Economy & Market
Budget Impact | Cement Industry Speaks Out
Published
9 years agoon
By
admin
Various corporate leaders, analysts and industry associations spoke to INDIAN CEMENT REVIEW after the Union Budget was presented to offer their views on how the recommendations will impact the cement industry.
Dr S Chouksey, President, Cement Manufacturers’ Association
I congratulate the Hon’ble Finance Minister Arun Jaitley on behalf of the Indian cement industry for presenting a Budget which is high on reforms, and will boost the rural economy and uplift the weaker sections of society. The government’s bold steps to usher in poll reforms, curb tax evasion, and the further push to the digital economy are all forward looking. The cement industry is buoyant with the government’s commitment to provide 10 million houses to the homeless or those with kachha houses. The granting of infrastructure status to affordable housing is yet another step which would be looked at positively by the cement industry, though we were expecting the housing sector in general would be granted infrastructure status.
Industry’s concerns on high taxation on the sector, of course, remain and is expected that they will definitely be taken care of while fixing the rates in the GST regime. We welcome the government’s other policy measures, including increasing the fund alloca?tion for infrastructure and particularly that of providing mason trai?ning to 5 lakh persons by 2022. This will increase employment opportu?nities and also bring in more efficiency to the construction sector. The target of 100 per cent rural electrification by April 2018 will bring in development oppor?tunities right up to the core of rural India. Similarly, the thrust on rail mo?dernisation and station redevelopment would also boost the construction sector. This sector has the potential for creation of employment opportunities and the government’s various steps to boost the construction sector will neutralise the unemployment created in some medium and small scale industries due to demonetisation.
Vaibhav Agarwal, Vice President – Research, PhillipCapital
In our opinion, this Budget is the most stru?cturally positive one for the cement sector in the last decade. Although there were no direct announcements by the Finance Minster for the cement sector, a number of his announcements will lead to increased and sustained consumption of cement.
10 million houses by 2019 for the houseless
-This provision will lead to incremental cement demand of ~75 million tonnes over the next two-three years.
100 per cent rural electrification by 1st May 2018
-This implies deeper penetration of development opportunities in rural India in the form of construction of houses and roads; hence a structural positive.
Continued focus on sanitation
-Sanitation coverage in rural India is currently 60 per cent. The budget commentary remained very positive on sanitation projects. In our recent ground checks, we found that sanitation projects are one of the key demand drivers for cement. The continued thrust on such projects will help boost cement demand.
Higher investment in affordable housing and affordable housing being granted ‘Infrastructure’ status will translate into more cement consum?ption for such projects. Grant of infrastructure status means more participation on the supply side by construction companies/contractors/builders and faster execution of such projects.
Fostering a conducive labour environment
Labour issues are one of the key ones in construction projects. Continuous availability of labour is frequently a problem at most sites (most labour is generally migrant). The government’s focus on developing a conducive labour environment will mean labour issues will be sorted out to a large extent, implying smooth execution of projects at construction sites with steady cement consumption. This will also mean the other regular labour concerns for contractors (wages, job benefits) are resolved, which will ameliorate labour migration concerns. In addition, there are a few other announcements in the Budget which will have a positive impact on the industry:
The thrust on rail modernisation/station redevelopment projects and 25 stations going in for redevelopment will lead to material cement consumption.
Similarly, the introduction of the Metro Rail Act and various Metro rail policies will lead to faster and structured execution of such projects, implying better visibility of cement demand.
Further, the Centre has increased investments in the roads sector and 2,000 km of coastal roads have been identified for development. This will lead to more cement demand from road projects. The various airport upgradation/maintenance projects may imply increased cement consumption. Consumption may be even higher if upgradation work involves runways.
Amendment of the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
This was one of the key demands from north Indian channel partners and distributors. Northern India is a largely a cash-and-carry economy and issuing post-dated cheques is a normal practice. Trade associations in these regions had approached the government for these amendments.
With this development, the supply chain should be more comfortable with such instruments. We found north India averse to digital wallets and the swipe machine culture, given the 1-2 per cent transaction charges involved. Change in dynamics of affordable housing (30/60 sq mt carpet from 30/60 sq mt built-up area) would lead to larger sizes of such houses, which in turn will mean higher cement consumption.
The ‘Notional Rent Income’ tax on unsold inventory for builders, post one year of receiving the commencement certificate if such houses remain unsold/unoccupied, will means correction in real estate prices/rentals, implying quicker-than-anticipated (though lower) cash flows to builders. The builder will be able to execute projects faster and transparently, implying better cement demand.
