Concrete
All-Weather Tunnel
Published
5 years agoon
By
admin
The Atal Tunnel in Himachal Pradesh was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi last year on October 3. The 9.02 km tunnel is the world?? longest road tunnel at an altitude of 3,000 m (10,000 ft) above sea level. Passing under the Rohtang Pass in the eastern Pir Panjal range, it connects Manali with Lahaul and Spiti valley, and subsequently with Leh, throughout the year. It has reduced the distance by 46 km and travel time by five hours.
The Atal Tunnel was envisaged in 1983 by the Government of India to provide all-weather connectivity between Manali and Leh. In 2002, then Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee declared the construction of Rohtang Tunnel and laid the foundation of the approach road to the tunnel. The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) subsequently engaged RITES the same year to undertake studies. The contract was finally awarded to Strabag-Afcons JV (SAJV) in September 2009.
The Atal Tunnel is horseshoe shaped, with a single tube and two lanes. It boasts many firsts, including the deployment of the Rowa Conveyor System.
Working at inverted levels
The Rowa Conveyor System was deployed to facilitate working at inverted levels. This offered various advantages, as Sunil Tyagi, Project Manager, Atal Tunnel Project, lists:
-
Activities were carried out side by side without hampering other activities in the tunnel with due care to manpower safety.
-
Unnecessary transportation of muck for dumping was eliminated and generation of harmful gases in the tunnel reduced.
-
Shifting the muck on the conveyor belt from the inbuilt crusher to the outside of the tunnel helped reduce the number of machines, equipment and transport, lowering vehicle pollution. This provided clean and healthy conditions in the tunnel for workers.
-
The time cycle of all activities was reduced, so the workers spent less time inside the tunnel.
-
Precast members were placed using an EOT crane mounted on Rowa.
Point of escape
This is one of the few tunnels in the world, and the first in India, that has been built with an emergency escape below the pavement level. The clear dimensions of the escape tunnel are 3.6 m ? 2.2 m.
Having the emergency escape tunnel within the main tunnel eliminated the need to build an additional, parallel escape tunnel. ??n the Atal Tunnel, passages have been provided to access the escape tunnel at every 500 m, where a stairway leads to the escape route,??shares Tyagi. ??n times of any adversity in the main tunnel, this escape tunnel can be used by personnel to evacuate people.
Drill and blast
The New Austrian Tunnelling Method (NATM) was adopted during excavation. As Tyagi says, ??his method was useful in complex and diverse geological conditions, where forecasting of the rock mass was difficult owing to the rapidly changing geology.??He adds that in this method, the surrounding soil or rock mass of tunnel is integrated into the overall support structure, and the rock is activated to a load-bearing ring around the tunnel. Every deformation of the excavation is measured.
NATM requires the installation of sophisticated measurement instrumentation that is embedded in the excavated surface, such as optical targets, load cells and multipoint borehole extensometers. As NATM is based on monitoring measurements, changes in the support and construction method are possible during the execution phase.

The challenge
There were several challenges faced during the construction of the tunnel. Heading excavation through the Seri Nalla Zone was the biggest one. ??lthough the Nalla we encountered was of a mere length of 526 m, the excavation took around four years to complete,??reveals Tyagi. ??he project team put their energies into getting over this stretch during heading operations, as successful execution of the tunnel was totally dependent on its excavation.??/p>
Seri Nalla consisted of a sheared, weathered rock mass, mostly river-borne material with heavy water ingress, as high as 127 litre per sec. The face of the tunnel literally used to flow like a river of mud and boulders. Securing the face under these circumstances and excavating further was a huge task. ??he brave and skilled efforts of our workforce helped overcome this extremely challenging geology,??he adds.
Successful execution of the Seri Nalla heading boosted the morale of the execution team and ??hereafter, we were able to excavate the tunnel in the heading drive at a much accelerated speed,??says Tyagi. The maximum heading achieved in a month after completion of Seri Nalla was 217 m.
