Concrete
How Upgrades Can Deliver Energy Savings Across the Cement Process
Published
8 months agoon
By
admin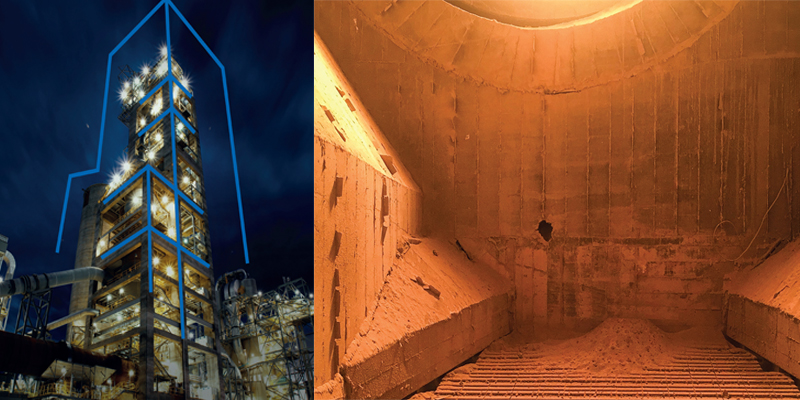
Jacob Brinch-Nielsen, Vice President of Professional Services, FLSmidth Cement, brings together recommendations from experts across the flow sheet to demonstrate the role of upgrades in optimising the cement manufacturing process.
Improving Preheater Efficiency and Heat Retention
Preheaters play a critical role in cement plant energy efficiency, but outdated cyclone designs and corroded components can lead to excessive heat loss and higher fuel consumption. Plants that optimise preheater separation efficiency can reduce fuel use by up to 5 – 10 kcal/kg clinker while improving downstream performance. One area where upgrades can make a difference is in the central pipe elements. By switching to an advanced suspension design, plants can improve separation efficiency and extend wear life — offering both energy savings and operational benefits.
“The cast central pipe is installed in the preheater cyclones to improve separation and thermal efficiency,” explains Muthukumar Muthu, Senior Product Specialist, “Our patented design for the suspension of the cast pipe reduces corrosion (extending pipe life), while also making it easier to carry out maintenance work. Installation of one cast pipe in the lower cyclone stages can save customers 5 – 10 kcal/kg clinker, reducing power consumption in the ID fan drive by 4 to 8 per cent – a significant energy saving. Customers can choose whether to claim these benefits in cost savings or convert them to a 1 to 2 per cent increase in production. Either way, the cast pipe provides a quick ROI.”
The improvements to the cast central pipe elements reduce the stress across the element, and make it simpler to manufacture, which results in a more consistent quality, more durable product. This upgrade can be implemented during the annual maintenance shutdown with no disruption to operations.
Maximising Efficiency in Combustion
False air leaks and inefficient fuel combustion are two of the biggest sources of energy waste in cement kilns. Uncontrolled air ingress forces plants to burn more fuel to maintain operating temperatures, while the inefficient combustion of alternative fuels can create a volatile environment that reduces both efficiency and clinker quality. To address these issues, plants can implement sealing upgrades that prevent air leaks and burner modifications that optimise fuel-air mixing, ensuring more complete combustion and greater flexibility in alternative fuel use.
“We’ve introduced the new Spring Tensioned Graphite Seals to reduce false air entry and increase thermal efficiency – effectively lowering fuel consumption without affecting clinker quality,” says, Karthikeyan Arumugam, Senior Product Specialist.
In addition, advanced burner designs such as a JETFLEX® partial upgrade allow plants to retain the existing kiln burner pipe while improving fuel-air mixing, increasing alternative fuel utilisation and efficiency. This burner enables cement producers to use pulverised coal or petcoke, anthracite, oil, natural gas – or any mixture of these – as well as alternative fuels (such as plastic and wood chips, sewage sludge) with no difference in performance and minimal volatility in the kiln to support reliable and consistent production of high-quality clinker with low NOx emissions.
Cooling Efficiency as Easy as ABC Inlet
An inefficient or older generation cooler inlet leads to higher fuel consumption. Alternative fuels and petcoke produce dusty, sticky clinker that builds up easily, creating ‘snowmen’ in the cooler that disrupt the system, leading to inefficiencies and even unplanned shutdowns.
“The ABC Inlet upgrade continues to be one of our most successful cooler inlet upgrades because it resolves issues as a result alternative fuels usage and enables better heat recovery back to system,” explains Rene Hede, Cooler Product Specialist. “The ABC Inlet prevents snowmen formation with a patented in-grate design that pushes compressed air up through the grates, blasting agglomerations.”
In addition, the ABC Inlet’s rapid quenching process enables faster clinker cooling while maximising heat recovery to the pyro line, resulting in heat consumption savings of 10–30 kcal/kg of clinker. This also enhances clinker quality, providing greater flexibility in cement product formulation and allowing for clinker factor reductions that further improve grinding energy efficiency.
Part 2 of 3. Read Part 1 in the May issue of Indian Cement Review. Part 3 will be found in the July issue.
You may like
-


