our commitment to provide high-quality cement products while maintaining operational efficiency.
Cement capacity and production
The production capacity of Prism Johnson’s Unit-2 in FY-21 was at 8000 TPD. The plant was operating close to full capacity, with production data indicating steady growth trajectory, and it was evident that the current capacity was reaching its limits, thereby necessitating the need for expansion.
New capacity: The project entailed increasing the production capacity from 8000 TPD to 9100 TPD, thereby accommodating the rising market demand.
Timeline: The project was anticipated to span across 60 days.
Technology and process improvements: To optimise efficiency, the capacity enhancement project incorporates state-of-the-art technologies and process improvements. These advancements aim to reduce energy consumption, enhance product quality and ensure sustainable production practices.
The following technical upgradations has been implemented in order to support the upgraded production:
- 1. Kiln feed transport bucket elevators 352.BE250 and BE340 were upgraded (to 723 tph) to increase kiln tonnage.
- 2. Preheater ID Fans (2) were retrofitted to suit 9100 TPD.
- 3. Kiln feed rotary valves, ID Fan motors and VFDs have been changed.
- 4. Cooler was upgraded from SF 5×6 to SF-CB 5×7 (177 to 206 m2 grate area).
- 5. Clinker crusher was changed from hammer to heavy duty roller breaker HRB MF-418.
- 6. Expansion of kiln riser duct and connection of TAD to calciner.
- The areas where major upgradations took place are highlighted in these figures:
Risk assessment: Potential risks, including construction delays, regulatory approvals and associated delays, and market fluctuations, have been identified. A comprehensive risk mitigation strategy is in place to address and minimise these challenges.
Performance evaluation: Kiln started operating in January 2023 following the upgrade. We encountered several problems with M/s FLS’s cooler hydraulics. In January and February of 2023, a new hydraulic system was installed to replace the entire one. Kiln has produced 9100 TPD of clinker since April 2023. The plant performance before and after upgrading is tabulated below.
The chart indicates that an increase in clinker production resulted in a specific heat consumption reduction of around 5 Kcal/kg of clinker.
Presently, kiln volumetric loading is about 7.0, which is significantly higher than what is specified in the design. Additionally, with enhanced clinker production, we are meeting all quality targets (C3S, litre weight, free lime, etc.) for the clinker.
Challenges
• Crushed limestone size: Limestone size was in the higher side (+100mm to 5 per cent) and the gap between blow bar tip and lower grinding path was adjusted at 50mm previous the same was 70mm
• Pile homogeneity: The homogeneity of the pile was the biggest challenge due to huge variation in the mine’s limestone quality (6 different sources of mines). We increased the stacker speed from 11m/s to 13m/s to get better homogeneity. Also, CBA was installed to control variation in input materials from mines and standard deviation of pile was reduced from 80 to 20.
• Raw mills output: To fulfil raw meal requirements with increased kiln production, various modifications were done in the raw mill like replacement of old nozzle rings with new design nozzles etc.
• Kiln burner replacement: Old duo flex burner replaced with Pyrojet burner to reduce frequent snowman formation, increase utilisation of high sulphur petcoke and enhance flame quality.

Conclusion
The capacity enhancement by modification from 8000 TPD to 9100 TPD is a strategic move for Prism Johnson. It positions the company to meet market demands efficiently, contribute to regional development, and ensure the long-term sustainability and competitiveness of our operations.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Amarkant Pandey, Deputy General Manager (Process), Prism Johnson (Cement Division), Satna, holds an engineering degree in mechanical with specialisation in heat and power from Institution of Engineers (India). He has an in-depth understanding of cement manufacturing processes, including raw material preparation, clinker production and cement grinding. His responsibilities include process optimisation, quality control, production planning, etc.

