Technology
Roller press is well-accepted technology in India
Published
4 years agoon
By
admin
With the focus of industry towards WHR systems, roller press grinding has further got acceptance as it uses no water for bed stabilisation and uses minimum hot gases as compared to other contemporary technologies, explains A K Dembla, President & Managing Director, Humboldt Wedag India.
With the focus of industry towards WHR systems, roller press grinding has further got acceptance as it uses no water for bed stabilisation and uses minimum hot gases as compared to other contemporary technologies, explains A K Dembla, President & Managing Director, Humboldt Wedag India.
Today, the requirement for the cement industry is to reduce the use of energy in the grinding process and make it more efficient. Please share your views on how this can be achieved.
Grinding constitutes about 65-70 percent of the electrical energy consumption of cement manufacturing, any saving in grinding energy can be good for operating cost reduction. The energy cost is also increasing with time; therefore, cement manufacturing companies are looking for new technologies for low electrical energy consumption. Machinery manufacturers are putting a lot of R & D efforts in the grinding process to reduce electrical energy consumption in the cement industry which also helps in reduction in carbon footprints.
What is the latest energy-efficient grinding technologies/solution? What benefits cement companies can achieve in terms of energy consumption, quality, cost, etc?
The latest development related to raw materials grinding in finish grinding in Roller Press has paid dividends even for soft and medium to hard material. Hard raw materials are giving a higher bonus factor in finish grinding roller press systems and cement manufactures are getting 2-4 Kwh/t saving in electrical energy in raw material grinding itself by using this technology as compared to Vertical Mill technology. KHD has supplied 33 raw material grinding circuits in the last 10 years up to 10,000 tpd capacity plants. Typical circuit offered by KHD for raw materials grinding in ComFlex Grinding circuit has advantages to process raw materials with high moistures with the incorporation of V-Separator below the roller press and use of hot gases to dry the raw materials. With the focus of industry towards WHR systems, roller press grinding has further got acceptance as it uses no water for bed stabilisation and uses minimum hot gases as compared to other contemporary technologies.
In the case of cement grinding, again two technologies are being accepted –Vertical Roller Mill or Roller Press in semi-finish or finish grinding. Roller Press in finish grinding has the advantage of further saving of 3-4 Kwh/t as compared to Semi-finish grinding and Vertical Mill technology. With more acceptance of blended cement like PPC, PSC, and composite cement, roller press in finish grinding is accepted as advanced technology in cement grinding. KHD has sold 75 Cement Grinding Circuits in the last 10 years because of the need to save electrical energy. Typical Finish & Semi-finish Grinding circuits offered by KHD are very popular in the cement industry that includes the use of Roller Press alone or in a combination of Roller Press & Ball Mill respectively.
In the case of Slag grinding, the acceptance of roller press in finish grinding is well recognised. It offers the distinct advantage of saving of about 6-7 Kwh/t as compared to Vertical Roller Mill at 4200 Blaine. KHD has sold 27 Sag Grinding Circuits and maintains about 70 % market share in slag grinding in India. The advantage comes due to the hardness of Slag and pressure grinding in roller press instead of attrition and low pressure in Vertical Roller Press. Moisture issue is also tackled with the problem of coating by incorporating V-separator below roller press.
The most important properties of cement are strength and workability. This could be achieved by modifying the grinding equipment. Please share your views. What grinding technique/equipment can be used to ensure strength and workability?