Prioritise durability—use premium basic bricks
-


Cement Beyond Carbon
-


Fuller Institute Launches Major Training Programme
-


Adani Cement to Deploy World’s First Commercial RDH System
-


Pacific Avenue Completes Acquisition of FLSmidth Cement; Rebrands as Fuller Technologies
-


Decarbonising Indian Cement: A Net-Zero Roadmap
Concrete
Refractory demands in our kiln have changed
Published
3 days agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Radha Singh, Senior Manager (P&Q), Shree Digvijay Cement, points out why performance, predictability and life-cycle value now matter more than routine replacement in cement kilns.
As Indian cement plants push for higher throughput, increased alternative fuel usage and tighter shutdown cycles, refractory performance in kilns and pyro-processing systems is under growing pressure. In this interview, Radha Singh, Senior Manager (P&Q), Shree Digvijay Cement, shares how refractory demands have evolved on the ground and how smarter digital monitoring is improving kiln stability, uptime and clinker quality.
How have refractory demands changed in your kiln and pyro-processing line over the last five years?
Over the last five years, refractory demands in our kiln and pyro line have changed. Earlier, the focus was mostly on standard grades and routine shutdown-based replacement. But now, because of higher production loads, more alternative fuels and raw materials (AFR) usage and greater temperature variation, the expectation from refractory has increased.
In our own case, the current kiln refractory has already completed around 1.5 years, which itself shows how much more we now rely on materials that can handle thermal shock, alkali attack and coating fluctuations. We have moved towards more stable, high-performance linings so that we don’t have to enter the kiln frequently for repairs.
Overall, the shift has been from just ‘installation and run’ to selecting refractories that give longer life, better coating behaviour and more predictable performance under tougher operating conditions.
What are the biggest refractory challenges in the preheater, calciner and cooler zones?
• Preheater: Coating instability, chloride/sulphur cycles and brick erosion.
• Calciner: AFR firing, thermal shock and alkali infiltration.
• Cooler: Severe abrasion, red-river formation and mechanical stress on linings.
Overall, the biggest challenge is maintaining lining stability under highly variable operating conditions.
How do you evaluate and select refractory partners for long-term performance?
In real plant conditions, we don’t select a refractory partner just by looking at price. First, we see their past performance in similar kilns and whether their material has actually survived our operating conditions. We also check how strong their technical support is during shutdowns, because installation quality matters as much as the material itself.
Another key point is how quickly they respond during breakdowns or hot spots. A good partner should be available on short notice. We also look at their failure analysis capability, whether they can explain why a lining failed and suggest improvements.
On top of this, we review the life they delivered in the last few campaigns, their supply reliability and their willingness to offer plant-specific custom solutions instead of generic grades. Only a partner who supports us throughout the life cycle, which includes selection, installation, monitoring and post-failure analysis, fits our long-term requirement.
Can you share a recent example where better refractory selection improved uptime or clinker quality?
Recently, we upgraded to a high-abrasion basic brick at the kiln outlet. Earlier we had frequent chipping and coating loss. With the new lining, thermal stability improved and the coating became much more stable. As a result, our shutdown interval increased and clinker quality remained more consistent. It had a direct impact on our uptime.
How is increased AFR use affecting refractory behaviour?
Increased AFR use is definitely putting more stress on the refractory. The biggest issue we see daily is the rise in chlorine, alkalis and volatiles, which directly attack the lining, especially in the calciner and kiln inlet. AFR firing is also not as stable as conventional fuel, so we face frequent temperature fluctuations, which cause more thermal shock and small cracks in the lining.
Another real problem is coating instability. Some days the coating builds too fast, other days it suddenly drops, and both conditions impact refractory life. We also notice more dust circulation and buildup inside the calciner whenever the AFR mix changes, which again increases erosion.
Because of these practical issues, we have started relying more on alkali-resistant, low-porosity and better thermal shock–resistant materials to handle the additional stress coming from AFR.
What role does digital monitoring or thermal profiling play in your refractory strategy?
Digital tools like kiln shell scanners, IR imaging and thermal profiling help us detect weakening areas much earlier. This reduces unplanned shutdowns, helps identify hotspots accurately and allows us to replace only the critical sections. Overall, our maintenance has shifted from reactive to predictive, improving lining life significantly.