Surviving the pandemic
Construction commenced in 2010, and the Atal Tunnel was launched in 2020. The question remains: How did the project survive the pandemic months? One of the significant challenges faced during the pandemic was availability of raw materials at site. Cement and steel factories were closed in the lockdown, thus limiting supplies substantially. ??ontinuous discussions were held with the management of these factories to start the required production, so that our demands could be met,??says Tyagi. ??e are grateful for a favourable response from them, which certainly helped achieve project timelines as per schedule.??/p>
The tunnel has consumed 14,508 metric tonne (mt) of steel and 237,596 mt of cement. Almost 14 lakh cu m soil and rock was excavated during construction. As the project is of immense national importance, efforts were made by all stakeholders to restart work with minimal time loss. ??e were able to get a go ahead for the commencement of project-related activities from April 2, 2020, by the local district administration on the condition that the strict COVID protocols laid down by the government shall be adhered to,??confirms Tyagi. The work was started with minimum staff and workers, and only critical works for project completion were taken up initially.
Safety first!
The unique and marvellous tunnel is the outcome of over 1,000 workmen and 150 engineers working tirelessly and efficiently in extreme weather conditions. Safety was given primary importance, which led to the achievement of more than 28 million safe man hours till the end of the project. Prescheduled training programmes were conducted during the project period; these focused on each and every activity and aspect of construction. Training was conducted even during peak working periods.
Almost every month, safety motivational sessions were conducted for workers and awards and appreciation certificates presented to further motivate them to do their best while ensuring all safety protocols and practices were followed. Hazard identification and risk assessment were carried out regularly for all activities.
Secret to success
??eamwork and integrity among staff and workers made this project successful,??says Tyagi. Working under harsh conditions, countering extreme climatic challenges ranging from harsh winters, heavy snowfall and avalanches to cloudbursts, the team did not lose hope and remained focused on the ultimate goal.
Indeed, all the young engineers who got the opportunity to work on this project have gained enormous knowledge and have become national assets. Work in the project included open excavation, underground excavation, precast concreting, cast-in-situ concreting, building works in the form of portal buildings, structural steel fabrication, ground anchoring to the tune of 4,000 kN and PQC works inside the tunnel, providing extensive experience to one and all.
Project: Atal Tunnel, Rohtang, Himachal Pradesh
Project value (civil works): Rs 26 billion
Client: Border Roads Organisation (BRO)
Contractor: Strabag-Afcons Joint Venture (SAJV)
Highest altitude (north portal): 3,017 m
Lowest altitude (south portal): 3,060 m
Tunnel type: Single-tube, double-lane, horseshoe shaped
Tunnel length: 9.02 km
Finishes width of road level: 11.4 m
Overhead clearance: 5.525 m
Tunnels: 18
Egress tunnel dimensions: 3.6 m (W) x 2.25 m (H)

Precautions for avalanche emergencies
There was a constant avalanche threat with over 20 avalanche areas surrounding the tunnel portals.
-
A rescue team was deployed at site for constant monitoring of now conditions.
-
The team provided directions and instructions for safe movement of staff and worker vehicles from Solang Valley to the site location.
-
The rescue team took care of route planning for the movement of vehicles, ensuring safe movement.
-
RICCO chips were provided to all individuals, so that in case of an avalanche the trapped person could be rescued by the sensor tracking system.
Concrete
Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation
Published
3 seconds agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Professor Procyon Mukherjee discusses how as the cement industry accelerates its shift towards digitalisation, data-driven technologies are becoming the mainstay of sustainability and control across the value chain.
The cement industry, long perceived as traditional and resistant to change, is undergoing a profound transformation driven by digital technologies. As global infrastructure demand grows alongside increasing pressure to decarbonise and improve productivity, cement manufacturers are adopting data-centric tools to enhance performance across the value chain. Nowhere is this shift more impactful than in grinding, which is the energy-intensive final stage of cement production, and in the materials that make grinding more efficient: grinding media and grinding aids.
The imperative for digitalisation
Cement production accounts for roughly 7 per cent to 8 per cent of global CO2 emissions, largely due to the energy intensity of clinker production and grinding processes. Digital solutions, such as AI-driven process controls and digital twins, are helping plants improve stability, cut fuel use and reduce emissions while maintaining consistent product quality. In one deployment alongside ABB’s process controls at a Heidelberg plant in Czechia, AI tools cut fuel use by 4 per cent and emissions by 2 per cent, while also improving operational stability.