Strength and workability are two important parameters for cement when it is used as binding material in the form of concrete. Workability is one of the physical parameters of concrete which affects the strength and durability and can be defined as the ease with which the concrete can be mixed, placed, compacted, and finished. Concrete is said to be workable when it is easily placed and compacted homogenously i.e without bleeding or segregation. Technically speaking, workable concrete is the amount of useful internal work necessary to produce 100 percent compaction. Wet concrete is more workable than dry concrete and is a function of particle size distribution and water demand during the application of concrete in construction work. In this context 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days strength is important.
Similarly, the strength of cement depends upon the particle size distribution in cement which is achieved through a suitable grinding process and separator. Normally 3-32 micron size offers maximum strength and it should be in the range of 70-80 percent in cement. This range was established by conventional grinding in 2 chambers ball mill before acceptance of newer technology like Vertical Mill Roller Press technology. Semi-finish grinding in roller press has ball Mill along with roller press and therefore offers best particle size distribution (comparable to ball mill product). However, in the case of roller press in finish grinding and Vertical Mill, particle size distribution is steeper which is corrected through a high-efficiency separator. Also, with the advent of blended cement, the concept of particles in the range of 3-32 microns has also got diluted.
Two-compartment ball mills and air separators used to be the main process equipment in clinker grinding circuits. How has been the evolution in terms of technical innovations in this area?
Two compartments ball mill with separator has been conventional cement grinding technology which is still existing in many countries where electrical energy costs are low. Subsequent developments like the use of Roller Press and Vertical Mill offers saving of 5-10 Kwh/t electrical energy consumption for a typical 3200 Blaine cement as compared to a ball mill.
Ball mill technology has also gone through innovations in terms of various modified impact liners, classifying liners, and flow control diaphragms. But these modifications have the potential of limited savings in the range of 1-2 Kwh/t as compared to conventional liners and diaphragms.
Separators have also gone through various technological developments, and we are offering 4th generation high-efficiency separators nowadays. These separators offer a sharp cut point and minimum bypass (particle below 3 microns).
The usage of cement additive materials is on a rise. Please share your views on the same. What kind of grinding aids are in demand and what are the advantages?
Grinding aid or grinding additives are materials, which are added with raw mix while grinding the cement in either a ball mill or vertical roller mill to reduce the agglomeration of cement particles by neutralising the static charges and increasing the rate of size reduction to improve the throughput and performance of the cement. Grinding aids are mainly of two types-
a) Strength Enhancer which is used to increase the mechanical strength by chemical activation, without changing the cement surface and particle size distribution. Alkanolamines are frequently used and can increase the compressive strength (at different or all ages) by max. five MPa. These admixtures increase the productivity of the grinding aid at the same time.
b) Performance Enhancers which are supplementary cementitious materials such as granulated blast furnace slag, natural Pozzolanic, and fly ash to reduce CO2 emissions and material cost. However, supplementary cementitious materials may counteract strength development, powder flowability, mortar workability, and durability, which are critical for cement quality. Generally, the grinding aids can be Amine-based or Alcohol Based, or Ethyl Based Grinding Aids. Overall benefits include enhanced production process and the quality of cement, improved powder followability, strength development, mortar workability, and durability, adjusting the cement quality to meet the demands set by relevant standards and cement customers. Above all, it ensures less environmental impact by reducing utilisation of energy and resources combined with minimised carbon footprint.

