Economy & Market
Being Proactive about Sustainability
Published
4 years agoon
By
admin
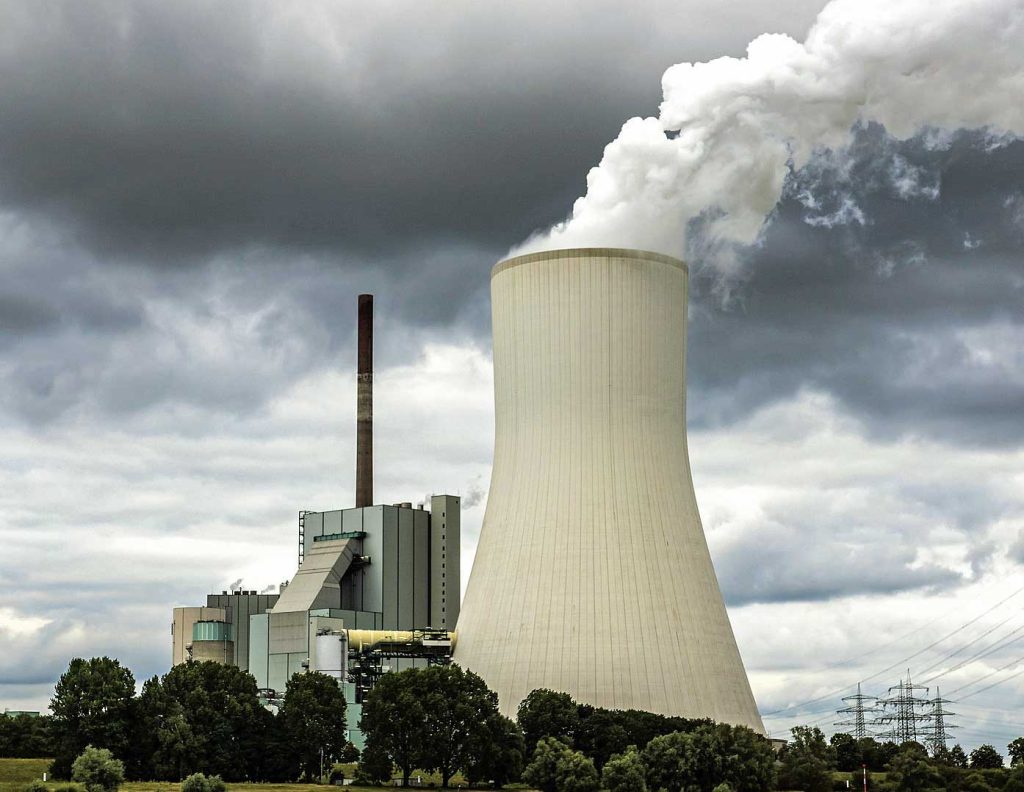
Hard-hitting facts such as scarcity and price hike of fossil fuels and challenges of waste management warn of difficult times ahead, unless players strive to increase the capacity of Waste Heat Recovery Systems to meet energy requirements.
Waste heat recovery has long been the base standard for setting up cement manufacturing units. In China, a cement kiln will not get an official sign-off unless it has waste heat recovery systems. In Europe, any industry requiring large quantities of heat input for manufacturing must have waste heat recovery as a natural corollary, and sometimes its use could be extended to providing heat input to the neighbourhood and community for simple needs such as room and water heating systems.
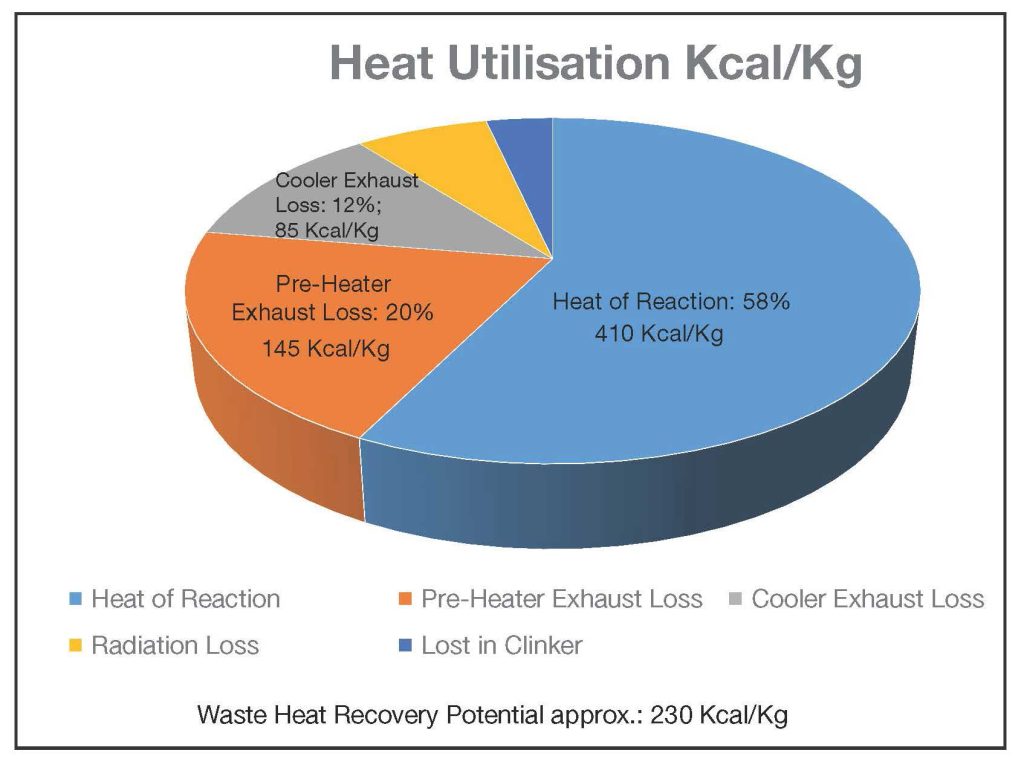
The economics of Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS) is preceded by sustainability concerns, as cement manufacturing in kilns continues to produce 8 per cent of the global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The conversion of limestone to clinker is where the bulk of the heat energy is expended. However, this bulk of heat energy that is generated in six-stage preheater kilns by burning of any fossil fuel input actually gets wasted as shown in the pie-chart Fig 1, and only 58 per cent is used in the conversion process yielding clinker.
Theoretically 710 Kcal needs to be generated to convert 1 kg of clinker, out of which actual conversion process would need 410 Kcal, the rest ending up as losses, which can be recovered. In reality, the Indian cement industry average is 744 Kcal of heat input for producing 1 kg of clinker, which means the actual losses are even more than the theoretical possibility.
Out of the total generated heat there are some unavoidable losses, that include radiation loss, loss for evaporation of residual moisture in fine coal and raw meal and some part of heat going with clinker from cooler. The balance loss in pre-heater exhaust gases and the cooler exhaust gases are completely recoverable through WHRS.

