Economy & Market
AAC production in cement plant
Published
12 years agoon
By
admin
Cement companies can manufacture AAC blocks and can compete with stand alone AAC units in the country.
The raw materials required for AAC production are readily available in any cement manufacturing plant. The process does not require installation of a steam boiler or a power plant and can utilise the waste-heat from the clinker cooler exhaust gases for steam curing of aerated concrete. The method also earns carbon credits not only for the green product being made, but also for waste-heat utilisation. Although, there are more than 35 standalone AAC manufacturing units in India, very limited attempts have been made to manufacture AAC by the cement plants. One reason behind this is the lack of awareness about the new technologies that were developed recently in this field. DS Venkatesh elaborates on the technology offered by Cemeng for AAC production in a cement plant.
What is AAC
AAC is lightweight autoclaved aerated concrete, which is completely cured, inert and stable form of calcium silicate hydrate. It is a structural material, approximately one quarter in weight of the conventional concrete. It is composed of minute cells/air pockets, which give the material its lightweight and high thermal insulation characteristics. It is available as blocks and as pre-cast reinforced units for building floors, roofs, walls and lintels.
Raw material
Raw materials for AAC vary with the manufacturer and the location. The kinds of materials that could be used are detailed in the ASTM C1386 specifications. They include some, or all, of the following: fine silica sand; Class F fly ash; hydraulic cements; calcined lime; gypsum; expansive agents such as finely ground aluminium powder or paste; and water.
AAC is produced by mixing quartz sand and/or pulverised fly ash (PFA), lime, cement, gypsum/anhydrite, water and aluminium and is hardened by steam-curing in autoclaves. The silica is obtained from silica sand, fly ash (PFA), crushed silica rock and/or stone. It is possible to obtain silica as a by-product coming from other processes such as foundry sand or burgee from glass grinding; although, it can be used only if the levels of alkali or other impurities are not too high. The calcium is obtained from quick lime, hydrated lime and cement. Gypsum acts as a catalyst and enhances the properties of AAC. Careful regulation of the amount of aluminium powder gives accurate control over the density of the final product.
Cement with the least per cent of clinker would be the cheapest and suitable, e.g., Portland limestone cement. If milling of siliceous material is required, Cemeng suggests grinding of a composite mix of siliceous materials together with cement clinker, lime and gypsum/anhydrous. The ground material can be stored in a single bin. It also eliminates the need for multiple handling of individual constituents and weigh batchers. Cemeng employs a PSRG mill function in open circuit to produce the desired fineness of the composite mix.
Process flow
Cemeng has simplified the process flow to minimise the number of equipment and material handling requirements in mini AAC plants. The process gets rid of ?wet cutting? the green cake as it is possible only if the plant is involved in exclusive production of smaller blocks. Other AAC products with or without reinforcement certainly require ?dry milling? of cured cakes for profiling. Cemeng moulds for AAC are wheel-mounted units with a base plate and sliding sidewalls. There is no need for rotation or dismantling and re-assembling of side plates. Loaded moulds are transferred directly into the autoclaves for steam curing. Cemeng autoclaves generate the required steam in the autoclave itself. Separate boiler is not required. For mini AAC plants, Cemeng suggests after-cutting/milling of cured blocks for economic benefits.
The important unit operations involved in AAC production are gravimetric proportioning and mixing of constituents with water to form the slurry. This is followed with secondary mixing with expansive agents, pouring the slurry into casting moulds and then allowing sufficient time for initial hydration. Once the material is hydrated it gains enough strength to support its own weight and can undergo de-moulding/cutting. The cakes are then transferred into autoclave for high pressure steam curing. Once cooled, the autoclaved blocks are ready for after-cutting/milling as per the required profile. The AAC cost depends mainly on the cost of mineral binders and the expansive agents used. The cost of silica can vary from location to location.
Cement plant and Cemeng mini AAC production line
Cemeng mini AAC production line can be installed in an existing cement plant. Cement plants are already processing and handling both siliceous and mineral binder constituents, except for lime and sand. Also, ground raw meal, preheater ESP dust, pre-calcined meal from bottom most stage of preheater can partially or wholly replace lime. Sand may be replaced by ground slag and cinder. Clinker dust from cooler ESP and gypsum can replace cement. Besides, clinker cooler exhaust air may be effectively utilised for production of steam required for autoclaving, thus eliminating the need for a separate boiler set up.
AAC production capacity, on a thumb rule basis, can be considered as twenty cubic meter per day for every 100 tpd production capacity of the clinkerisation unit. This is based on steam production using gases only from the from clinker cooler exhaust.