Exemption of capital gains tax where land is being pooled for the creation of Andhra Pradesh’s capital city if the person was holding the land as on 2 June, 2014, implies more transparent and faster execution of the capital city and quicker-than-anticipated cement demand. India Cements will be the key gainer followed by Dalmia Bharat, Ramco and other southern cement companies.
Reduction in holding period for considering capital gains tax to two years from three years and change of base year for indexation to 2001 from 1981 reduces the capital gains tax liability. This will mean quicker decisions in the real-estate markets to buy/sell (as the holding period comes down) and will also prompt builders for faster execution of projects, implying more sustained demand for cement from the real estate sector.
The increase in disposable income by a marginal reduction in tax rates in the Rs 2,50,000-Rs 5,00,000 tax bracket to 5 per cent from 10 per cent is a sentiment booster for those within this bracket, aspiring to buy new houses.
In short, the Budget’s overall impact on the cement sector is positive. All cement companies are winners, especially India Cements, Dalmia Bharat, JK Cement, JK Lakshmi Cement and UltraTech Cement.
Sameer Nagpal, CEO – Refractories, Dalmia Bharat Group
For refractories, which are the backbone for core manufacturing sectors like steel and cement, increase in expenditure allocation, particularly in railways, highways and housing should help build demand. I was expecting more for the manufacturing sector in terms of reforms and some specific measures to safeguard domestic manufacturing from cheaper, unreliable imports and that has not happened. Overall, it is a mixed Budget.
Crisil Research
The Budget has had a positive impact on the cement sector with infrastructure investments and affordable housing to drive demand.
Here are the key Budget proposals:
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) allo?cation increased by 39 per cent to Rs 290 billion;
Allocation from Ministry of Rural Development increased by 10 per cent to Rs 1.05 trillion in FY18;
Investments in cement-intensive infrastructure segments (excluding power) are up 9.8 per cent to Rs 4.2 trillion. The total outlay towards National Highways is at Rs 1.24 trillion, up 11.1 per cent over the previous fiscal’s revised estimates;
Affordable housing to be accorded infrastructure status.
Crisil’s view:
The increased government spending on PMAY will provide an impetus to the housing segment, which has been fairly muted over the last few years. Further, grant of infrastructure status to affordable housing would facilitate easier access to low-cost finance and thereby support demand.
A 9.1 per cent increase in allocation to rural development and 44 per cent rise in PMAY-Gramin is likely to catalyse growth in cement demand from rural housing, which typically constitutes 35 per cent of cement demand.
Further, increased government spending on infrastructure, especially cement-intensive sectors such as National Highways (up by 11.1 per cent), metros (15 per cent ), and other schemes (e.g., Swachh Bharat up by 27 per cent ), will augment cement sales.
Sundeep Kumar, Executive Director – Corporate Affairs & Communications, Dalmia Bharat Group
It is a positive and decisive Budget coming especially against the backdrop of the Government’s boldest measure of demonetisation. The Finance Minister has spelled out a forward-looking regimen for the infrastructure sector with a total allocation of up to Rs 3.96 trillion. Giving industry status will greatly ease financing for affordable housing. With the Metro rail emerging in cities and railway lines of 3,500 km to be commissioned next, along with tier-II city airports, there is a greater scope for public- partnership to thrive, which will aid construction activity and lead to a boom in demand for cement as well.
Further, enhancing expenditure on National Highways will give the much needed fillip to the cement industry. Overall, with a focus on rural and agricultural development, housing, clean energy, elimination of poverty, providing basic necessities to the farmers, waivers for senior citizens in government schemes and a promise of aiding the Skill India and Digital India campaigns, the government has presented an all-inclusive Budget this time around. On tax reforms, there has been no relief or relaxation on corporate tax for larger corporates, which is disappointing.
Shishir Baijal, Chairman & Managing Director, Knight Frank India
This has been one of the path-breaking bud?gets with far-reaching changes, especially for the real estate sector. It is positive that the real estate sector has come in the central spectrum of the Union Budget. This has come at a time when the beleaguered sector has been looking at measures to boost the sentiments. The real estate sector, which was the hardest hit by demonetisation move, will be one of the major beneficiaries of this Budget.
Prudence in fiscal discipline is welcome and will encourage the RBI to look at a lower interest rate regime that will provide the much-needed fillip to this stressed sector. Increased focus on infrastructure, especially construction of new roads, improvement of existing roads and coastal connectivity, will go a long way to benefit the real estate sector.