electricity consumption to make a significant dent in the
energy intake the industry
Let us look at some statistics from the Indian cement industry. On an average, Indian cement plants require electrical power of 20 billion kWh per year. The coal needed for generating this much power accounts to 32 million tonnes per year. A significant portion of this power could be replaced by the WHRS that will use waste heat from the kilns to generate electricity.
In sustainability terms, this is equivalent to replacing a large component of the 32 million tonnes of coal to be otherwise burnt for producing electricity. WHRS are also very stable systems that operate on the Rankine cycle and it provides an avenue for utilising waste water from the process as well.
Balancing the investments
Let us now see the economics of putting up a captive power generating unit versus putting up a WHRS. The capital investment for WHRS is high at Rs 8 cr per MW going by the current costs, whereas the CPP units can come at Rs 4.5 cr per MW. However, the project Internal Rate of Return (IRR) would be very different as the cost of generation would be as low as Rs 0.40 per unit for the former while Rs 4.5 per unit for the latter, which given the current trajectory of fossil fuel prices is already under severe stress of upward correction. It is only the initial cost that continues to act as a deterrent for putting up a waste heat recovery unit.
The Indian cement industry must act responsibly and move quickly to put in investments that could raise the waste heat recovery installed capacity to cross the minimum threshold of 25 per cent of electricity consumption. That will still be far from the 20 billion KWhr of total electricity consumption by the industry.
The other area of concern is the price trajectory of fossil fuels, which would continue to move northwards. WHRS is one of the simpler ways of insulating the industry from the vagaries of future price increases.
Thus WHRS could be the natural hedge to fossil fuel price increases for a substantial portion of the electrical consumption. As matters stand today most WHRS would be the highest IRR projects that the industry as an ensemble can think of
-Procyon Mukherjee
Concrete
Refractory demands in our kiln have changed
Published
21 hours agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Radha Singh, Senior Manager (P&Q), Shree Digvijay Cement, points out why performance, predictability and life-cycle value now matter more than routine replacement in cement kilns.
As Indian cement plants push for higher throughput, increased alternative fuel usage and tighter shutdown cycles, refractory performance in kilns and pyro-processing systems is under growing pressure. In this interview, Radha Singh, Senior Manager (P&Q), Shree Digvijay Cement, shares how refractory demands have evolved on the ground and how smarter digital monitoring is improving kiln stability, uptime and clinker quality.
How have refractory demands changed in your kiln and pyro-processing line over the last five years?
Over the last five years, refractory demands in our kiln and pyro line have changed. Earlier, the focus was mostly on standard grades and routine shutdown-based replacement. But now, because of higher production loads, more alternative fuels and raw materials (AFR) usage and greater temperature variation, the expectation from refractory has increased.
In our own case, the current kiln refractory has already completed around 1.5 years, which itself shows how much more we now rely on materials that can handle thermal shock, alkali attack and coating fluctuations. We have moved towards more stable, high-performance linings so that we don’t have to enter the kiln frequently for repairs.
Overall, the shift has been from just ‘installation and run’ to selecting refractories that give longer life, better coating behaviour and more predictable performance under tougher operating conditions.
What are the biggest refractory challenges in the preheater, calciner and cooler zones?
• Preheater: Coating instability, chloride/sulphur cycles and brick erosion.
• Calciner: AFR firing, thermal shock and alkali infiltration.
• Cooler: Severe abrasion, red-river formation and mechanical stress on linings.
Overall, the biggest challenge is maintaining lining stability under highly variable operating conditions.
How do you evaluate and select refractory partners for long-term performance?
In real plant conditions, we don’t select a refractory partner just by looking at price. First, we see their past performance in similar kilns and whether their material has actually survived our operating conditions. We also check how strong their technical support is during shutdowns, because installation quality matters as much as the material itself.
Another key point is how quickly they respond during breakdowns or hot spots. A good partner should be available on short notice. We also look at their failure analysis capability, whether they can explain why a lining failed and suggest improvements.
On top of this, we review the life they delivered in the last few campaigns, their supply reliability and their willingness to offer plant-specific custom solutions instead of generic grades. Only a partner who supports us throughout the life cycle, which includes selection, installation, monitoring and post-failure analysis, fits our long-term requirement.
Can you share a recent example where better refractory selection improved uptime or clinker quality?
Recently, we upgraded to a high-abrasion basic brick at the kiln outlet. Earlier we had frequent chipping and coating loss. With the new lining, thermal stability improved and the coating became much more stable. As a result, our shutdown interval increased and clinker quality remained more consistent. It had a direct impact on our uptime.