Manufacturing process
To make AAC, sand is ground to the required fineness in a ball mill and is stored along with other raw materials. The raw materials are then batched by weight and are delivered to the mixer. Measured amounts of water and expansive agent is added to the mixer to prepare a cementitious slurry.
Preparation of slurry
Slurry preparation is a batch process. When AAC is being made from dry constituents, Cemeng employs separate weighbin augur dosers for each constituent the Cemeng weighbin augur doser, which uses a combination of weight and volumetric filling. A vertical auger looks like a corkscrew. The auger rotates in the hopper filled with lose powder. As it turns, it drives the powder through the bottom of the hopper into a narrow tube, where the powder is drawn down by a turning screw. The auger runs through the narrow tube, creating a tight fit. As the screw turns, it pulls the prescribed amount of powder down the tube. The agitator keeps the feed flowing to the centre of the auger. You can control the amount of powder delivered by setting the number of revolution made by the auger.
The augur screw discharges into a tubular disc conveyor for conveying and transferring directly into the AAC mixer. Subsequently, aluminium paste is added, secondary mixing is carried out and the final slurry is discharged into the AAC moulds.
Casting in moulds
Steel moulds are prepared to receive fresh AAC. If reinforced AAC panels are to be produced, steel reinforcing cages are secured within the moulds. After mixing, the slurry is poured into the moulds. The expansive agent creates small, finely dispersed voids in the fresh mixture, which increases the volume by about 50 per cent within three hours. The moulding of AAC in the mould box, holding for initial strength and de-moulding prior to autoclaving is an important step in reducing the material handling. Conventionally, the base of the moulds-box and three sides are welded together with only one side plate of mountable type. This calls for mould rotation to load the green mould on to the mountable side plate.
Cemeng moulds for AAC are trolley-mounted units with a base plate and sliding sidewalls. During casting, the sidewalls are slided inwards to form a box holding the slurry. The sidewalls keep space all around the green cake for the passage of steam. No rotation or dismantling of the side plates and reassembling are required. After curing in autoclaves, the cake is picked up by a grab and is transferred to the trolley.
Cemeng also offers ?FlexiMold? wherein rectangular shaped pre-stitched permeable cloth bags with open top are held at the base of the trolley. The flexibag is filled half with slurry and the top half is left empty to allow for expansion. As the green cake attains strength, it attains the shape of the flexibag. The telescopic brackets are then lowered. The bracket is held in its lowest position when the trolley is moved into the autoclave. The green cake along with FlexiMold is left undisturbed. After curing, the trolley is moved out and the cured cake in the moulding bag is lifted and transferred to storage. FlexiMold serves as a protective cover for cured block and it is also disposable. The size of the green cake can be set as required and several green cakes can be mounted on a single trolley.
Autoclaving
Autoclaving is steam curing at high temperature and pressure. It is required to achieve the desired structural properties and dimensional stability. The chemical reactions that produce the final calcium silicate hydrate structure happen in the autoclave. The process takes about eight to 12 hours under pressure of about 174 psi (12 bar) and a temperature of about 360?F (180?C), depending on the grade of material produced. Preferably, two autoclaves are used with the casting and precuring section in between. The mixing station is located near the discharge end of the autoclave. The thermic fluid reservoir is located at the feed end of the autoclave. This permits the precuring shed to store the cast moulds for the required duration. The waste heat from grate cooler exhaust is utilised for the heating the thermic fluid in a simple heat exchanger. It is estimated that at least 350-400 kg/hr of steam could be generated per 100 tpd production capacity of clinkerisation unit. To initiate the curing cycle, the thermic fluid, heated to 205?C, is passed through the coils in the reservoir at the bottom of each autoclave to generate steam. The hot steam pressure rises up to 1.75Mpa.
After-cutting/milling of cured AAC Blocks
Steam cured AAC blocks can be transported directly to the marketing yards. After-cutting can be carried out by the stockists or at the construction site itself. Existing granite/stone cutting and polishing units at different cities in the marketing zone can be used to saw the AAC blocks to the required size/dimensions. It is always possible to saw cut the large size AAC blocks to the required size at the construction site. Any broken pieces could be used as lightweight filler, thus nothing is wasted.
Conclusion
Every cement plant has to take green initiatives to safeguard sustainability. Using waste-heat for steam generation is highly cost effective and adds to the profits of AAC production. Besides, the plant will also be a captive consumer of cement. Every cement plant can produce AAC at considerably lower cost and can compete with standalone AAC units. AAC products can save time, labour, cement and sand during construction.