Digitalisation in cement manufacturing encompasses a suite of technologies, broadly termed as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), AI and machine learning, predictive analytics, cloud-based platforms, advanced process control and digital twins, each playing a role in optimising various stages of production from quarrying to despatch.
Grinding: The crucible of efficiency and cost
Of all the stages in cement production, grinding is among the most energy-intensive, historically consuming large amounts of electricity and representing a significant portion of plant operating costs. As a result, optimising grinding operations has become central to digital transformation strategies.
Modern digital systems are transforming grinding mills from mechanical workhorses into intelligent, interconnected assets. Sensors throughout the mill measure parameters such as mill load, vibration, mill speed, particle size distribution, and power consumption. This real-time data, fed into machine learning and advanced process control (APC) systems, can dynamically adjust operating conditions to maintain optimal throughput and energy usage.
For example, advanced grinding systems now predict inefficient conditions, such as impending mill overload, by continuously analysing acoustic and vibration signatures. The system can then proactively adjust clinker feed rates and grinding media distribution to sustain optimal conditions, reducing energy consumption and improving consistency.
Digital twins: Seeing grinding in the virtual world
One of the most transformative digital tools applied in cement grinding is the digital twin, which a real-time virtual replica of physical equipment and processes. By integrating sensor data and
process models, digital twins enable engineers to simulate process variations and run ‘what-if’
scenarios without disrupting actual production. These simulations support decisions on variables such as grinding media charge, mill speed and classifier settings, allowing optimisation of energy use and product fineness.
Digital twins have been used to optimise kilns and grinding circuits in plants worldwide, reducing unplanned downtime and allowing predictive maintenance to extend the life of expensive grinding assets.
Grinding media and grinding aids in a digital era
While digital technologies improve control and prediction, materials science innovations in grinding media and grinding aids have become equally crucial for achieving performance gains.
Grinding media, which comprise the balls or cylinders inside mills, directly influence the efficiency of clinker comminution. Traditionally composed of high-chrome cast iron or forged steel, grinding media account for nearly a quarter of global grinding media consumption by application, with efficiency improvements translating directly to lower energy intensity.
Recent advancements include ceramic and hybrid media that combine hardness and toughness to reduce wear and energy losses. For example, manufacturers such as Sanxin New Materials in China and Tosoh Corporation in Japan have developed sub-nano and zirconia media with exceptional wear resistance. Other innovations include smart media embedded with sensors to monitor wear, temperature, and impact forces in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and optimal media replacement scheduling. These digitally-enabled media solutions can increase grinding efficiency by as much as 15 per cent.
Complementing grinding media are grinding aids, which are chemical additives that improve mill throughput and reduce energy consumption by altering the surface properties of particles, trapping air, and preventing re-agglomeration. Technology leaders like SIKA AG and GCP Applied Technologies have invested in tailored grinding aids compatible with AI-driven dosing platforms that automatically adjust additive concentrations based on real-time mill conditions. Trials in South America reported throughput improvements nearing 19 per cent when integrating such digital assistive dosing with process control systems.
The integration of grinding media data and digital dosing of grinding aids moves the mill closer to a self-optimising system, where AI not only predicts media wear or energy losses but prescribes optimal interventions through automated dosing and operational adjustments.
Global case studies in digital adoption
Several cement companies around the world exemplify digital transformation in practice.
Heidelberg Materials has deployed digital twin technologies across global plants, achieving up to 15 per cent increases in production efficiency and 20 per cent reductions in energy consumption by leveraging real-time analytics and predictive algorithms.
Holcim’s Siggenthal plant in Switzerland piloted AI controllers that autonomously adjusted kiln operations, boosting throughput while reducing specific energy consumption and emissions.
Cemex, through its AI and predictive maintenance initiatives, improved kiln availability and reduced maintenance costs by predicting failures before they occurred. Global efforts also include AI process optimisation initiatives to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
Challenges and the road ahead
Despite these advances, digitalisation in cement grinding faces challenges. Legacy equipment may lack sensor readiness, requiring retrofits and edge-cloud connectivity upgrades. Data governance and integration across plants and systems remains a barrier for many mid-tier producers. Yet, digital transformation statistics show momentum: more than half of cement companies have implemented IoT sensors for equipment monitoring, and digital twin adoption is growing rapidly as part of broader Industry 4.0 strategies.