Please share your roadmap in the grinding technology area.
At present focus is to use Roller Press in finish grinding to get maximum energy advantage as compared to Ball Mill Grinding especially for blended cement. Apart from electrical energy focus is also on the Roller Press surface which has minimum wear and offers trouble and maintenance-free operation. Stud technology has proven a boon for the industry in this area, Tungsten Carbide Studs are fixed on the roller surface by pressing in pre-drilled rollers which offer autogenous grinding and minimum wear. Life expected out of these roller surfaces varies from 25000-40000 hours of operations without any surface maintenance. Fig 2 gives a picture of the stud surface roller. Apart from this, developments are on optimising the process circuit for energy efficiency & pollution-free operation. Developments in actuated dosing gate for feeding material to Roller press and online monitoring of roller press surface are also worth noticing.
You may like
Concrete
Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation
Published
6 days agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Professor Procyon Mukherjee discusses how as the cement industry accelerates its shift towards digitalisation, data-driven technologies are becoming the mainstay of sustainability and control across the value chain.
The cement industry, long perceived as traditional and resistant to change, is undergoing a profound transformation driven by digital technologies. As global infrastructure demand grows alongside increasing pressure to decarbonise and improve productivity, cement manufacturers are adopting data-centric tools to enhance performance across the value chain. Nowhere is this shift more impactful than in grinding, which is the energy-intensive final stage of cement production, and in the materials that make grinding more efficient: grinding media and grinding aids.
The imperative for digitalisation
Cement production accounts for roughly 7 per cent to 8 per cent of global CO2 emissions, largely due to the energy intensity of clinker production and grinding processes. Digital solutions, such as AI-driven process controls and digital twins, are helping plants improve stability, cut fuel use and reduce emissions while maintaining consistent product quality. In one deployment alongside ABB’s process controls at a Heidelberg plant in Czechia, AI tools cut fuel use by 4 per cent and emissions by 2 per cent, while also improving operational stability.
Digitalisation in cement manufacturing encompasses a suite of technologies, broadly termed as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), AI and machine learning, predictive analytics, cloud-based platforms, advanced process control and digital twins, each playing a role in optimising various stages of production from quarrying to despatch.
Grinding: The crucible of efficiency and cost
Of all the stages in cement production, grinding is among the most energy-intensive, historically consuming large amounts of electricity and representing a significant portion of plant operating costs. As a result, optimising grinding operations has become central to digital transformation strategies.
Modern digital systems are transforming grinding mills from mechanical workhorses into intelligent, interconnected assets. Sensors throughout the mill measure parameters such as mill load, vibration, mill speed, particle size distribution, and power consumption. This real-time data, fed into machine learning and advanced process control (APC) systems, can dynamically adjust operating conditions to maintain optimal throughput and energy usage.
For example, advanced grinding systems now predict inefficient conditions, such as impending mill overload, by continuously analysing acoustic and vibration signatures. The system can then proactively adjust clinker feed rates and grinding media distribution to sustain optimal conditions, reducing energy consumption and improving consistency.
Digital twins: Seeing grinding in the virtual world
One of the most transformative digital tools applied in cement grinding is the digital twin, which a real-time virtual replica of physical equipment and processes. By integrating sensor data and
process models, digital twins enable engineers to simulate process variations and run ‘what-if’
scenarios without disrupting actual production. These simulations support decisions on variables such as grinding media charge, mill speed and classifier settings, allowing optimisation of energy use and product fineness.
Digital twins have been used to optimise kilns and grinding circuits in plants worldwide, reducing unplanned downtime and allowing predictive maintenance to extend the life of expensive grinding assets.