References
Eco-Care Building products: www.primeaac.com
Raw material formulae: Dearye Brick machine
Silica, calcium joined in premium products, by Sandy Herod Pit and Quarry Dec 1987 Pg.72 – 74
Brick manufacture in a Cement Plant by DS Venkatesh, Cemtec Engineering, Secunderabad. Indian Cement Review May 1989, Pages ICR-19 to ICR-25 Green Concrete by Yuvraj Patil, Flycrete. Indian Cement Review, May 2014 ?Let us employ PSRG Milling Technology? by DS Venkatesh, Indian Cement Industry Desk Book, March 2014. www.victoryenergy.com
DS Venkatesh,
Freelance Industrial Consultant
Email: dsvenkatesh40@gmail.com
Former CEO and Director of Cemtec Engineering at Secunderabad, DS Venkatesh is currently working as a freelance industrial consultant. He started as a Design Engineer at ACC and later had a long stint at Holtec-India holding several responsible positions. He has been one of the lead consultants to many rotary based mini cement plants and expansions.
DS Venkatesh has provided technical know-how, design and manufacturing drawings for cement production machinery to many Indian machinery manufacturers. Re-engineering and retrofitting of plant/machinery for enhanced productivity is his forte. His work has helped in enhancement of PSRG milling technology applied in media grinding.
You may like
Concrete
Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships
Published
6 hours agoon
February 19, 2026By
admin
Jean-Jacques Bois, President, Nanolike, discusses how real-time data is reshaping cement delivery planning and fleet performance.
As cement producers look to extract efficiency gains beyond the plant gate, real-time visibility and data-driven logistics are becoming critical levers of competitiveness. In this interview with Jean-Jacques Bois, President, Nanolike, we discover how the company is helping cement brands optimise delivery planning by digitally connecting RMC silos, improving fleet utilisation and reducing overall logistics costs.
How does SiloConnect enable cement plants to optimise delivery planning and logistics in real time?
In simple terms, SiloConnect is a solution developed to help cement suppliers optimise their logistics by connecting RMC silos in real time, ensuring that the right cement is delivered at the right time and to the right location. The core objective is to provide real-time visibility of silo levels at RMC plants, allowing cement producers to better plan deliveries.
SiloConnect connects all the silos of RMC plants in real time and transmits this data remotely to the logistics teams of cement suppliers. With this information, they can decide when to dispatch trucks, how to prioritise customers, and how to optimise fleet utilisation. The biggest savings we see today are in logistics efficiency. Our customers are able to sell and ship more cement using the same fleet. This is achieved by increasing truck rotation, optimising delivery routes, and ultimately delivering the same volumes at a lower overall logistics cost.
Additionally, SiloConnect is designed as an open platform. It offers multiple connectors that allow data to be transmitted directly to third-party ERP systems. For example, it can integrate seamlessly with SAP or other major ERP platforms, enabling automatic order creation whenever replenishment is required.
How does your non-exclusive sensor design perform in the dusty, high-temperature, and harsh operating conditions typical of cement plants?
Harsh operating conditions such as high temperatures, heavy dust, extreme cold in some regions, and even heavy rainfall are all factored into the product design. These environmental challenges are considered from the very beginning of the development process.
Today, we have thousands of sensors operating reliably across a wide range of geographies, from northern Canada to Latin America, as well as in regions with heavy rainfall and extremely high temperatures, such as southern Europe. This extensive field experience demonstrates that, by design, the SiloConnect solution is highly robust and well-suited for demanding cement plant environments.
Have you initiated any pilot projects in India, and what outcomes do you expect from them?
We are at the very early stages of introducing SiloConnect in India. Recently, we installed our
first sensor at an RMC plant in collaboration with FDC Concrete, marking our initial entry into the Indian market.
In parallel, we are in discussions with a leading cement producer in India to potentially launch a pilot project within the next three months. The goal of these pilots is to demonstrate real-time visibility, logistics optimisation and measurable efficiency gains, paving the way for broader adoption across the industry.
What are your long-term plans and strategic approach for working with Indian cement manufacturers?
For India, our strategy is to establish strong and reliable local partnerships, which will allow us to scale the technology effectively. We believe that on-site service, local presence, and customer support are critical to delivering long-term value to cement producers.
Ideally, our plan is to establish an Indian entity within the next 24 months. This will enable us to serve customers more closely, provide faster support and contribute meaningfully to the digital transformation of logistics and supply chain management in the Indian cement industry.