Furthermore, as digital systems mature, they increasingly support sustainability goals: reduced energy use, optimised media consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions. By embedding intelligence into grinding circuits and material inputs like grinding aids, cement manufacturers can strike a balance between efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
Digitalisation is not merely an add-on to cement manufacturing. It is reshaping the competitive and sustainability landscape of an industry often perceived as inertia-bound. With grinding representing a nexus of energy intensity and cost, digital technologies from sensor networks and predictive analytics to digital twins offer new levers of control. When paired with innovations in grinding media and grinding aids, particularly those with embedded digital capabilities, plants can achieve unprecedented gains in efficiency, predictability and performance.
For global cement producers aiming to reduce costs and carbon footprints simultaneously, the future belongs to those who harness digital intelligence not just to monitor operations, but to optimise and evolve them continuously.
About the author:
Professor Procyon Mukherjee, ex-CPO Lafarge-Holcim India, ex-President Hindalco, ex-VP Supply Chain Novelis Europe, has been an industry leader in logistics, procurement, operations and supply chain management. His career spans 38 years starting from Philips, Alcan Inc (Indian Aluminum Company), Hindalco, Novelis and Holcim. He authored the book, ‘The Search for Value in Supply Chains’. He serves now as Visiting Professor in SP Jain Global, SIOM and as the Adjunct Professor at SBUP. He advises leading Global Firms including Consulting firms on SCM and Industrial Leadership and is a subject matter expert in aluminum and cement. An Alumnus of IIM Calcutta and Jadavpur University, he has completed the LH Senior Leadership Programme at IVEY Academy at Western University, Canada.
Concrete
Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency
Published
5 minutes agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Shreesh A Khadilkar discusses how advanced additive formulations allow customised, high-performance and niche cements—offering benefits while supporting blended cements and long-term cost and carbon reduction.
Cement additives are chemicals (inorganic and organic) added in small amounts (0.01 per cent to 0.2 per cent by weight) during cement grinding. Their main job? Reduce agglomeration, prevent pack-set, and keep the mill running smoother. Thus, these additions primarily improve, mill thru-puts, achieve lower clinker factor in blended cements PPC/PSC/PCC. Additionally, these additives improve concrete performance of cements or even for specific special premium cements with special USPs like lower setting times or for reduced water permeability in the resultant cement mortars and concrete (water repellent /permeation resistant cements), corrosion resistance etc.
The cement additives are materials which could be further differentiated as:
Grinding aids:
• Bottlenecks in cement grinding capacity, such materials can enhance throughputs
• Low specific electrical energy consumption during cement grinding
• Reduce “Pack set” problem and improve powder flowability
Quality improvers:
• Opportunity for further clinker factor reduction
• Solution for delayed cement setting or strength development issues at early or later ages.
Others: materials which are used for specific special cements with niche properties as discussed in the subsequent pages.
When cement additives are used as grinding aids or quality improvers, in general the additives reduce the inter-particle forces; reduce coating over grinding media and mill internals. Due to creation of like charges on cement particles, there is decreased agglomeration, much improved flowability, higher generation of fines better dispersion of particles in separator feed and reduction of mill filling level (decrease of residence time). However, in VRM grinding; actions need to be taken to have stable bed formation on the table.
It has been reported in literature and also substantiated by a number of detailed evaluations of different cement additive formulations in market, that the cement additive formulations are a combination of different chemical compounds, typically composed of:
- Accelerator/s for the hydration reaction of cements which are dependent on the acceleration effect desired in mortar compressive strengths at early or later ages, the choice of the materials is also dependent on clinker quality and blending components (flyash / slag) or a mix of both.
- Water reducer / workability / wet-ability enhancer, which would show impact on the resultant cement mortars and concrete. Some of the compounds (retarders) like polysaccharide derivatives, gluconates etc., show an initial retarding action towards hydration which result in reducing the water requirements for the cements thus act as water reducers, or it could be some appropriate polymeric molecules which show improved wet-ability and reduce water demand. These are selected based on the mineral component and type of cements (PPC/PSC /PCC).