How do you balance cost, durability and installation speed during refractory shutdowns?
We focus on three points:
• Material quality that suits our thermal profile and chemistry.
• Installation speed, in fast turnarounds, we prefer monolithic.
• Life-cycle cost—the cheapest material is not the most economical. We look at durability, future downtime and total cost of ownership.
This balance ensures reliable performance without unnecessary expenditure.
What refractory or pyro-processing innovations could transform Indian cement operations?
Some promising developments include:
• High-performance, low-porosity and nano-bonded refractories
• Precast modular linings to drastically reduce shutdown time
• AI-driven kiln thermal analytics
• Advanced coating management solutions
• More AFR-compatible refractory mixes
These innovations can significantly improve kiln stability, efficiency and maintenance planning across the industry.
Concrete
Digital supply chain visibility is critical
Published
3 days agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
MSR Kali Prasad, Chief Digital and Information Officer, Shree Cement, discusses how data, discipline and scale are turning Industry 4.0 into everyday business reality.
Over the past five years, digitalisation in Indian cement manufacturing has moved decisively beyond experimentation. Today, it is a strategic lever for cost control, operational resilience and sustainability. In this interview, MSR Kali Prasad, Chief Digital and Information Officer, Shree Cement, explains how integrated digital foundations, advanced analytics and real-time visibility are helping deliver measurable business outcomes.
How has digitalisation moved from pilot projects to core strategy in Indian cement manufacturing over the past five years?
Digitalisation in Indian cement has evolved from isolated pilot initiatives into a core business strategy because outcomes are now measurable, repeatable and scalable. The key shift has been the move away from standalone solutions toward an integrated digital foundation built on standardised processes, governed data and enterprise platforms that can be deployed consistently across plants and functions.
At Shree Cement, this transition has been very pragmatic. The early phase focused on visibility through dashboards, reporting, and digitisation of critical workflows. Over time, this has progressed into enterprise-level analytics and decision support across manufacturing and the supply chain,
with clear outcomes in cost optimisation, margin protection and revenue improvement through enhanced customer experience.
Equally important, digital is no longer the responsibility of a single function. It is embedded into day-to-day operations across planning, production, maintenance, despatch and customer servicing, supported by enterprise systems, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) data platforms, and a structured approach to change management.
Which digital interventions are delivering the highest ROI across mining, production and logistics today?
In a capital- and cost-intensive sector like cement, the highest returns come from digital interventions that directly reduce unit costs or unlock latent capacity without significant capex.
Supply chain and planning (advanced analytics): Tools for demand forecasting, S&OP, network optimisation and scheduling deliver strong returns by lowering logistics costs, improving service levels, and aligning production with demand in a fragmented and regionally diverse market.
Mining (fleet and productivity analytics): Data-led mine planning, fleet analytics, despatch discipline, and idle-time reduction improve fuel efficiency and equipment utilisation, generating meaningful savings in a cost-heavy operation.
Manufacturing (APC and process analytics): Advanced Process Control, mill optimisation, and variability reduction improve thermal and electrical efficiency, stabilise quality and reduce rework and unplanned stoppages.
Customer experience and revenue enablement (digital platforms): Dealer and retailer apps, order visibility and digitally enabled technical services improve ease of doing business and responsiveness. We are also empowering channel partners with transparent, real-time information on schemes, including eligibility, utilisation status and actionable recommendations, which improves channel satisfaction and market execution while supporting revenue growth.
Overall, while Artificial Intelligence (AI) and IIoT are powerful enablers, it is advanced analytics anchored in strong processes that typically delivers the fastest and most reliable ROI.
How is real-time data helping plants shift from reactive maintenance to predictive and prescriptive operations?
Real-time and near real-time data is driving a more proactive and disciplined maintenance culture, beginning with visibility and progressively moving toward prediction and prescription.
At Shree Cement, we have implemented a robust SAP Plant Maintenance framework to standardise maintenance workflows. This is complemented by IIoT-driven condition monitoring, ensuring consistent capture of equipment health indicators such as vibration, temperature, load, operating patterns and alarms.