How is increased AFR use affecting refractory behaviour?
Increased AFR use is definitely putting more stress on the refractory. The biggest issue we see daily is the rise in chlorine, alkalis and volatiles, which directly attack the lining, especially in the calciner and kiln inlet. AFR firing is also not as stable as conventional fuel, so we face frequent temperature fluctuations, which cause more thermal shock and small cracks in the lining.
Another real problem is coating instability. Some days the coating builds too fast, other days it suddenly drops, and both conditions impact refractory life. We also notice more dust circulation and buildup inside the calciner whenever the AFR mix changes, which again increases erosion.
Because of these practical issues, we have started relying more on alkali-resistant, low-porosity and better thermal shock–resistant materials to handle the additional stress coming from AFR.
What role does digital monitoring or thermal profiling play in your refractory strategy?
Digital tools like kiln shell scanners, IR imaging and thermal profiling help us detect weakening areas much earlier. This reduces unplanned shutdowns, helps identify hotspots accurately and allows us to replace only the critical sections. Overall, our maintenance has shifted from reactive to predictive, improving lining life significantly.
How do you balance cost, durability and installation speed during refractory shutdowns?
We focus on three points:
• Material quality that suits our thermal profile and chemistry.
• Installation speed, in fast turnarounds, we prefer monolithic.
• Life-cycle cost—the cheapest material is not the most economical. We look at durability, future downtime and total cost of ownership.
This balance ensures reliable performance without unnecessary expenditure.
What refractory or pyro-processing innovations could transform Indian cement operations?
Some promising developments include:
• High-performance, low-porosity and nano-bonded refractories
• Precast modular linings to drastically reduce shutdown time
• AI-driven kiln thermal analytics
• Advanced coating management solutions
• More AFR-compatible refractory mixes
These innovations can significantly improve kiln stability, efficiency and maintenance planning across the industry.
Concrete
Digital supply chain visibility is critical
Published
21 hours agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
MSR Kali Prasad, Chief Digital and Information Officer, Shree Cement, discusses how data, discipline and scale are turning Industry 4.0 into everyday business reality.
Over the past five years, digitalisation in Indian cement manufacturing has moved decisively beyond experimentation. Today, it is a strategic lever for cost control, operational resilience and sustainability. In this interview, MSR Kali Prasad, Chief Digital and Information Officer, Shree Cement, explains how integrated digital foundations, advanced analytics and real-time visibility are helping deliver measurable business outcomes.
How has digitalisation moved from pilot projects to core strategy in Indian cement manufacturing over the past five years?
Digitalisation in Indian cement has evolved from isolated pilot initiatives into a core business strategy because outcomes are now measurable, repeatable and scalable. The key shift has been the move away from standalone solutions toward an integrated digital foundation built on standardised processes, governed data and enterprise platforms that can be deployed consistently across plants and functions.
At Shree Cement, this transition has been very pragmatic. The early phase focused on visibility through dashboards, reporting, and digitisation of critical workflows. Over time, this has progressed into enterprise-level analytics and decision support across manufacturing and the supply chain,
with clear outcomes in cost optimisation, margin protection and revenue improvement through enhanced customer experience.
Equally important, digital is no longer the responsibility of a single function. It is embedded into day-to-day operations across planning, production, maintenance, despatch and customer servicing, supported by enterprise systems, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) data platforms, and a structured approach to change management.
Which digital interventions are delivering the highest ROI across mining, production and logistics today?
In a capital- and cost-intensive sector like cement, the highest returns come from digital interventions that directly reduce unit costs or unlock latent capacity without significant capex.
Supply chain and planning (advanced analytics): Tools for demand forecasting, S&OP, network optimisation and scheduling deliver strong returns by lowering logistics costs, improving service levels, and aligning production with demand in a fragmented and regionally diverse market.
Mining (fleet and productivity analytics): Data-led mine planning, fleet analytics, despatch discipline, and idle-time reduction improve fuel efficiency and equipment utilisation, generating meaningful savings in a cost-heavy operation.
Manufacturing (APC and process analytics): Advanced Process Control, mill optimisation, and variability reduction improve thermal and electrical efficiency, stabilise quality and reduce rework and unplanned stoppages.
Customer experience and revenue enablement (digital platforms): Dealer and retailer apps, order visibility and digitally enabled technical services improve ease of doing business and responsiveness. We are also empowering channel partners with transparent, real-time information on schemes, including eligibility, utilisation status and actionable recommendations, which improves channel satisfaction and market execution while supporting revenue growth.