- Grinding aids: Compounds that work as Grinding Aid i.e. which would enhance Mill thru-put on one hand as well as would increase the early strengths due to the higher fines generation/ or activation of cement components. These compounds could be like alkanol-amines such as TIPA, DEIPA, TEA etc. or could be compounds like glycols and other poly-ols, depending on whether it is OPC or PPC or PSC or PCC manufacture.
Mechanism of action — Step By Step—
- Reduce Agglomeration, Cement particles get electrostatically charged during grinding, stick together, form “flocs”, block mill efficiency, waste energy. Grinding aid molecules adsorb onto particle surfaces, neutralise charge, prevent re-agglomeration.
- Improve Powder Flowability, Adsorbed molecules create a lubricating layer, particles slide past each other easier, better mill throughput, less “dead zone” buildup.
Also reduces caking on mill liners, diaphragms, and separator screens, less downtime for cleaning. - Enhance Grinding Efficiency (Finer Product Faster), By preventing agglomeration, particles stay dispersed more surface area exposed to grinding media, finer grind achieved with same energy input, Or: same fineness achieved with less energy, huge savings.
Example:
• Without aid ? 3500 cm²/g Blaine needs 40 kWh/ton
• With use of optimum grinding aid same fineness at 32 kWh/ton 20 per cent energy savings - Reduce Pack Set and Silo Caking Grinding aids (GA) inhibit hydration of free lime (CaO) during storage prevents premature hardening or “pack set” in silos. especially critical in humid climates or with high free lime clinker.
It may be stated here that Overdosing of GA can cause: – Foaming in mill (especially with glycols) reduces grinding efficiency, retardation of cement setting (especially with amines/acids), odor issues (in indoor mills) – Corrosion of mill components (if acidic aids used improperly)
The best practice to optimise use of GA is Start with 0.02 per cent to 0.05 per cent dosage test fineness, flow, and set time adjust up/down. Due to static charge of particles, the sample may stick to the sides of sampler pipe and so sampling need to be properly done.
Depending on type of cements i.e. OPC, PPC, PSC, PCC, the grinding aids combinations need to be optimised, a typical Poly carboxylate ether also could be a part of the combo grinding aids
Cement additives for niche properties of the cement in concrete.
The cement additives can also be tailor made to create specific niche properties in cements, OPC, PPC, PSC and PCC to create premium or special brands. The special niche properties of the cement being its additional USP of such cement products, and are useful for customers to build a durable concrete structure with increased service life.
Such properties could be:
• Additives for improved concrete performance of cements, high early strength in PPC/PSC/PCC, much reduced water demand in cement, cements with improved slump retentivity in concrete, self-compacting, self levelling in concrete, cements with improved adhesion property of the cement mortar
• Water repellence / water proofing, permeability resistance in mortars and concrete.
• Biocidal cement
• Photo catalytic cements
• Cements with negligible ASR reactions etc.
Additives for cements for improved concrete performance
High early strengths: Use of accelerators. These are chemical compounds which enhance the degree of hydration of cement. These can include setting or hardening accelerators depending on whether their action occurs in the plastic or hardened state respectively. Thus, the setting accelerators reduce the setting time, whereas the hardening accelerators increase the early age strengths. The setting accelerators act during the initial minutes of the cement hydration, whereas the hardening accelerators act mainly during the initial days of hydration.
Chloride salts are the best in class. However, use of chloride salts as hardening accelerators are strongly discouraged for their action in promoting the corrosion of rebar, thus, chloride-free accelerators are preferred. The hardening accelerators could be combinations of compounds like nitrate, nitrite and thiocyanate salts of alkali or alkaline earth metals or thiosulphate, formate, and alkanol amines depending on the cement types.
However, especially in blended cements (PPC/PSC/PCC the increased early strengths invariably decrease the 28 day strengths. These aspects lead to creating combo additives along with organic polymers to achieve improved early strengths as well as either same or marginally improved 28 days strengths with reduced clinker factor in the blended cement, special OPC with reduced admixture requirements. With use of appropriate combination of inorganic and organic additives we could create an OPC with substantially reduced water demand or improved slump retentivity. Use of such an OPC would show exceptional concrete performance in high grade concretes as it would exhibit lower admixture requirements in High Grade Concretes.
PPC with OPC like properties: With the above concept we could have a PPC, having higher percentage flyash, with a combo cement additive which would have with concrete performance similar to OPC in say M40/M50 concrete. Such a PPC would produce a high-strength PPC concrete (= 60 MPa @ 28d) + improved workability, durability and sustainability.