Real-time visibility enables early detection of abnormal conditions, allowing teams to intervene before failures occur. As data quality improves and failure histories become structured, predictive models can anticipate likely failure modes and recommend timely interventions, improving MTBF and reducing downtime. Over time, these insights will evolve into prescriptive actions, including spares readiness, maintenance scheduling, and operating parameter adjustments, enabling reliability optimisation with minimal disruption.
A critical success factor is adoption. Predictive insights deliver value only when they are embedded into daily workflows, roles and accountability structures. Without this, they remain insights without action.
In a cost-sensitive market like India, how do cement companies balance digital investment with price competitiveness?
In India’s intensely competitive cement market, digital investments must be tightly linked to tangible business outcomes, particularly cost reduction, service improvement, and faster decision-making.
This balance is achieved by prioritising high-impact use cases such as planning efficiency, logistics optimisation, asset reliability, and process stability, all of which typically deliver quick payback. Equally important is building scalable and governed digital foundations that reduce the marginal cost of rolling out new use cases across plants.
Digitally enabled order management, live despatch visibility, and channel partner platforms also improve customer centricity while controlling cost-to-serve, allowing service levels to improve without proportionate increases in headcount or overheads.
In essence, the most effective digital investments do not add cost. They protect margins by reducing variability, improving planning accuracy, and strengthening execution discipline.
How is digitalisation enabling measurable reductions in energy consumption, emissions, and overall carbon footprint?
Digitalisation plays a pivotal role in improving energy efficiency, reducing emissions and lowering overall carbon intensity.
Real-time monitoring and analytics enable near real-time tracking of energy consumption and critical operating parameters, allowing inefficiencies to be identified quickly and corrective actions to be implemented. Centralised data consolidation across plants enables benchmarking, accelerates best-practice adoption, and drives consistent improvements in energy performance.
Improved asset reliability through predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime and process instability, directly lowering energy losses. Digital platforms also support more effective planning and control of renewable energy sources and waste heat recovery systems, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Most importantly, digitalisation enables sustainability progress to be tracked with greater accuracy and consistency, supporting long-term ESG commitments.
What role does digital supply chain visibility play in managing demand volatility and regional market dynamics in India?
Digital supply chain visibility is critical in India, where demand is highly regional, seasonality is pronounced, and logistics constraints can shift rapidly.
At Shree Cement, planning operates across multiple horizons. Annual planning focuses on capacity, network footprint and medium-term demand. Monthly S&OP aligns demand, production and logistics, while daily scheduling drives execution-level decisions on despatch, sourcing and prioritisation.
As digital maturity increases, this structure is being augmented by central command-and-control capabilities that manage exceptions such as plant constraints, demand spikes, route disruptions and order prioritisation. Planning is also shifting from aggregated averages to granular, cost-to-serve and exception-based decision-making, improving responsiveness, lowering logistics costs and strengthening service reliability.
How prepared is the current workforce for Industry 4.0, and what reskilling strategies are proving most effective?
Workforce preparedness for Industry 4.0 is improving, though the primary challenge lies in scaling capabilities consistently across diverse roles.
The most effective approach is to define capability requirements by role and tailor enablement accordingly. Senior leadership focuses on digital literacy for governance, investment prioritisation, and value tracking. Middle management is enabled to use analytics for execution discipline and adoption. Frontline sales and service teams benefit from
mobile-first tools and KPI-driven workflows, while shop-floor and plant teams focus on data-driven operations, APC usage, maintenance discipline, safety and quality routines.
Personalised, role-based learning paths, supported by on-ground champions and a clear articulation of practical benefits, drive adoption far more effectively than generic training programmes.
Which emerging digital technologies will fundamentally reshape cement manufacturing in the next decade?
AI and GenAI are expected to have the most significant impact, particularly when combined with connected operations and disciplined processes.