Overall, while Artificial Intelligence (AI) and IIoT are powerful enablers, it is advanced analytics anchored in strong processes that typically delivers the fastest and most reliable ROI.
How is real-time data helping plants shift from reactive maintenance to predictive and prescriptive operations?
Real-time and near real-time data is driving a more proactive and disciplined maintenance culture, beginning with visibility and progressively moving toward prediction and prescription.
At Shree Cement, we have implemented a robust SAP Plant Maintenance framework to standardise maintenance workflows. This is complemented by IIoT-driven condition monitoring, ensuring consistent capture of equipment health indicators such as vibration, temperature, load, operating patterns and alarms.
Real-time visibility enables early detection of abnormal conditions, allowing teams to intervene before failures occur. As data quality improves and failure histories become structured, predictive models can anticipate likely failure modes and recommend timely interventions, improving MTBF and reducing downtime. Over time, these insights will evolve into prescriptive actions, including spares readiness, maintenance scheduling, and operating parameter adjustments, enabling reliability optimisation with minimal disruption.
A critical success factor is adoption. Predictive insights deliver value only when they are embedded into daily workflows, roles and accountability structures. Without this, they remain insights without action.
In a cost-sensitive market like India, how do cement companies balance digital investment with price competitiveness?
In India’s intensely competitive cement market, digital investments must be tightly linked to tangible business outcomes, particularly cost reduction, service improvement, and faster decision-making.
This balance is achieved by prioritising high-impact use cases such as planning efficiency, logistics optimisation, asset reliability, and process stability, all of which typically deliver quick payback. Equally important is building scalable and governed digital foundations that reduce the marginal cost of rolling out new use cases across plants.
Digitally enabled order management, live despatch visibility, and channel partner platforms also improve customer centricity while controlling cost-to-serve, allowing service levels to improve without proportionate increases in headcount or overheads.
In essence, the most effective digital investments do not add cost. They protect margins by reducing variability, improving planning accuracy, and strengthening execution discipline.
How is digitalisation enabling measurable reductions in energy consumption, emissions, and overall carbon footprint?
Digitalisation plays a pivotal role in improving energy efficiency, reducing emissions and lowering overall carbon intensity.
Real-time monitoring and analytics enable near real-time tracking of energy consumption and critical operating parameters, allowing inefficiencies to be identified quickly and corrective actions to be implemented. Centralised data consolidation across plants enables benchmarking, accelerates best-practice adoption, and drives consistent improvements in energy performance.
Improved asset reliability through predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime and process instability, directly lowering energy losses. Digital platforms also support more effective planning and control of renewable energy sources and waste heat recovery systems, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Most importantly, digitalisation enables sustainability progress to be tracked with greater accuracy and consistency, supporting long-term ESG commitments.
What role does digital supply chain visibility play in managing demand volatility and regional market dynamics in India?
Digital supply chain visibility is critical in India, where demand is highly regional, seasonality is pronounced, and logistics constraints can shift rapidly.
At Shree Cement, planning operates across multiple horizons. Annual planning focuses on capacity, network footprint and medium-term demand. Monthly S&OP aligns demand, production and logistics, while daily scheduling drives execution-level decisions on despatch, sourcing and prioritisation.
As digital maturity increases, this structure is being augmented by central command-and-control capabilities that manage exceptions such as plant constraints, demand spikes, route disruptions and order prioritisation. Planning is also shifting from aggregated averages to granular, cost-to-serve and exception-based decision-making, improving responsiveness, lowering logistics costs and strengthening service reliability.
How prepared is the current workforce for Industry 4.0, and what reskilling strategies are proving most effective?
Workforce preparedness for Industry 4.0 is improving, though the primary challenge lies in scaling capabilities consistently across diverse roles.
The most effective approach is to define capability requirements by role and tailor enablement accordingly. Senior leadership focuses on digital literacy for governance, investment prioritisation, and value tracking. Middle management is enabled to use analytics for execution discipline and adoption. Frontline sales and service teams benefit from
mobile-first tools and KPI-driven workflows, while shop-floor and plant teams focus on data-driven operations, APC usage, maintenance discipline, safety and quality routines.
Personalised, role-based learning paths, supported by on-ground champions and a clear articulation of practical benefits, drive adoption far more effectively than generic training programmes.
Which emerging digital technologies will fundamentally reshape cement manufacturing in the next decade?