Another interesting aspect could also be of using ultrafine fine flyash /ultrafine slags as additions in OPC/PPC/PSC for achieving lower clinker factor as well as to achieve improved later age strengths with or without a combo cement additive.
The initial adhesion property at sites of especially PPC/PSC/PCC based mortars can be improved through use of appropriate organic polymers addition during the manufacture of these cements. Such cements would have a better adhesion property for plastering/brick bonding etc., as it has much lower rebound loss of their mortars in such applications.
It is needless to mention here that with use of additives, we could also have cement with viscosity modifying cement additives, for self-compaction and self-leveling concrete performance.
Use of Phosphogypsum retards the setting time of cements, we can use additive different additive combos to overcome retardation and improve the 1 day strengths of the cements and concretes.
About the author:
Shreesh Khadilkar, Consultant & Advisor, Former Director Quality & Product Development, ACC, a seasoned consultant and advisor, brings over 37 years of experience in cement manufacturing, having held leadership roles in R&D and product development at ACC Ltd. With deep expertise in innovative cement concepts, he is dedicated to sharing his knowledge and improving the performance of cement plants globally.
Concrete
Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing
Published
32 minutes agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Dr Y Chandri Naidu, Chief Technology Officer, Nextcem Consulting highlights how digital technologies are enabling Indian cement plants to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and transition toward sustainable, low-carbon manufacturing.
Cement manufacturing is inherently resource- and energy-intensive due to high-temperature clinkerisation and extensive material handling and grinding operations. In India, where cement demand continues to grow in line with infrastructure development, producers must balance capacity expansion with sustainability commitments. Energy costs constitute a major share of operating expenditure, while process-related carbon dioxide emissions from limestone calcination remain unavoidable.
Traditional optimisation approaches, which are largely dependent on operator experience, static control logic and offline laboratory analysis, have reached their practical limits. This is especially evident when higher levels of alternative fuel and raw materials (AFR) are introduced or when raw material variability increases.
Digital technologies provide a systematic pathway to manage this complexity by enabling
real-time monitoring, predictive optimisation and integrated decision-making across cement manufacturing operations.
Digital cement manufacturing is enabled through a layered architecture integrating operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT). At the base are plant instrumentation, analysers, and automation systems, which generate continuous process data. This data is contextualised and analysed using advanced analytics and AI platforms, enabling predictive and prescriptive insights for operators and management.
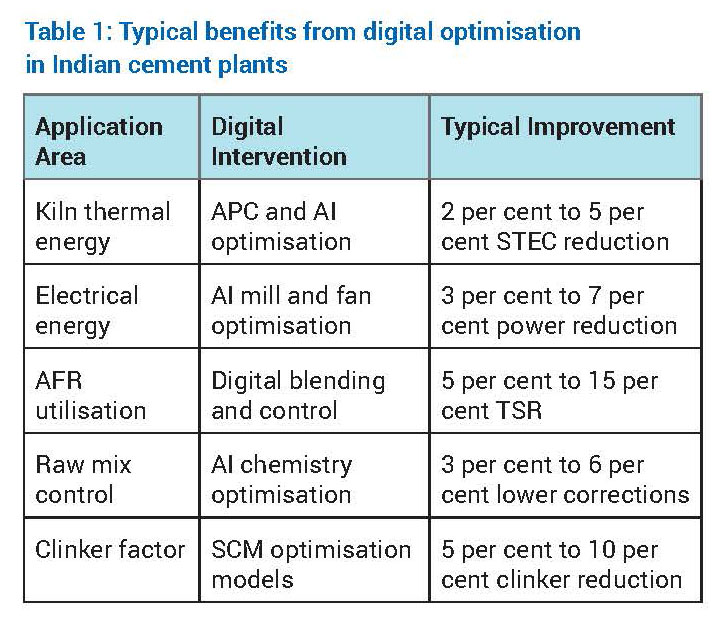
Digital optimisation of energy efficiency
- Thermal energy optimisation
The kiln and calciner system accounts for approximately 60 per cent to 65 per cent of total energy consumption in an integrated cement plant. Digital optimisation focuses on reducing specific thermal energy consumption (STEC) while maintaining clinker quality and operational stability.