Concrete
Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships
Published
9 hours agoon
February 19, 2026By
admin
Jean-Jacques Bois, President, Nanolike, discusses how real-time data is reshaping cement delivery planning and fleet performance.
As cement producers look to extract efficiency gains beyond the plant gate, real-time visibility and data-driven logistics are becoming critical levers of competitiveness. In this interview with Jean-Jacques Bois, President, Nanolike, we discover how the company is helping cement brands optimise delivery planning by digitally connecting RMC silos, improving fleet utilisation and reducing overall logistics costs.
How does SiloConnect enable cement plants to optimise delivery planning and logistics in real time?
In simple terms, SiloConnect is a solution developed to help cement suppliers optimise their logistics by connecting RMC silos in real time, ensuring that the right cement is delivered at the right time and to the right location. The core objective is to provide real-time visibility of silo levels at RMC plants, allowing cement producers to better plan deliveries.
SiloConnect connects all the silos of RMC plants in real time and transmits this data remotely to the logistics teams of cement suppliers. With this information, they can decide when to dispatch trucks, how to prioritise customers, and how to optimise fleet utilisation. The biggest savings we see today are in logistics efficiency. Our customers are able to sell and ship more cement using the same fleet. This is achieved by increasing truck rotation, optimising delivery routes, and ultimately delivering the same volumes at a lower overall logistics cost.
Additionally, SiloConnect is designed as an open platform. It offers multiple connectors that allow data to be transmitted directly to third-party ERP systems. For example, it can integrate seamlessly with SAP or other major ERP platforms, enabling automatic order creation whenever replenishment is required.
How does your non-exclusive sensor design perform in the dusty, high-temperature, and harsh operating conditions typical of cement plants?
Harsh operating conditions such as high temperatures, heavy dust, extreme cold in some regions, and even heavy rainfall are all factored into the product design. These environmental challenges are considered from the very beginning of the development process.
Today, we have thousands of sensors operating reliably across a wide range of geographies, from northern Canada to Latin America, as well as in regions with heavy rainfall and extremely high temperatures, such as southern Europe. This extensive field experience demonstrates that, by design, the SiloConnect solution is highly robust and well-suited for demanding cement plant environments.
Have you initiated any pilot projects in India, and what outcomes do you expect from them?
We are at the very early stages of introducing SiloConnect in India. Recently, we installed our
first sensor at an RMC plant in collaboration with FDC Concrete, marking our initial entry into the Indian market.
In parallel, we are in discussions with a leading cement producer in India to potentially launch a pilot project within the next three months. The goal of these pilots is to demonstrate real-time visibility, logistics optimisation and measurable efficiency gains, paving the way for broader adoption across the industry.
What are your long-term plans and strategic approach for working with Indian cement manufacturers?
For India, our strategy is to establish strong and reliable local partnerships, which will allow us to scale the technology effectively. We believe that on-site service, local presence, and customer support are critical to delivering long-term value to cement producers.
Ideally, our plan is to establish an Indian entity within the next 24 months. This will enable us to serve customers more closely, provide faster support and contribute meaningfully to the digital transformation of logistics and supply chain management in the Indian cement industry.

