LC3 is a new type of cement that is based on a blend of limestone and calcined clay. LC3 can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 40 percent, is made using limestone and low-grade clays which are available in abundant quantities,is cost effective and does not require capital intensive modifications to existing cement plants.
The objective of the LC3-Project is, through research and testing, to make LC3 standard and mainstream general-use cement in the global cement market.
The main research activities focus not only on specific thematic areas of cement research but also on production, environmental sustainability and cost effectiveness of this new cement.
With funding from the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation through its Global Programme in Climate Change, that has been able to bring the idea of the LC3-technology from the lab in Switzerland to all parts of the world.

Difference between LC3 and conventional Portland cement
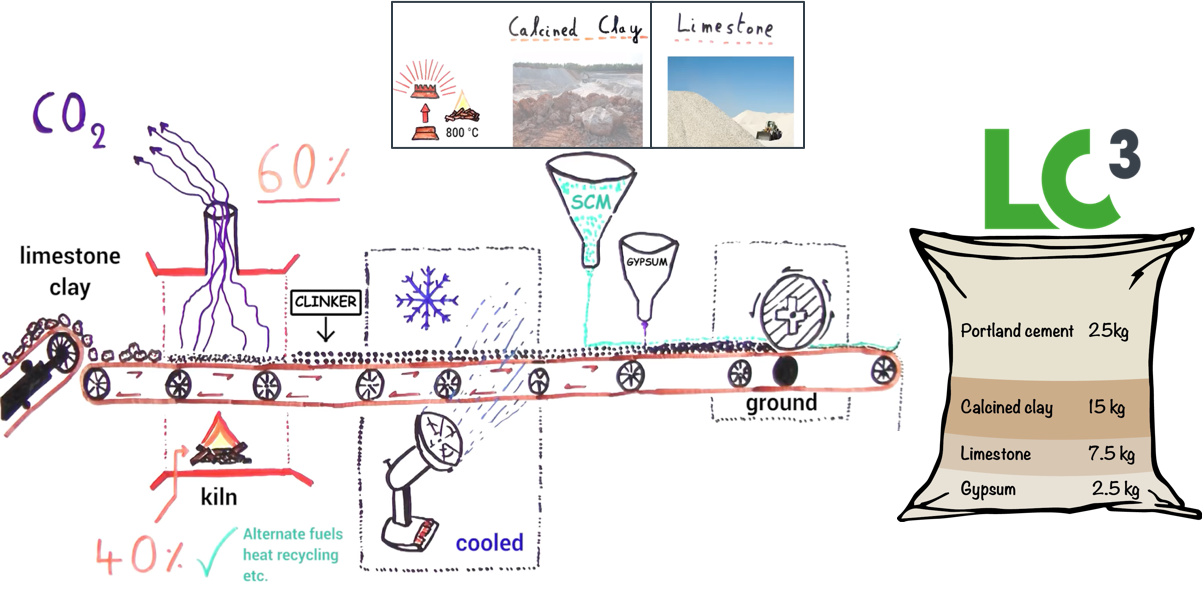
Traditional Portland cement consists of 95% clinker. The production of it is energy-intensive and responsible for most of the CO2 within the cement. By reducing the clinker-content with so called Supplementary Cementitious Materials (SCMs), large CO2-savings can be achieved.
LC3 is a new blend of two materials which have a synergetic effect. can reduce half of the clinker content and thereby cut up to 40% of the CO2-emissions. Furthermore, LC3 uses industrial waste materials which thereby increase the resource efficiency and reduce the utilization of the scarce raw materials that are necessary for producing clinker.

How to produce LC3?
To produce LC3, existing equipment can be used. The production line has to be adjusted since Limestone and Calcined Clay are added. The LC3-blend consists of the following materials:
Clinker that needs to be burnt at very high temperatures between 1400 and 1500?C.
LC3-has been used in many different regions and different scales. Overall, more than 25 applications were already built with LC3. In Latin America, several applications have been built. They are mainly in Cuba but also in other countries. Among those applications are a LC3-house, testing sites in the sea, art sculptures and pavements.
In India, the most prominent project is the model Jhansi, India. This house is made 98% out of LC3 and it used 26.6 t of industrial waste (192 kg/sqm) and Saved 15.5 t of CO2 (114 kg/sqm). These CO2-savings are similar to the emissions of 10 passengers traveling by plane from Switzerland to South Africa.

Model house in Jhansi
But there are also numerous other projects in India. For example, the offices of the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation in the compound of the Swiss Embassy in Delhi were built with LC3-prefab materials. Furthermore, some roads, a check damn and pavements were built.You find a selection of these applications on the photos.
Swiss Embassy building in Delhi Check dam in Orchha CO2-savings LC3 saves up to 40% of CO2 as compared to Ordinary Portland Cement. Most of the CO2 comes from the clinkerisation process. Therefore, reducing the clinker factor and replacing it with SCMs is the fastest intervention to save high numbers of CO2.
Within the clinker production, there are two main sources of CO2. Firstly, clinker needs to be burnt at very high temperatures between 1400 and 1500?C. Secondly, CO2 embodied in limestone is released during production. Reducing the clinker content therefore means to save both energy-related and emobied CO2.
Resource-savings
Utilization of lower grade material for LC3. Clay waste e.g. ceramic or cosmetic industry Less purity of limestone required, e.g. dolomite presence Using existing deposits of waste materials Low prices for the raw materials. Avoiding creating waste. Avoiding cost (e.g. for landfill taxes)

High performance
For more than 10 years, the prestigious research institutes EPFL, IIT Delhi and Madras and CIDEM have tested LC3 in all different aspects and came to the result LC3 reaches OPC – CEM I performance.
Not only in lab conditions but also through industrial trials and applications these findings were confirmed. They are constantly monitored in existing LC3-applications in different parts of the world and environments (e.g. marine or high-altitude applications).
Globally scalable
The raw materials limestone and calcined clay are abundantly available worldwide. Other commonly used Supplementary Cementitious Materials like fly ash or slag are already fully used and cannot be scaled for the use in cement. Furthermore, with increasing focus on sustainability more and more coal power and steel production plants are expected to be closed. This will further cut the supply of these materials as SCMs. The only material largely available and in sufficient quantity are kaolinitic clays.
Cost-effective
Different scenarios of producing LC3 were analysed financially in a study by the cement market experts. Their results showed that with a cement plant, grinding plant or Greenfield scenario the production of LC3 is profitable. The main indicator for driving the profitability is the close access to suitable clays.
Overall, the production cost can be up to 25% lower for LC3 than for OPC due to savings for energy and material. This is without additional policy incentives, such as green funds or carbon certificates, which can further increase the attractiveness for cement producers.
Ready to be implemented
LC3 is a technology which is market-ready and it is already produced in several plants in the world. The sooner the technology is rolled out globally; the more CO2-emissions can be avoided.
The already existing readiness of the technology for the industrial uptake is an important distinction compared to other green technologies.
Furthermore, LC3 can be used without additional training by builders. In India, demo constructions were built without further providing training.
Source: LC3 website.