AI and GenAI are expected to have the most significant impact, particularly when combined with connected operations and disciplined processes.
Key technologies likely to reshape the sector include GenAI and agentic AI for faster root-cause analysis, knowledge access, and standardisation of best practices; industrial foundation models that learn patterns across large sensor datasets; digital twins that allow simulation of process changes before implementation; and increasingly autonomous control systems that integrate sensors, AI, and APC to maintain stability with minimal manual intervention.
Over time, this will enable more centralised monitoring and management of plant operations, supported by strong processes, training and capability-building.
Concrete
Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency
Published
22 hours agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Shreesh A Khadilkar discusses how advanced additive formulations allow customised, high-performance and niche cements—offering benefits while supporting blended cements and long-term cost and carbon reduction.
Cement additives are chemicals (inorganic and organic) added in small amounts (0.01 per cent to 0.2 per cent by weight) during cement grinding. Their main job? Reduce agglomeration, prevent pack-set, and keep the mill running smoother. Thus, these additions primarily improve, mill thru-puts, achieve lower clinker factor in blended cements PPC/PSC/PCC. Additionally, these additives improve concrete performance of cements or even for specific special premium cements with special USPs like lower setting times or for reduced water permeability in the resultant cement mortars and concrete (water repellent /permeation resistant cements), corrosion resistance etc.
The cement additives are materials which could be further differentiated as:
Grinding aids:
• Bottlenecks in cement grinding capacity, such materials can enhance throughputs
• Low specific electrical energy consumption during cement grinding
• Reduce “Pack set” problem and improve powder flowability
Quality improvers:
• Opportunity for further clinker factor reduction
• Solution for delayed cement setting or strength development issues at early or later ages.
Others: materials which are used for specific special cements with niche properties as discussed in the subsequent pages.
When cement additives are used as grinding aids or quality improvers, in general the additives reduce the inter-particle forces; reduce coating over grinding media and mill internals. Due to creation of like charges on cement particles, there is decreased agglomeration, much improved flowability, higher generation of fines better dispersion of particles in separator feed and reduction of mill filling level (decrease of residence time). However, in VRM grinding; actions need to be taken to have stable bed formation on the table.
It has been reported in literature and also substantiated by a number of detailed evaluations of different cement additive formulations in market, that the cement additive formulations are a combination of different chemical compounds, typically composed of:
- Accelerator/s for the hydration reaction of cements which are dependent on the acceleration effect desired in mortar compressive strengths at early or later ages, the choice of the materials is also dependent on clinker quality and blending components (flyash / slag) or a mix of both.
- Water reducer / workability / wet-ability enhancer, which would show impact on the resultant cement mortars and concrete. Some of the compounds (retarders) like polysaccharide derivatives, gluconates etc., show an initial retarding action towards hydration which result in reducing the water requirements for the cements thus act as water reducers, or it could be some appropriate polymeric molecules which show improved wet-ability and reduce water demand. These are selected based on the mineral component and type of cements (PPC/PSC /PCC).
- Grinding aids: Compounds that work as Grinding Aid i.e. which would enhance Mill thru-put on one hand as well as would increase the early strengths due to the higher fines generation/ or activation of cement components. These compounds could be like alkanol-amines such as TIPA, DEIPA, TEA etc. or could be compounds like glycols and other poly-ols, depending on whether it is OPC or PPC or PSC or PCC manufacture.
Mechanism of action — Step By Step—
- Reduce Agglomeration, Cement particles get electrostatically charged during grinding, stick together, form “flocs”, block mill efficiency, waste energy. Grinding aid molecules adsorb onto particle surfaces, neutralise charge, prevent re-agglomeration.
- Improve Powder Flowability, Adsorbed molecules create a lubricating layer, particles slide past each other easier, better mill throughput, less “dead zone” buildup.
Also reduces caking on mill liners, diaphragms, and separator screens, less downtime for cleaning. - Enhance Grinding Efficiency (Finer Product Faster), By preventing agglomeration, particles stay dispersed more surface area exposed to grinding media, finer grind achieved with same energy input, Or: same fineness achieved with less energy, huge savings.
Example:
• Without aid ? 3500 cm²/g Blaine needs 40 kWh/ton
• With use of optimum grinding aid same fineness at 32 kWh/ton 20 per cent energy savings - Reduce Pack Set and Silo Caking Grinding aids (GA) inhibit hydration of free lime (CaO) during storage prevents premature hardening or “pack set” in silos. especially critical in humid climates or with high free lime clinker.
It may be stated here that Overdosing of GA can cause: – Foaming in mill (especially with glycols) reduces grinding efficiency, retardation of cement setting (especially with amines/acids), odor issues (in indoor mills) – Corrosion of mill components (if acidic aids used improperly)