Increase in allocation of funds under PMAY (Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana) shows the focus of the government towards making ‘Housing for All’ a reality by 2020. Providing infrastructure status to affordable housing, a long-standing demand of the real estate industry, will not only bring the cost of financing down, but will also open up additional avenues for developers to raise funds. We believe that the shift in eligibility criteria for affordable housing from built-up area to carpet area will increase the unit size by 20-30 per cent and will offer home buyers the benefit of owning larger units. This will also encourage leading real estate players to enter the affordable housing segment.
The move to reduce the tenure of the Long Term Capital Gains Tax from three years to two years is extremely welcome and will help the marketability of real estate as an asset class. Changes in the taxation aspect of JDAs (Joint Development Agreements) will greatly encourage more land owners to partner with developers that will benefit the real estate developers, and in turn is likely to benefit the end consumers.
You may like
Concrete
Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships
Published
7 hours agoon
February 19, 2026By
admin
Jean-Jacques Bois, President, Nanolike, discusses how real-time data is reshaping cement delivery planning and fleet performance.
As cement producers look to extract efficiency gains beyond the plant gate, real-time visibility and data-driven logistics are becoming critical levers of competitiveness. In this interview with Jean-Jacques Bois, President, Nanolike, we discover how the company is helping cement brands optimise delivery planning by digitally connecting RMC silos, improving fleet utilisation and reducing overall logistics costs.
How does SiloConnect enable cement plants to optimise delivery planning and logistics in real time?
In simple terms, SiloConnect is a solution developed to help cement suppliers optimise their logistics by connecting RMC silos in real time, ensuring that the right cement is delivered at the right time and to the right location. The core objective is to provide real-time visibility of silo levels at RMC plants, allowing cement producers to better plan deliveries.
SiloConnect connects all the silos of RMC plants in real time and transmits this data remotely to the logistics teams of cement suppliers. With this information, they can decide when to dispatch trucks, how to prioritise customers, and how to optimise fleet utilisation. The biggest savings we see today are in logistics efficiency. Our customers are able to sell and ship more cement using the same fleet. This is achieved by increasing truck rotation, optimising delivery routes, and ultimately delivering the same volumes at a lower overall logistics cost.
Additionally, SiloConnect is designed as an open platform. It offers multiple connectors that allow data to be transmitted directly to third-party ERP systems. For example, it can integrate seamlessly with SAP or other major ERP platforms, enabling automatic order creation whenever replenishment is required.
How does your non-exclusive sensor design perform in the dusty, high-temperature, and harsh operating conditions typical of cement plants?
Harsh operating conditions such as high temperatures, heavy dust, extreme cold in some regions, and even heavy rainfall are all factored into the product design. These environmental challenges are considered from the very beginning of the development process.
Today, we have thousands of sensors operating reliably across a wide range of geographies, from northern Canada to Latin America, as well as in regions with heavy rainfall and extremely high temperatures, such as southern Europe. This extensive field experience demonstrates that, by design, the SiloConnect solution is highly robust and well-suited for demanding cement plant environments.
Have you initiated any pilot projects in India, and what outcomes do you expect from them?
We are at the very early stages of introducing SiloConnect in India. Recently, we installed our
first sensor at an RMC plant in collaboration with FDC Concrete, marking our initial entry into the Indian market.
In parallel, we are in discussions with a leading cement producer in India to potentially launch a pilot project within the next three months. The goal of these pilots is to demonstrate real-time visibility, logistics optimisation and measurable efficiency gains, paving the way for broader adoption across the industry.
What are your long-term plans and strategic approach for working with Indian cement manufacturers?
For India, our strategy is to establish strong and reliable local partnerships, which will allow us to scale the technology effectively. We believe that on-site service, local presence, and customer support are critical to delivering long-term value to cement producers.
Ideally, our plan is to establish an Indian entity within the next 24 months. This will enable us to serve customers more closely, provide faster support and contribute meaningfully to the digital transformation of logistics and supply chain management in the Indian cement industry.