Key technologies likely to reshape the sector include GenAI and agentic AI for faster root-cause analysis, knowledge access, and standardisation of best practices; industrial foundation models that learn patterns across large sensor datasets; digital twins that allow simulation of process changes before implementation; and increasingly autonomous control systems that integrate sensors, AI, and APC to maintain stability with minimal manual intervention.
Over time, this will enable more centralised monitoring and management of plant operations, supported by strong processes, training and capability-building.
Concrete
Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation
Published
3 days agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Professor Procyon Mukherjee discusses how as the cement industry accelerates its shift towards digitalisation, data-driven technologies are becoming the mainstay of sustainability and control across the value chain.
The cement industry, long perceived as traditional and resistant to change, is undergoing a profound transformation driven by digital technologies. As global infrastructure demand grows alongside increasing pressure to decarbonise and improve productivity, cement manufacturers are adopting data-centric tools to enhance performance across the value chain. Nowhere is this shift more impactful than in grinding, which is the energy-intensive final stage of cement production, and in the materials that make grinding more efficient: grinding media and grinding aids.
The imperative for digitalisation
Cement production accounts for roughly 7 per cent to 8 per cent of global CO2 emissions, largely due to the energy intensity of clinker production and grinding processes. Digital solutions, such as AI-driven process controls and digital twins, are helping plants improve stability, cut fuel use and reduce emissions while maintaining consistent product quality. In one deployment alongside ABB’s process controls at a Heidelberg plant in Czechia, AI tools cut fuel use by 4 per cent and emissions by 2 per cent, while also improving operational stability.
Digitalisation in cement manufacturing encompasses a suite of technologies, broadly termed as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), AI and machine learning, predictive analytics, cloud-based platforms, advanced process control and digital twins, each playing a role in optimising various stages of production from quarrying to despatch.
Grinding: The crucible of efficiency and cost
Of all the stages in cement production, grinding is among the most energy-intensive, historically consuming large amounts of electricity and representing a significant portion of plant operating costs. As a result, optimising grinding operations has become central to digital transformation strategies.
Modern digital systems are transforming grinding mills from mechanical workhorses into intelligent, interconnected assets. Sensors throughout the mill measure parameters such as mill load, vibration, mill speed, particle size distribution, and power consumption. This real-time data, fed into machine learning and advanced process control (APC) systems, can dynamically adjust operating conditions to maintain optimal throughput and energy usage.
For example, advanced grinding systems now predict inefficient conditions, such as impending mill overload, by continuously analysing acoustic and vibration signatures. The system can then proactively adjust clinker feed rates and grinding media distribution to sustain optimal conditions, reducing energy consumption and improving consistency.
Digital twins: Seeing grinding in the virtual world
One of the most transformative digital tools applied in cement grinding is the digital twin, which a real-time virtual replica of physical equipment and processes. By integrating sensor data and
process models, digital twins enable engineers to simulate process variations and run ‘what-if’
scenarios without disrupting actual production. These simulations support decisions on variables such as grinding media charge, mill speed and classifier settings, allowing optimisation of energy use and product fineness.
Digital twins have been used to optimise kilns and grinding circuits in plants worldwide, reducing unplanned downtime and allowing predictive maintenance to extend the life of expensive grinding assets.
Grinding media and grinding aids in a digital era
While digital technologies improve control and prediction, materials science innovations in grinding media and grinding aids have become equally crucial for achieving performance gains.
Grinding media, which comprise the balls or cylinders inside mills, directly influence the efficiency of clinker comminution. Traditionally composed of high-chrome cast iron or forged steel, grinding media account for nearly a quarter of global grinding media consumption by application, with efficiency improvements translating directly to lower energy intensity.
Recent advancements include ceramic and hybrid media that combine hardness and toughness to reduce wear and energy losses. For example, manufacturers such as Sanxin New Materials in China and Tosoh Corporation in Japan have developed sub-nano and zirconia media with exceptional wear resistance. Other innovations include smart media embedded with sensors to monitor wear, temperature, and impact forces in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and optimal media replacement scheduling. These digitally-enabled media solutions can increase grinding efficiency by as much as 15 per cent.