The best practice to optimise use of GA is Start with 0.02 per cent to 0.05 per cent dosage test fineness, flow, and set time adjust up/down. Due to static charge of particles, the sample may stick to the sides of sampler pipe and so sampling need to be properly done.
Depending on type of cements i.e. OPC, PPC, PSC, PCC, the grinding aids combinations need to be optimised, a typical Poly carboxylate ether also could be a part of the combo grinding aids
Cement additives for niche properties of the cement in concrete.
The cement additives can also be tailor made to create specific niche properties in cements, OPC, PPC, PSC and PCC to create premium or special brands. The special niche properties of the cement being its additional USP of such cement products, and are useful for customers to build a durable concrete structure with increased service life.
Such properties could be:
• Additives for improved concrete performance of cements, high early strength in PPC/PSC/PCC, much reduced water demand in cement, cements with improved slump retentivity in concrete, self-compacting, self levelling in concrete, cements with improved adhesion property of the cement mortar
• Water repellence / water proofing, permeability resistance in mortars and concrete.
• Biocidal cement
• Photo catalytic cements
• Cements with negligible ASR reactions etc.
Additives for cements for improved concrete performance
High early strengths: Use of accelerators. These are chemical compounds which enhance the degree of hydration of cement. These can include setting or hardening accelerators depending on whether their action occurs in the plastic or hardened state respectively. Thus, the setting accelerators reduce the setting time, whereas the hardening accelerators increase the early age strengths. The setting accelerators act during the initial minutes of the cement hydration, whereas the hardening accelerators act mainly during the initial days of hydration.
Chloride salts are the best in class. However, use of chloride salts as hardening accelerators are strongly discouraged for their action in promoting the corrosion of rebar, thus, chloride-free accelerators are preferred. The hardening accelerators could be combinations of compounds like nitrate, nitrite and thiocyanate salts of alkali or alkaline earth metals or thiosulphate, formate, and alkanol amines depending on the cement types.
However, especially in blended cements (PPC/PSC/PCC the increased early strengths invariably decrease the 28 day strengths. These aspects lead to creating combo additives along with organic polymers to achieve improved early strengths as well as either same or marginally improved 28 days strengths with reduced clinker factor in the blended cement, special OPC with reduced admixture requirements. With use of appropriate combination of inorganic and organic additives we could create an OPC with substantially reduced water demand or improved slump retentivity. Use of such an OPC would show exceptional concrete performance in high grade concretes as it would exhibit lower admixture requirements in High Grade Concretes.
PPC with OPC like properties: With the above concept we could have a PPC, having higher percentage flyash, with a combo cement additive which would have with concrete performance similar to OPC in say M40/M50 concrete. Such a PPC would produce a high-strength PPC concrete (= 60 MPa @ 28d) + improved workability, durability and sustainability.
Another interesting aspect could also be of using ultrafine fine flyash /ultrafine slags as additions in OPC/PPC/PSC for achieving lower clinker factor as well as to achieve improved later age strengths with or without a combo cement additive.
The initial adhesion property at sites of especially PPC/PSC/PCC based mortars can be improved through use of appropriate organic polymers addition during the manufacture of these cements. Such cements would have a better adhesion property for plastering/brick bonding etc., as it has much lower rebound loss of their mortars in such applications.
It is needless to mention here that with use of additives, we could also have cement with viscosity modifying cement additives, for self-compaction and self-leveling concrete performance.
Use of Phosphogypsum retards the setting time of cements, we can use additive different additive combos to overcome retardation and improve the 1 day strengths of the cements and concretes.
About the author:
Shreesh Khadilkar, Consultant & Advisor, Former Director Quality & Product Development, ACC, a seasoned consultant and advisor, brings over 37 years of experience in cement manufacturing, having held leadership roles in R&D and product development at ACC Ltd. With deep expertise in innovative cement concepts, he is dedicated to sharing his knowledge and improving the performance of cement plants globally.

Refractory demands in our kiln have changed

Digital supply chain visibility is critical

Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation

Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency

Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing

Refractory demands in our kiln have changed

Digital supply chain visibility is critical

Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation

Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency

Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing
Trending News
-

 Concrete4 weeks ago
Concrete4 weeks agoAris Secures Rs 630 Million Concrete Supply Order
-

 Concrete3 weeks ago
Concrete3 weeks agoNITI Aayog Unveils Decarbonisation Roadmaps
-

 Concrete3 weeks ago
Concrete3 weeks agoJK Cement Commissions 3 MTPA Buxar Plant, Crosses 31 MTPA
-

 Economy & Market3 weeks ago
Economy & Market3 weeks agoBudget 2026–27 infra thrust and CCUS outlay to lift cement sector outlook