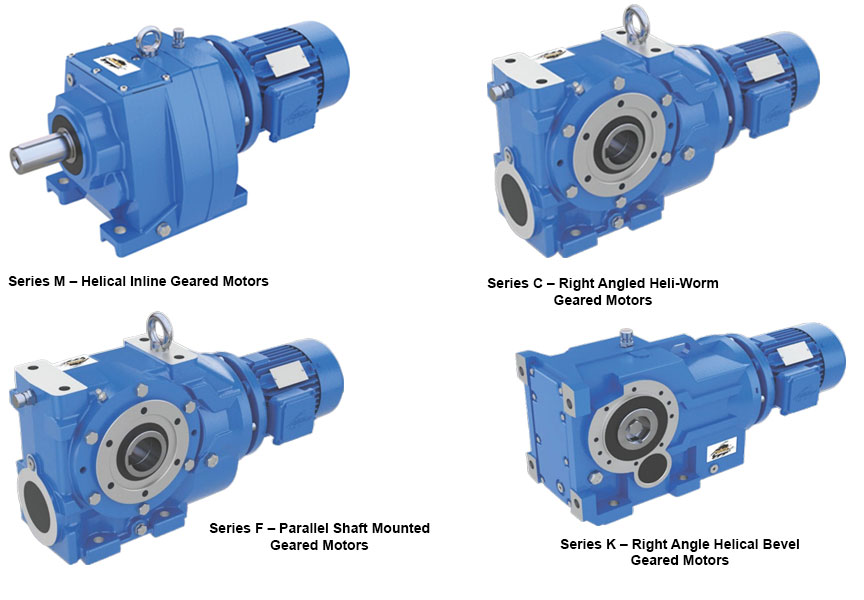
A deep dive into Core Gear Series of products M, C, F and K, by Power Build, and how they represent precision in motion.
At the heart of every high-performance industrial system lies the need for robust, reliable, and efficient power transmission. Power Build answers this need with its flagship geared motor series: M, C, F and K. Each series is meticulously engineered to serve specific operational demands while maintaining the universal promise of durability, efficiency, and performance.
Series M – Helical Inline Geared Motors
Compact and powerful, the Series M delivers exceptional drive solutions for a broad range of applications. With power handling up to 160kW and torque capacity reaching 20,000 Nm, it is the trusted solution for industries requiring quiet operation, high efficiency, and space-saving design. Series M is available with multiple mounting and motor options, making it a versatile choice for manufacturers and OEMs globally.
Series C – Right Angled Heli-Worm Geared Motors
Combining the benefits of helical and worm gearing, the Series C is designed for right-angled power transmission. With gear ratios of up to 16,000:1 and torque capacities of up to 10,000 Nm, this series is optimal for applications demanding precision in compact spaces. Industries looking for a smooth, low-noise operation with maximum torque efficiency rely on Series C for dependable performance.
Series F – Parallel Shaft Mounted Geared Motors
Built for endurance in the most demanding environments, Series F is widely adopted in steel plants, hoists, cranes and heavy-duty conveyors. Offering torque up to 10,000 Nm and high gear ratios up to 20,000:1, this product features an integral torque arm and diverse output configurations to meet industry-specific challenges head-on.
Series K – Right Angle Helical Bevel Geared Motors
For industries seeking high efficiency and torque-heavy performance, Series K is the answer. This right-angled geared motor series delivers torque up to 50,000 Nm, making it a preferred choice in core infrastructure sectors such as cement, power, mining and material handling. Its flexibility in mounting and broad motor options offer engineers the freedom in design and reliability in execution.
Together, these four series reflect Power Build’s commitment to excellence in mechanical power transmission. From compact inline designs to robust right-angle drives, each geared motor is a result of decades of engineering innovation, customer-focused design and field-tested reliability. Whether the requirement is speed control, torque multiplication or space efficiency, Radicon’s Series M, C, F and K stand as trusted powerhouses for global industries.
http://www.powerbuild.in
Call: +919727719344

Pankaj Kejriwal, Whole Time Director and COO, Star Cement, on driving efficiency today and designing sustainability for tomorrow.
In an era where the cement industry is under growing pressure to decarbonise while scaling capacity, Star Cement is charting a pragmatic yet forward-looking path. In this conversation, Pankaj Kejriwal, Whole Time Director and COO, Star Cement, shares how the company is leveraging waste heat recovery, alternative fuels, low-carbon products and clean energy innovations to balance operational efficiency with long-term sustainability.
How has your Lumshnong plant implemented the 24.8 MW Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS), and what impact has it had on thermal substitution and energy costs?
Earlier, the cost of coal in the Northeast was quite reasonable, but over the past few years, global price increases have also impacted the region. We implemented the WHRS project about five years ago, and it has resulted in significant savings by reducing our overall power costs.