Grinding media and grinding aids in a digital era
While digital technologies improve control and prediction, materials science innovations in grinding media and grinding aids have become equally crucial for achieving performance gains.
Grinding media, which comprise the balls or cylinders inside mills, directly influence the efficiency of clinker comminution. Traditionally composed of high-chrome cast iron or forged steel, grinding media account for nearly a quarter of global grinding media consumption by application, with efficiency improvements translating directly to lower energy intensity.
Recent advancements include ceramic and hybrid media that combine hardness and toughness to reduce wear and energy losses. For example, manufacturers such as Sanxin New Materials in China and Tosoh Corporation in Japan have developed sub-nano and zirconia media with exceptional wear resistance. Other innovations include smart media embedded with sensors to monitor wear, temperature, and impact forces in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and optimal media replacement scheduling. These digitally-enabled media solutions can increase grinding efficiency by as much as 15 per cent.
Complementing grinding media are grinding aids, which are chemical additives that improve mill throughput and reduce energy consumption by altering the surface properties of particles, trapping air, and preventing re-agglomeration. Technology leaders like SIKA AG and GCP Applied Technologies have invested in tailored grinding aids compatible with AI-driven dosing platforms that automatically adjust additive concentrations based on real-time mill conditions. Trials in South America reported throughput improvements nearing 19 per cent when integrating such digital assistive dosing with process control systems.
The integration of grinding media data and digital dosing of grinding aids moves the mill closer to a self-optimising system, where AI not only predicts media wear or energy losses but prescribes optimal interventions through automated dosing and operational adjustments.
Global case studies in digital adoption
Several cement companies around the world exemplify digital transformation in practice.
Heidelberg Materials has deployed digital twin technologies across global plants, achieving up to 15 per cent increases in production efficiency and 20 per cent reductions in energy consumption by leveraging real-time analytics and predictive algorithms.
Holcim’s Siggenthal plant in Switzerland piloted AI controllers that autonomously adjusted kiln operations, boosting throughput while reducing specific energy consumption and emissions.
Cemex, through its AI and predictive maintenance initiatives, improved kiln availability and reduced maintenance costs by predicting failures before they occurred. Global efforts also include AI process optimisation initiatives to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
Challenges and the road ahead
Despite these advances, digitalisation in cement grinding faces challenges. Legacy equipment may lack sensor readiness, requiring retrofits and edge-cloud connectivity upgrades. Data governance and integration across plants and systems remains a barrier for many mid-tier producers. Yet, digital transformation statistics show momentum: more than half of cement companies have implemented IoT sensors for equipment monitoring, and digital twin adoption is growing rapidly as part of broader Industry 4.0 strategies.
Furthermore, as digital systems mature, they increasingly support sustainability goals: reduced energy use, optimised media consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions. By embedding intelligence into grinding circuits and material inputs like grinding aids, cement manufacturers can strike a balance between efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
Digitalisation is not merely an add-on to cement manufacturing. It is reshaping the competitive and sustainability landscape of an industry often perceived as inertia-bound. With grinding representing a nexus of energy intensity and cost, digital technologies from sensor networks and predictive analytics to digital twins offer new levers of control. When paired with innovations in grinding media and grinding aids, particularly those with embedded digital capabilities, plants can achieve unprecedented gains in efficiency, predictability and performance.
For global cement producers aiming to reduce costs and carbon footprints simultaneously, the future belongs to those who harness digital intelligence not just to monitor operations, but to optimise and evolve them continuously.
About the author:
Professor Procyon Mukherjee, ex-CPO Lafarge-Holcim India, ex-President Hindalco, ex-VP Supply Chain Novelis Europe, has been an industry leader in logistics, procurement, operations and supply chain management. His career spans 38 years starting from Philips, Alcan Inc (Indian Aluminum Company), Hindalco, Novelis and Holcim. He authored the book, ‘The Search for Value in Supply Chains’. He serves now as Visiting Professor in SP Jain Global, SIOM and as the Adjunct Professor at SBUP. He advises leading Global Firms including Consulting firms on SCM and Industrial Leadership and is a subject matter expert in aluminum and cement. An Alumnus of IIM Calcutta and Jadavpur University, he has completed the LH Senior Leadership Programme at IVEY Academy at Western University, Canada.
Concrete
Digital Pathways for Sustainable Manufacturing
Published
6 days agoon
February 20, 2026By
admin
Dr Y Chandri Naidu, Chief Technology Officer, Nextcem Consulting highlights how digital technologies are enabling Indian cement plants to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and transition toward sustainable, low-carbon manufacturing.
Cement manufacturing is inherently resource- and energy-intensive due to high-temperature clinkerisation and extensive material handling and grinding operations. In India, where cement demand continues to grow in line with infrastructure development, producers must balance capacity expansion with sustainability commitments. Energy costs constitute a major share of operating expenditure, while process-related carbon dioxide emissions from limestone calcination remain unavoidable.
Traditional optimisation approaches, which are largely dependent on operator experience, static control logic and offline laboratory analysis, have reached their practical limits. This is especially evident when higher levels of alternative fuel and raw materials (AFR) are introduced or when raw material variability increases.
Digital technologies provide a systematic pathway to manage this complexity by enabling
real-time monitoring, predictive optimisation and integrated decision-making across cement manufacturing operations.
Digital cement manufacturing is enabled through a layered architecture integrating operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT). At the base are plant instrumentation, analysers, and automation systems, which generate continuous process data. This data is contextualised and analysed using advanced analytics and AI platforms, enabling predictive and prescriptive insights for operators and management.
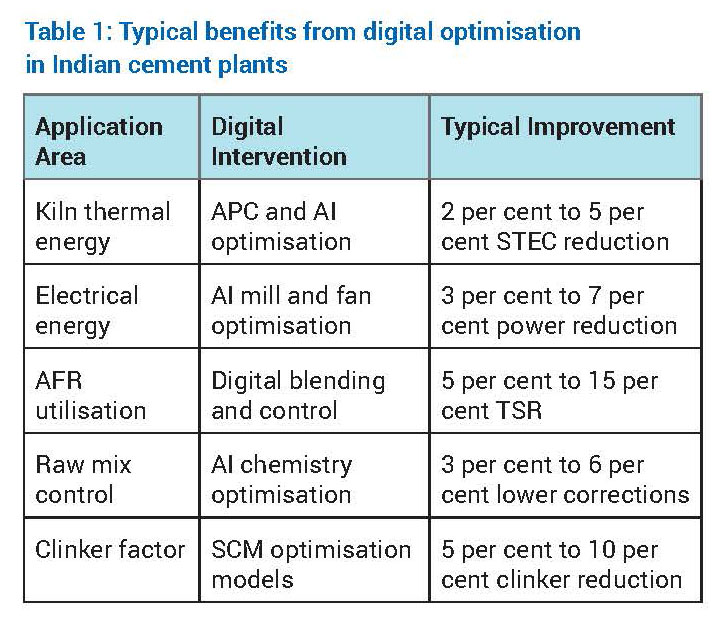
Digital optimisation of energy efficiency
- Thermal energy optimisation
The kiln and calciner system accounts for approximately 60 per cent to 65 per cent of total energy consumption in an integrated cement plant. Digital optimisation focuses on reducing specific thermal energy consumption (STEC) while maintaining clinker quality and operational stability.
Advanced Process Control (APC) stabilises critical parameters such as burning zone temperature, oxygen concentration, kiln feed rate and calciner residence time. By minimising process variability, APC reduces the need for conservative over-firing. Artificial intelligence further enhances optimisation by learning nonlinear relationships between raw mix chemistry, AFR characteristics, flame dynamics and heat consumption.
Digital twins of kiln systems allow engineers to simulate operational scenarios such as increased AFR substitution, altered burner momentum or changes in raw mix burnability without operational risk. Indian cement plants adopting these solutions typically report STEC reductions in the range of 2 per cent to 5 per cent. - Electrical energy optimisation
Electrical energy consumption in cement plants is dominated by grinding systems, fans and material transport equipment. Machine learning–based optimisation continuously adjusts mill parameters such as separator speed, grinding pressure and feed rate to minimise specific power consumption while maintaining product fineness.
Predictive maintenance analytics identify inefficiencies caused by wear, fouling or imbalance in fans and motors. Plants implementing plant-wide electrical energy optimisation typically achieve
3 per cent to 7 per cent reduction in specific power consumption, contributing to both cost savings and indirect CO2 reduction.
Digital enablement of AFR
AFR challenges in the Indian context: Indian cement plants increasingly utilise biomass, refuse-derived fuel (RDF), plastic waste and industrial by-products. However, variability in calorific value, moisture, particle size, chlorine and sulphur content introduces combustion instability, build-up formation and emission risks.