Pankaj Kejriwal, Whole Time Director and COO, Star Cement, on driving efficiency today and designing sustainability for tomorrow.
In an era where the cement industry is under growing pressure to decarbonise while scaling capacity, Star Cement is charting a pragmatic yet forward-looking path. In this conversation, Pankaj Kejriwal, Whole Time Director and COO, Star Cement, shares how the company is leveraging waste heat recovery, alternative fuels, low-carbon products and clean energy innovations to balance operational efficiency with long-term sustainability.
How has your Lumshnong plant implemented the 24.8 MW Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS), and what impact has it had on thermal substitution and energy costs?
Earlier, the cost of coal in the Northeast was quite reasonable, but over the past few years, global price increases have also impacted the region. We implemented the WHRS project about five years ago, and it has resulted in significant savings by reducing our overall power costs.
That is why we first installed WHRS in our older kilns, and now it has also been incorporated into our new projects. Going forward, WHRS will be essential for any cement plant. We are also working on utilising the waste gases exiting the WHRS, which are still at around 100 degrees Celsius. To harness this residual heat, we are exploring systems based on the Organic Rankine Cycle, which will allow us to extract additional power from the same process.
With the launch of Star Smart Building Solutions and AAC blocks, how are you positioning yourself in the low-carbon construction materials segment?
We are actively working on low-carbon cement products and are currently evaluating LC3 cement. The introduction of autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks provided us with an effective entry into the consumer-facing segment of the industry. Since we already share a strong dealer network across products, this segment fits well into our overall strategy.
This move is clearly supporting our transition towards products with lower carbon intensity and aligns with our broader sustainability roadmap.
With a diverse product portfolio, what are the key USPs that enable you to support India’s ongoing infrastructure projects across sectors?
Cement requirements vary depending on application. There is OPC, PPC and PSC cement, and each serves different infrastructure needs. We manufacture blended cements as well, which allows us to supply products according to specific project requirements.
For instance, hydroelectric projects, including those with NHPC, have their own technical norms, which we are able to meet. From individual home builders to road infrastructure, dam projects, and regions with heavy monsoon exposure, where weather-shield cement is required, we are equipped to serve all segments. Our ability to tailor cement solutions across diverse climatic and infrastructure conditions is a key strength.
How are you managing biomass usage, circularity, and waste reduction across
your operations?
The Northeast has been fortunate in terms of biomass availability, particularly bamboo. Earlier, much of this bamboo was supplied to paper plants, but many of those facilities have since shut down. As a result, large quantities of bamboo biomass are now available, which we utilise in our thermal power plants, achieving a Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) of nearly 60 per cent.
We have also started using bamboo as a fuel in our cement kilns, where the TSR is currently around 10 per cent to 12 per cent and is expected to increase further. From a circularity perspective, we extensively use fly ash, which allows us to reuse a major industrial waste product. Additionally, waste generated from HDPE bags is now being processed through our alternative fuel and raw material (AFR) systems. These initiatives collectively support our circular economy objectives.
As Star Cement expands, what are the key logistical and raw material challenges you face in scaling operations?
Fly ash availability in the Northeast is a constraint, as there are no major thermal power plants in the region. We currently source fly ash from Bihar and West Bengal, which adds significant logistics costs. However, supportive railway policies have helped us manage this challenge effectively.
Beyond the Northeast, we are also expanding into other regions, including the western region, to cater to northern markets. We have secured limestone mines through auctions and are now in the process of identifying and securing other critical raw material resources to support this expansion.
With increasing carbon regulations alongside capacity expansion, how do you balance compliance while sustaining growth?
Compliance and growth go hand in hand for us. On the product side, we are working on LC3 cement and other low-carbon formulations. Within our existing product portfolio, we are optimising operations by increasing the use of green fuels and improving energy efficiency to reduce our carbon footprint.
We are also optimising thermal energy consumption and reducing electrical power usage. Notably, we are the first cement company in the Northeast to deploy EV tippers at scale for limestone transportation from mines to plants. Additionally, we have installed belt conveyors for limestone transfer, which further reduces emissions. All these initiatives together help us achieve regulatory compliance while supporting expansion.
Looking ahead to 2030 and 2050, what are the key innovation and sustainability priorities for Star Cement?
Across the cement industry, carbon capture is emerging as a major focus area, and we are also planning to work actively in this space. In parallel, we see strong potential in green hydrogen and are investing in solar power plants to support this transition.
With the rapid adoption of solar energy, power costs have reduced dramatically – from 10–12 per unit to around2.5 per unit. This reduction will enable the production of green hydrogen at scale. Once available, green hydrogen can be used for electricity generation, to power EV fleets, and even as a fuel in cement kilns.