Advanced Process Control (APC) stabilises critical parameters such as burning zone temperature, oxygen concentration, kiln feed rate and calciner residence time. By minimising process variability, APC reduces the need for conservative over-firing. Artificial intelligence further enhances optimisation by learning nonlinear relationships between raw mix chemistry, AFR characteristics, flame dynamics and heat consumption.
Digital twins of kiln systems allow engineers to simulate operational scenarios such as increased AFR substitution, altered burner momentum or changes in raw mix burnability without operational risk. Indian cement plants adopting these solutions typically report STEC reductions in the range of 2 per cent to 5 per cent. - Electrical energy optimisation
Electrical energy consumption in cement plants is dominated by grinding systems, fans and material transport equipment. Machine learning–based optimisation continuously adjusts mill parameters such as separator speed, grinding pressure and feed rate to minimise specific power consumption while maintaining product fineness.
Predictive maintenance analytics identify inefficiencies caused by wear, fouling or imbalance in fans and motors. Plants implementing plant-wide electrical energy optimisation typically achieve
3 per cent to 7 per cent reduction in specific power consumption, contributing to both cost savings and indirect CO2 reduction.
Digital enablement of AFR
AFR challenges in the Indian context: Indian cement plants increasingly utilise biomass, refuse-derived fuel (RDF), plastic waste and industrial by-products. However, variability in calorific value, moisture, particle size, chlorine and sulphur content introduces combustion instability, build-up formation and emission risks.
Digital AFR management: Digital platforms integrate real-time AFR quality data from online analysers with historical kiln performance data. Machine learning models predict combustion behaviour, flame stability and emission trends for different AFR combinations. Based on these predictions, fuel feed distribution, primary and secondary air ratios, and burner momentum are dynamically adjusted to ensure stable kiln operation. Digitally enabled AFR management in cement plants will result in increased thermal substitution rates by 5-15 percentage points, reduced fossil fuel dependency, and improved kiln stability.
Digital resource and raw material optimisation
Raw mix control: Raw material variability directly affects kiln operation and clinker quality. AI-driven raw mix optimisation systems continuously adjust feed proportions to maintain target chemical parameters such as Lime Saturation Factor (LSF), Silica Modulus (SM), and Alumina Modulus (AM). This reduces corrective material usage and improves kiln thermal efficiency.
Clinker factor reduction: Reducing clinker factor through supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) such as fly ash, slag and calcined clay is a key decarbonisation lever. Digital models simulate blended cement performance, enabling optimisation of SCM proportions while maintaining strength and durability requirements.
Challenges and strategies for digital adoption
Key challenges in Indian cement plants include data quality limitations due to legacy instrumentation, resistance to algorithm-based decision-making, integration complexity across multiple OEM systems, and site-specific variability in raw materials and fuels.
Successful digital transformation requires strengthening the data foundation, prioritising high-impact use cases such as kiln APC and energy optimisation, adopting a human-in-the-loop approach, and deploying modular, scalable digital platforms with cybersecurity by design.
Future Outlook
Future digital cement plants will evolve toward autonomous optimisation, real-time carbon intensity tracking, and integration with emerging decarbonisation technologies such as carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS). Digital platforms will also support ESG reporting and regulatory compliance.
Digital pathways offer a practical and scalable solution for sustainable cement manufacturing in India. By optimising energy consumption, enabling higher AFR substitution and improving resource efficiency, digital technologies deliver measurable environmental and economic benefits. With appropriate data infrastructure, organisational alignment and phased implementation, digital transformation will remain central to the Indian cement industry’s low-carbon transition.
About the author:
Dr Y Chandri Naidu is a cement industry professional with 30+ years of experience in process optimisation, quality control and quality assistance, energy conservation and sustainable manufacturing, across leading organisations including NCB, Ramco, Prism, Ultratech, HIL, NCL and Vedanta. He is known for guiding teams, developing innovative plant solutions and promoting environmentally responsible cement production. He is also passionate about mentoring professionals and advancing durable, resource efficient technologies for future of construction materials.

Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation

Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency

Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation

Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency

Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships






