Digital AFR management: Digital platforms integrate real-time AFR quality data from online analysers with historical kiln performance data. Machine learning models predict combustion behaviour, flame stability and emission trends for different AFR combinations. Based on these predictions, fuel feed distribution, primary and secondary air ratios, and burner momentum are dynamically adjusted to ensure stable kiln operation. Digitally enabled AFR management in cement plants will result in increased thermal substitution rates by 5-15 percentage points, reduced fossil fuel dependency, and improved kiln stability.
Digital resource and raw material optimisation
Raw mix control: Raw material variability directly affects kiln operation and clinker quality. AI-driven raw mix optimisation systems continuously adjust feed proportions to maintain target chemical parameters such as Lime Saturation Factor (LSF), Silica Modulus (SM), and Alumina Modulus (AM). This reduces corrective material usage and improves kiln thermal efficiency.
Clinker factor reduction: Reducing clinker factor through supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) such as fly ash, slag and calcined clay is a key decarbonisation lever. Digital models simulate blended cement performance, enabling optimisation of SCM proportions while maintaining strength and durability requirements.
Challenges and strategies for digital adoption
Key challenges in Indian cement plants include data quality limitations due to legacy instrumentation, resistance to algorithm-based decision-making, integration complexity across multiple OEM systems, and site-specific variability in raw materials and fuels.
Successful digital transformation requires strengthening the data foundation, prioritising high-impact use cases such as kiln APC and energy optimisation, adopting a human-in-the-loop approach, and deploying modular, scalable digital platforms with cybersecurity by design.
Future Outlook
Future digital cement plants will evolve toward autonomous optimisation, real-time carbon intensity tracking, and integration with emerging decarbonisation technologies such as carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS). Digital platforms will also support ESG reporting and regulatory compliance.
Digital pathways offer a practical and scalable solution for sustainable cement manufacturing in India. By optimising energy consumption, enabling higher AFR substitution and improving resource efficiency, digital technologies deliver measurable environmental and economic benefits. With appropriate data infrastructure, organisational alignment and phased implementation, digital transformation will remain central to the Indian cement industry’s low-carbon transition.
About the author:
Dr Y Chandri Naidu is a cement industry professional with 30+ years of experience in process optimisation, quality control and quality assistance, energy conservation and sustainable manufacturing, across leading organisations including NCB, Ramco, Prism, Ultratech, HIL, NCL and Vedanta. He is known for guiding teams, developing innovative plant solutions and promoting environmentally responsible cement production. He is also passionate about mentoring professionals and advancing durable, resource efficient technologies for future of construction materials.
Concrete
Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence
Published
7 days agoon
February 19, 2026By
admin
Stoppage Insights instantly identifies root causes and maps their full operational impact.
In cement, mining and minerals processing operations, every unplanned stoppage equals lost production and reduced profitability. Yet identifying what caused a stoppage remains frustratingly complex. A single motor failure can trigger cascading interlocks and alarm floods, burying the root cause under layers of secondary events. Operators and maintenance teams waste valuable time tracing event chains when they should be solving problems. Until now.
Our latest innovation to our ECS Process Control Solution(1) eliminates this complexity. Stoppage Insights, available with the combined updates to our ECS/ControlCenter™ (ECS) software and ACESYS programming library, transforms stoppage events into clear, actionable intelligence. The system automatically identifies the root cause of every stoppage – whether triggered by alarms, interlocks, or operator actions – and maps all affected equipment. Operators can click any stopped motor’s faceplate to view what caused the shutdown instantly. The Stoppage UI provides a complete record of all stoppages with drill-down capabilities, replacing manual investigation with immediate answers.
Understanding root cause in Stoppage Insights