Burning green hydrogen produces only water and oxygen, eliminating carbon emissions from that part of the process. While process-related CO2 emissions from limestone calcination remain a challenge, carbon capture technologies will help address this. Ultimately, while becoming a carbon-negative industry is challenging, it is a goal we must continue to work towards.
Concrete
Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence
Published
10 hours agoon
February 19, 2026By
admin
Stoppage Insights instantly identifies root causes and maps their full operational impact.
In cement, mining and minerals processing operations, every unplanned stoppage equals lost production and reduced profitability. Yet identifying what caused a stoppage remains frustratingly complex. A single motor failure can trigger cascading interlocks and alarm floods, burying the root cause under layers of secondary events. Operators and maintenance teams waste valuable time tracing event chains when they should be solving problems. Until now.
Our latest innovation to our ECS Process Control Solution(1) eliminates this complexity. Stoppage Insights, available with the combined updates to our ECS/ControlCenter™ (ECS) software and ACESYS programming library, transforms stoppage events into clear, actionable intelligence. The system automatically identifies the root cause of every stoppage – whether triggered by alarms, interlocks, or operator actions – and maps all affected equipment. Operators can click any stopped motor’s faceplate to view what caused the shutdown instantly. The Stoppage UI provides a complete record of all stoppages with drill-down capabilities, replacing manual investigation with immediate answers.
Understanding root cause in Stoppage Insights
In Stoppage Insights, ‘root cause’ refers to the first alarm, interlock, or operator action detected by the control system. While this may not reveal the underlying mechanical, electrical or process failure that a maintenance team may later discover, it provides an actionable starting point for rapid troubleshooting and response. And this is where Stoppage Insights steps ahead of traditional first-out alarm systems (ISA 18.2). In this older type of system, the first alarm is identified in a group. This is useful, but limited, as it doesn’t show the complete cascade of events, distinguish between operator-initiated and alarm-triggered stoppages, or map downstream impacts. In contrast, Stoppage Insights provides complete transparency:
- Comprehensive capture: Records both regular operator stops and alarm-triggered shutdowns.
- Complete impact visibility: Maps all affected equipment automatically.
- Contextual clarity: Eliminates manual tracing through alarm floods, saving critical response time.
David Campain, Global Product Manager for Process Control Systems, says, “Stoppage Insights takes fault analysis to the next level. Operators and maintenance engineers no longer need to trace complex event chains. They see the root cause clearly and can respond quickly.”
Driving results
1.Driving results for operations teams
Stoppage Insights maximises clarity to minimise downtime, enabling operators to:
• Rapidly identify root causes to shorten recovery time.
• View initiating events and all affected units in one intuitive interface.
• Access complete records of both planned and unplanned stoppages
- Driving results for maintenance and reliability teams
Stoppage Insights helps prioritise work based on evidence, not guesswork:
• Access structured stoppage data for reliability programmes.
• Replace manual logging with automated, exportable records for CMMS, ERP or MES.(2)
• Identify recurring issues and target preventive maintenance effectively.
A future-proof and cybersecure foundation
Our Stoppage Insights feature is built on the latest (version 9) update to our ACESYS advanced programming library. This industry-leading solution lies at the heart of the ECS process control system. Its structured approach enables fast engineering and consistent control logic across hardware platforms from Siemens, Schneider, Rockwell, and others.
In addition to powering Stoppage Insights, ACESYS v9 positions the ECS system for open, interoperable architectures and future-proof automation. The same structured data used by Stoppage Insights supports AI-driven process control, providing the foundation for machine learning models and advanced analytics.
The latest releases also respond to the growing risk of cyberattacks on industrial operational technology (OT) infrastructure, delivering robust cybersecurity. The latest ECS software update (version 9.2) is certified to IEC 62443-4-1 international cybersecurity standards, protecting your process operations and reducing system vulnerability.
What’s available now and what’s coming next?
The ECS/ControlCenter 9.2 and ACESYS 9 updates, featuring Stoppage Insights, are available now for:
- Greenfield projects.
- ECS system upgrades.
- Brownfield replacement of competitor systems.
Stoppage Insights will also soon integrate with our ECS/UptimeGo downtime analysis software. Stoppage records, including root cause identification and affected equipment, will flow seamlessly into UptimeGo for advanced analytics, trending and long-term reliability reporting. This integration creates a complete ecosystem for managing and improving plant uptime.
(1) The ECS Process Control Solution for cement, mining and minerals processing combines proven control strategies with modern automation architecture to optimise plant performance, reduce downtime and support operational excellence.
(2) CMMS refers to computerised maintenance management systems; ERP, to enterprise resource planning; and MES to manufacturing execution systems.

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Compliance and growth go hand in h and

Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence

FORNNAX Appoints Dieter Jerschl as Sales Partner for Central Europe

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Compliance and growth go hand in h and

Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence