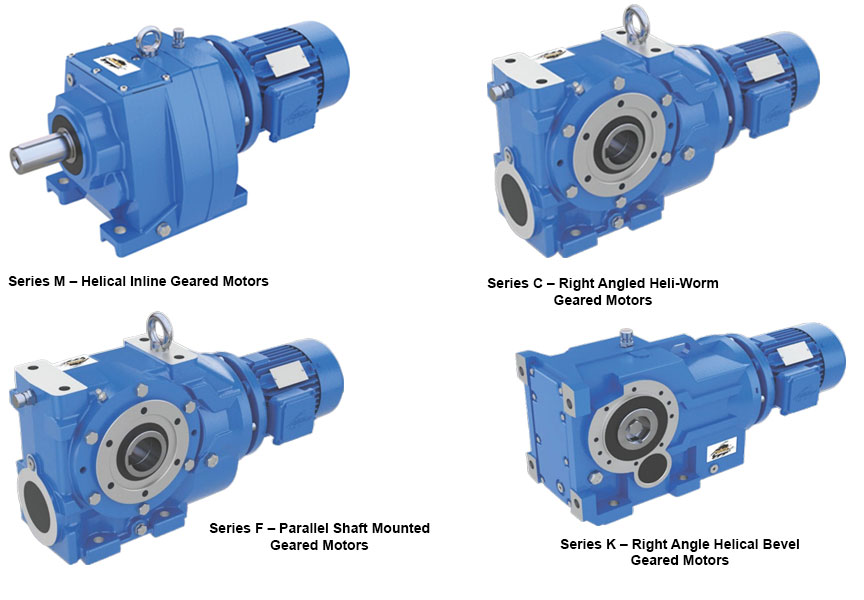
A deep dive into Core Gear Series of products M, C, F and K, by Power Build, and how they represent precision in motion.
At the heart of every high-performance industrial system lies the need for robust, reliable, and efficient power transmission. Power Build answers this need with its flagship geared motor series: M, C, F and K. Each series is meticulously engineered to serve specific operational demands while maintaining the universal promise of durability, efficiency, and performance.
Series M – Helical Inline Geared Motors
Compact and powerful, the Series M delivers exceptional drive solutions for a broad range of applications. With power handling up to 160kW and torque capacity reaching 20,000 Nm, it is the trusted solution for industries requiring quiet operation, high efficiency, and space-saving design. Series M is available with multiple mounting and motor options, making it a versatile choice for manufacturers and OEMs globally.
Series C – Right Angled Heli-Worm Geared Motors
Combining the benefits of helical and worm gearing, the Series C is designed for right-angled power transmission. With gear ratios of up to 16,000:1 and torque capacities of up to 10,000 Nm, this series is optimal for applications demanding precision in compact spaces. Industries looking for a smooth, low-noise operation with maximum torque efficiency rely on Series C for dependable performance.
Series F – Parallel Shaft Mounted Geared Motors
Built for endurance in the most demanding environments, Series F is widely adopted in steel plants, hoists, cranes and heavy-duty conveyors. Offering torque up to 10,000 Nm and high gear ratios up to 20,000:1, this product features an integral torque arm and diverse output configurations to meet industry-specific challenges head-on.
Series K – Right Angle Helical Bevel Geared Motors
For industries seeking high efficiency and torque-heavy performance, Series K is the answer. This right-angled geared motor series delivers torque up to 50,000 Nm, making it a preferred choice in core infrastructure sectors such as cement, power, mining and material handling. Its flexibility in mounting and broad motor options offer engineers the freedom in design and reliability in execution.
Together, these four series reflect Power Build’s commitment to excellence in mechanical power transmission. From compact inline designs to robust right-angle drives, each geared motor is a result of decades of engineering innovation, customer-focused design and field-tested reliability. Whether the requirement is speed control, torque multiplication or space efficiency, Radicon’s Series M, C, F and K stand as trusted powerhouses for global industries.
http://www.powerbuild.in
Call: +919727719344

Pankaj Kejriwal, Whole Time Director and COO, Star Cement, on driving efficiency today and designing sustainability for tomorrow.
In an era where the cement industry is under growing pressure to decarbonise while scaling capacity, Star Cement is charting a pragmatic yet forward-looking path. In this conversation, Pankaj Kejriwal, Whole Time Director and COO, Star Cement, shares how the company is leveraging waste heat recovery, alternative fuels, low-carbon products and clean energy innovations to balance operational efficiency with long-term sustainability.
How has your Lumshnong plant implemented the 24.8 MW Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS), and what impact has it had on thermal substitution and energy costs?
Earlier, the cost of coal in the Northeast was quite reasonable, but over the past few years, global price increases have also impacted the region. We implemented the WHRS project about five years ago, and it has resulted in significant savings by reducing our overall power costs.
That is why we first installed WHRS in our older kilns, and now it has also been incorporated into our new projects. Going forward, WHRS will be essential for any cement plant. We are also working on utilising the waste gases exiting the WHRS, which are still at around 100 degrees Celsius. To harness this residual heat, we are exploring systems based on the Organic Rankine Cycle, which will allow us to extract additional power from the same process.
With the launch of Star Smart Building Solutions and AAC blocks, how are you positioning yourself in the low-carbon construction materials segment?
We are actively working on low-carbon cement products and are currently evaluating LC3 cement. The introduction of autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks provided us with an effective entry into the consumer-facing segment of the industry. Since we already share a strong dealer network across products, this segment fits well into our overall strategy.
This move is clearly supporting our transition towards products with lower carbon intensity and aligns with our broader sustainability roadmap.
With a diverse product portfolio, what are the key USPs that enable you to support India’s ongoing infrastructure projects across sectors?
Cement requirements vary depending on application. There is OPC, PPC and PSC cement, and each serves different infrastructure needs. We manufacture blended cements as well, which allows us to supply products according to specific project requirements.
For instance, hydroelectric projects, including those with NHPC, have their own technical norms, which we are able to meet. From individual home builders to road infrastructure, dam projects, and regions with heavy monsoon exposure, where weather-shield cement is required, we are equipped to serve all segments. Our ability to tailor cement solutions across diverse climatic and infrastructure conditions is a key strength.
How are you managing biomass usage, circularity, and waste reduction across
your operations?
The Northeast has been fortunate in terms of biomass availability, particularly bamboo. Earlier, much of this bamboo was supplied to paper plants, but many of those facilities have since shut down. As a result, large quantities of bamboo biomass are now available, which we utilise in our thermal power plants, achieving a Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) of nearly 60 per cent.
We have also started using bamboo as a fuel in our cement kilns, where the TSR is currently around 10 per cent to 12 per cent and is expected to increase further. From a circularity perspective, we extensively use fly ash, which allows us to reuse a major industrial waste product. Additionally, waste generated from HDPE bags is now being processed through our alternative fuel and raw material (AFR) systems. These initiatives collectively support our circular economy objectives.
As Star Cement expands, what are the key logistical and raw material challenges you face in scaling operations?
Fly ash availability in the Northeast is a constraint, as there are no major thermal power plants in the region. We currently source fly ash from Bihar and West Bengal, which adds significant logistics costs. However, supportive railway policies have helped us manage this challenge effectively.
Beyond the Northeast, we are also expanding into other regions, including the western region, to cater to northern markets. We have secured limestone mines through auctions and are now in the process of identifying and securing other critical raw material resources to support this expansion.
With increasing carbon regulations alongside capacity expansion, how do you balance compliance while sustaining growth?
Compliance and growth go hand in hand for us. On the product side, we are working on LC3 cement and other low-carbon formulations. Within our existing product portfolio, we are optimising operations by increasing the use of green fuels and improving energy efficiency to reduce our carbon footprint.
We are also optimising thermal energy consumption and reducing electrical power usage. Notably, we are the first cement company in the Northeast to deploy EV tippers at scale for limestone transportation from mines to plants. Additionally, we have installed belt conveyors for limestone transfer, which further reduces emissions. All these initiatives together help us achieve regulatory compliance while supporting expansion.
Looking ahead to 2030 and 2050, what are the key innovation and sustainability priorities for Star Cement?
Across the cement industry, carbon capture is emerging as a major focus area, and we are also planning to work actively in this space. In parallel, we see strong potential in green hydrogen and are investing in solar power plants to support this transition.
With the rapid adoption of solar energy, power costs have reduced dramatically – from 10–12 per unit to around2.5 per unit. This reduction will enable the production of green hydrogen at scale. Once available, green hydrogen can be used for electricity generation, to power EV fleets, and even as a fuel in cement kilns.
Burning green hydrogen produces only water and oxygen, eliminating carbon emissions from that part of the process. While process-related CO2 emissions from limestone calcination remain a challenge, carbon capture technologies will help address this. Ultimately, while becoming a carbon-negative industry is challenging, it is a goal we must continue to work towards.

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Compliance and growth go hand in h and

Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence

FORNNAX Appoints Dieter Jerschl as Sales Partner for Central Europe

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Compliance and growth go hand in h and

Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence





