In Stoppage Insights, ‘root cause’ refers to the first alarm, interlock, or operator action detected by the control system. While this may not reveal the underlying mechanical, electrical or process failure that a maintenance team may later discover, it provides an actionable starting point for rapid troubleshooting and response. And this is where Stoppage Insights steps ahead of traditional first-out alarm systems (ISA 18.2). In this older type of system, the first alarm is identified in a group. This is useful, but limited, as it doesn’t show the complete cascade of events, distinguish between operator-initiated and alarm-triggered stoppages, or map downstream impacts. In contrast, Stoppage Insights provides complete transparency:
- Comprehensive capture: Records both regular operator stops and alarm-triggered shutdowns.
- Complete impact visibility: Maps all affected equipment automatically.
- Contextual clarity: Eliminates manual tracing through alarm floods, saving critical response time.
David Campain, Global Product Manager for Process Control Systems, says, “Stoppage Insights takes fault analysis to the next level. Operators and maintenance engineers no longer need to trace complex event chains. They see the root cause clearly and can respond quickly.”
Driving results
1.Driving results for operations teams
Stoppage Insights maximises clarity to minimise downtime, enabling operators to:
• Rapidly identify root causes to shorten recovery time.
• View initiating events and all affected units in one intuitive interface.
• Access complete records of both planned and unplanned stoppages
- Driving results for maintenance and reliability teams
Stoppage Insights helps prioritise work based on evidence, not guesswork:
• Access structured stoppage data for reliability programmes.
• Replace manual logging with automated, exportable records for CMMS, ERP or MES.(2)
• Identify recurring issues and target preventive maintenance effectively.
A future-proof and cybersecure foundation
Our Stoppage Insights feature is built on the latest (version 9) update to our ACESYS advanced programming library. This industry-leading solution lies at the heart of the ECS process control system. Its structured approach enables fast engineering and consistent control logic across hardware platforms from Siemens, Schneider, Rockwell, and others.
In addition to powering Stoppage Insights, ACESYS v9 positions the ECS system for open, interoperable architectures and future-proof automation. The same structured data used by Stoppage Insights supports AI-driven process control, providing the foundation for machine learning models and advanced analytics.
The latest releases also respond to the growing risk of cyberattacks on industrial operational technology (OT) infrastructure, delivering robust cybersecurity. The latest ECS software update (version 9.2) is certified to IEC 62443-4-1 international cybersecurity standards, protecting your process operations and reducing system vulnerability.
What’s available now and what’s coming next?
The ECS/ControlCenter 9.2 and ACESYS 9 updates, featuring Stoppage Insights, are available now for:
- Greenfield projects.
- ECS system upgrades.
- Brownfield replacement of competitor systems.
Stoppage Insights will also soon integrate with our ECS/UptimeGo downtime analysis software. Stoppage records, including root cause identification and affected equipment, will flow seamlessly into UptimeGo for advanced analytics, trending and long-term reliability reporting. This integration creates a complete ecosystem for managing and improving plant uptime.
(1) The ECS Process Control Solution for cement, mining and minerals processing combines proven control strategies with modern automation architecture to optimise plant performance, reduce downtime and support operational excellence.
(2) CMMS refers to computerised maintenance management systems; ERP, to enterprise resource planning; and MES to manufacturing execution systems.

Cement Demand Revives As Prices Decline In Q3 FY26

Refractory demands in our kiln have changed

Digital supply chain visibility is critical

Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation

Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency

Cement Demand Revives As Prices Decline In Q3 FY26

Refractory demands in our kiln have changed

Digital supply chain visibility is critical

Redefining Efficiency with Digitalisation

Cement Additives for Improved Grinding Efficiency
Trending News
-

 Concrete4 weeks ago
Concrete4 weeks agoAris Secures Rs 630 Million Concrete Supply Order
-

 Concrete4 weeks ago
Concrete4 weeks agoNITI Aayog Unveils Decarbonisation Roadmaps
-

 Economy & Market3 weeks ago
Economy & Market3 weeks agoBudget 2026–27 infra thrust and CCUS outlay to lift cement sector outlook
-

 Concrete4 weeks ago
Concrete4 weeks agoJK Cement Commissions 3 MTPA Buxar Plant, Crosses 31 MTPA