Complementing grinding media are grinding aids, which are chemical additives that improve mill throughput and reduce energy consumption by altering the surface properties of particles, trapping air, and preventing re-agglomeration. Technology leaders like SIKA AG and GCP Applied Technologies have invested in tailored grinding aids compatible with AI-driven dosing platforms that automatically adjust additive concentrations based on real-time mill conditions. Trials in South America reported throughput improvements nearing 19 per cent when integrating such digital assistive dosing with process control systems.
The integration of grinding media data and digital dosing of grinding aids moves the mill closer to a self-optimising system, where AI not only predicts media wear or energy losses but prescribes optimal interventions through automated dosing and operational adjustments.
Global case studies in digital adoption
Several cement companies around the world exemplify digital transformation in practice.
Heidelberg Materials has deployed digital twin technologies across global plants, achieving up to 15 per cent increases in production efficiency and 20 per cent reductions in energy consumption by leveraging real-time analytics and predictive algorithms.
Holcim’s Siggenthal plant in Switzerland piloted AI controllers that autonomously adjusted kiln operations, boosting throughput while reducing specific energy consumption and emissions.
Cemex, through its AI and predictive maintenance initiatives, improved kiln availability and reduced maintenance costs by predicting failures before they occurred. Global efforts also include AI process optimisation initiatives to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
Challenges and the road ahead
Despite these advances, digitalisation in cement grinding faces challenges. Legacy equipment may lack sensor readiness, requiring retrofits and edge-cloud connectivity upgrades. Data governance and integration across plants and systems remains a barrier for many mid-tier producers. Yet, digital transformation statistics show momentum: more than half of cement companies have implemented IoT sensors for equipment monitoring, and digital twin adoption is growing rapidly as part of broader Industry 4.0 strategies.
Furthermore, as digital systems mature, they increasingly support sustainability goals: reduced energy use, optimised media consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions. By embedding intelligence into grinding circuits and material inputs like grinding aids, cement manufacturers can strike a balance between efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
Digitalisation is not merely an add-on to cement manufacturing. It is reshaping the competitive and sustainability landscape of an industry often perceived as inertia-bound. With grinding representing a nexus of energy intensity and cost, digital technologies from sensor networks and predictive analytics to digital twins offer new levers of control. When paired with innovations in grinding media and grinding aids, particularly those with embedded digital capabilities, plants can achieve unprecedented gains in efficiency, predictability and performance.
For global cement producers aiming to reduce costs and carbon footprints simultaneously, the future belongs to those who harness digital intelligence not just to monitor operations, but to optimise and evolve them continuously.
About the author:
Professor Procyon Mukherjee, ex-CPO Lafarge-Holcim India, ex-President Hindalco, ex-VP Supply Chain Novelis Europe, has been an industry leader in logistics, procurement, operations and supply chain management. His career spans 38 years starting from Philips, Alcan Inc (Indian Aluminum Company), Hindalco, Novelis and Holcim. He authored the book, ‘The Search for Value in Supply Chains’. He serves now as Visiting Professor in SP Jain Global, SIOM and as the Adjunct Professor at SBUP. He advises leading Global Firms including Consulting firms on SCM and Industrial Leadership and is a subject matter expert in aluminum and cement. An Alumnus of IIM Calcutta and Jadavpur University, he has completed the LH Senior Leadership Programme at IVEY Academy at Western University, Canada.

Refractory demands in our kiln have changed

Digital supply chain visibility is critical

Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation

Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency

Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing

Refractory demands in our kiln have changed

Digital supply chain visibility is critical

Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation

Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency

Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing
Trending News
-

 Concrete4 weeks ago
Concrete4 weeks agoAris Secures Rs 630 Million Concrete Supply Order
-

 Concrete4 weeks ago
Concrete4 weeks agoNITI Aayog Unveils Decarbonisation Roadmaps
-

 Concrete3 weeks ago
Concrete3 weeks agoJK Cement Commissions 3 MTPA Buxar Plant, Crosses 31 MTPA
-

 Economy & Market3 weeks ago
Economy & Market3 weeks agoBudget 2026–27 infra thrust and CCUS outlay to lift cement sector outlook