That is why we first installed WHRS in our older kilns, and now it has also been incorporated into our new projects. Going forward, WHRS will be essential for any cement plant. We are also working on utilising the waste gases exiting the WHRS, which are still at around 100 degrees Celsius. To harness this residual heat, we are exploring systems based on the Organic Rankine Cycle, which will allow us to extract additional power from the same process.
With the launch of Star Smart Building Solutions and AAC blocks, how are you positioning yourself in the low-carbon construction materials segment?
We are actively working on low-carbon cement products and are currently evaluating LC3 cement. The introduction of autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks provided us with an effective entry into the consumer-facing segment of the industry. Since we already share a strong dealer network across products, this segment fits well into our overall strategy.
This move is clearly supporting our transition towards products with lower carbon intensity and aligns with our broader sustainability roadmap.
With a diverse product portfolio, what are the key USPs that enable you to support India’s ongoing infrastructure projects across sectors?
Cement requirements vary depending on application. There is OPC, PPC and PSC cement, and each serves different infrastructure needs. We manufacture blended cements as well, which allows us to supply products according to specific project requirements.
For instance, hydroelectric projects, including those with NHPC, have their own technical norms, which we are able to meet. From individual home builders to road infrastructure, dam projects, and regions with heavy monsoon exposure, where weather-shield cement is required, we are equipped to serve all segments. Our ability to tailor cement solutions across diverse climatic and infrastructure conditions is a key strength.
How are you managing biomass usage, circularity, and waste reduction across
your operations?
The Northeast has been fortunate in terms of biomass availability, particularly bamboo. Earlier, much of this bamboo was supplied to paper plants, but many of those facilities have since shut down. As a result, large quantities of bamboo biomass are now available, which we utilise in our thermal power plants, achieving a Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) of nearly 60 per cent.
We have also started using bamboo as a fuel in our cement kilns, where the TSR is currently around 10 per cent to 12 per cent and is expected to increase further. From a circularity perspective, we extensively use fly ash, which allows us to reuse a major industrial waste product. Additionally, waste generated from HDPE bags is now being processed through our alternative fuel and raw material (AFR) systems. These initiatives collectively support our circular economy objectives.
As Star Cement expands, what are the key logistical and raw material challenges you face in scaling operations?
Fly ash availability in the Northeast is a constraint, as there are no major thermal power plants in the region. We currently source fly ash from Bihar and West Bengal, which adds significant logistics costs. However, supportive railway policies have helped us manage this challenge effectively.
Beyond the Northeast, we are also expanding into other regions, including the western region, to cater to northern markets. We have secured limestone mines through auctions and are now in the process of identifying and securing other critical raw material resources to support this expansion.
With increasing carbon regulations alongside capacity expansion, how do you balance compliance while sustaining growth?
Compliance and growth go hand in hand for us. On the product side, we are working on LC3 cement and other low-carbon formulations. Within our existing product portfolio, we are optimising operations by increasing the use of green fuels and improving energy efficiency to reduce our carbon footprint.
We are also optimising thermal energy consumption and reducing electrical power usage. Notably, we are the first cement company in the Northeast to deploy EV tippers at scale for limestone transportation from mines to plants. Additionally, we have installed belt conveyors for limestone transfer, which further reduces emissions. All these initiatives together help us achieve regulatory compliance while supporting expansion.
Looking ahead to 2030 and 2050, what are the key innovation and sustainability priorities for Star Cement?
Across the cement industry, carbon capture is emerging as a major focus area, and we are also planning to work actively in this space. In parallel, we see strong potential in green hydrogen and are investing in solar power plants to support this transition.
With the rapid adoption of solar energy, power costs have reduced dramatically – from 10–12 per unit to around2.5 per unit. This reduction will enable the production of green hydrogen at scale. Once available, green hydrogen can be used for electricity generation, to power EV fleets, and even as a fuel in cement kilns.
Burning green hydrogen produces only water and oxygen, eliminating carbon emissions from that part of the process. While process-related CO2 emissions from limestone calcination remain a challenge, carbon capture technologies will help address this. Ultimately, while becoming a carbon-negative industry is challenging, it is a goal we must continue to work towards.

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Compliance and growth go hand in h and

Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence

FORNNAX Appoints Dieter Jerschl as Sales Partner for Central Europe

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Compliance and growth go hand in h and

Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence























