Economy & Market
JK Lakshmi, dark horse
Published
8 years agoon
By
admin
Vaibhav Agarwal of PhillipCapital assess the potential of JKLC.
JK Lakshmi (JKLC) currently has a total installed capacity of 12.5 MTPA, which is spread across the geographies of North (inclusive of Gujarat) and East India. North India has a total capacity of 9.8 MTPA of which 1.6 MTPA is at UCWL – JKLC’s 71 per cent subsidiary. UCWL plant has been very recently commissioned and the utilisations of this plant are being ramped up -currently operates at approximately 50-60 per cent. East India has a capacity of 2.7 MTPA (of which 0.9 MTPA of grinding recently commissioned production in Q1FY18). Another 0.6 MTPA of capacity addition (grinding unit) is due to be added in Odisha (East India) and slated to be commissioned by mid FY19. Once this is commissioned, JKLC’s total capacity will increase to 13.1 MTPA – 9.8 MTPA in North India and 3.3 MTPA in East India.
Current capacity utilisation
JKLC’s north unit are currently operating at an average utilisation of 70 per cent versus industry’s capacity utilisation of 68 per cent in this region. Similarly, JKLC’s east India plants are currently operating at 79 per cent utilisations as against industry capacity utilisation of 67 per cent. As per our understanding, UCWL and the newer grinding unit of JKLC in North (Gujarat) and East India respectively are yet to scale up capacity utilisations and currently operate at just about 50-60 per cent capacity utilisations.
Volume growth trajectory and utilisation roadmap is driven by capacity additions over the past few years JKLC’s volume’s has been robust over the past few years (7-17 per cent). As we now see the capacity additions getting muted for JKLC we expect the volume growth to taper down and grow in the range of 5-6 per cent over the next two years. But, we also expect capacity utilisations of newer units of JKLC to ramp up to the existing levels by end of FY19 (a key to drive cost savings) and expect overall utilisations of the company as a whole at approximately 83 per cent by end of FY19/H1FY20.
Contributors to cost savings for JKLC will derive cost savings from multiple factors – power cost, utilisation ramp up and logistics costs. Waste Heat recovery at East India has commissioned commercial production in Q3FY18 and the management has indicated a savings of about Rs 100/tonne already being delivered from this initiative. UCWL is also due to commission a WHR and thermal power plant. In East India, thermal power plants are due for commissioning in H2FY19.
Major chunk of the savings will come from here in H2FY19 and onwards. JKLC has acknowledged that it needs to make its logistics more effective and is working towards a cost saving of Rs 100-150/tonne. Though a major chunk of this will be again from East India operations, North will also contribute to logistics savings as and when we see utilisation ramp up of UCWL and newer grinding units (Surat) in this zone. Utilisation ramp up will help scale efficiencies. As per the interactions, the least which can be expected as a ballpark is about Rs10/tonne of savings with every percentage increase of utilisation ramp up. This can be higher and will vary on case to case basis.
Utilisations and volume roadmap
JKLC currently operates its capacities at an average capacity utilisation of 72 per cent. It estimates for JKLC factor in an overall utilisation improvement of about 10 per cent over the next two years. As nearly 25 per cent of JKLC’s existing capacity is new, we believe this utilisation ramp up is possible. It can also be seen from the graphs below that JKLC is always ahead of industry capacity utilisations in all regions of its operations.
Though the utilisations are being ramped up by nearly 10 per cent over the next two years, but from volume growth perspective, the volume growth will taper down at 5-6 per cent yoy as JKLC exits its capex mode and fall in-line to industry discipline. Low volume growth is largely because of base effect and a more realistic assumption. Despite a low volume growth, JKLC will start deriving all the cost savings in FY19 and onwards as all the support infrastructure such as captive power, better logistics etc. will be available to the company by mid FY19. We will now discuss the cost saving drivers individually.
Cost savings drivers, power
As far as efficiencies are concerned, JKLC is already best placed on consumption parameters. It consumes approximately 70-74 units of power per tonne of cement across all locations, which is largely in-line with best of industry parameters. The key hurdle is absence of power plants in two of its existing locations – East India site and UCWL. Our interactions suggests us that for Eastern operations, the cost of power for JKLC is as high as Rs 7.5-8 per unit as against an internal cost of generation of approximately Rs 3.5-4/unit. This translates to savings of approximately Rs 4 per unit of power and approximately Rs 280-300/tonne for East India operations standalone. At UCWL as well, JKLC is likely to deliver a savings of approximately Rs 2.5 per unit as and when its captive power unit starts generation. This is all likely to be completed by mid FY19.
Waste Heat Recovery at East India has already commissioned commercial production in Q3FY18. Management has indicated a savings of about Rs 100/tonne already accumulating from Q3FY18 for eastern operations. This number has the potential to increase as we see capacity ramp-up of the newer grinding unit at East India. On our current volume assumptions for FY20, JKLC is likely to deliver power savings of approximately Rs 1.16 billion by end of FY20, which converges to an EBITDA/tonne of approximately Rs 110 per tonne at consolidated company level. We are also factoring in a 20 per cent reduction in Waste Heat Recovery savings as the WHR will reach optimum utilisations with ramp up of capacity utilisations.
Utilisation scale up
As a ballpark, the minimum savings expected out of every percentage increase in capacity utilisation is Rs 10 per tonne. This is the least and the savings can be much higher and will vary on case to case basis. At consolidated level, for JKLC, we expect utilisations to improve by nearly 10 per cent . However, the picture looks different on a plant-wise basis.
JKLC’s UCWL plant is likely to see utilisation ramp up of 20-25 per cent while the other two plants in North and East India will see an increase of utilisations of 1-10 per cent. Most of the utilisation ramp up will be a function of recent capacity additions. At Rs 10 per tonne of cost savings with scale efficiencies, JKLC will deliver a cost savings of approximately Rs 920 million by FY20 translating to savings of about Rs 90 per tonne.
Logistics
On logistics front, JKLC has opportunities of installing railway sidings at East India. It is also recalibrating its lead distances and relooking and renegotiating its contracts and arrangements with transporters. As a company, JKLC has guided for cost savings of approximately Rs100-150 per tonne in logistics over the next 12-18 months.
Opportunities will logistics costs savings will become more visible as and when all the newer plants of JKLC reach optimum utilisations.
We will now summarise the potential of cost savings for each of the cost heads on a plant wise basis. Our estimates in the following table are conservative and we have not yet factored in any incremental savings on account of further reduction in power consumption/tonne (which is quite possible as JKLC increases production of blended cement – especially composite cement). We have assumed only Rs10 per tonne of savings with every percentage increase in capacity utilisations which can also be higher. We have factored in only 50 per cent of the minimum targeted savings in logistics by the management (Rs 100-150per tonne). Our calculations suggest that we can remain fairly confident of minimum Rs 250per tonne of cost savings through internal measures.
Concrete
Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships
Published
7 hours agoon
February 19, 2026By
admin
Jean-Jacques Bois, President, Nanolike, discusses how real-time data is reshaping cement delivery planning and fleet performance.
As cement producers look to extract efficiency gains beyond the plant gate, real-time visibility and data-driven logistics are becoming critical levers of competitiveness. In this interview with Jean-Jacques Bois, President, Nanolike, we discover how the company is helping cement brands optimise delivery planning by digitally connecting RMC silos, improving fleet utilisation and reducing overall logistics costs.
How does SiloConnect enable cement plants to optimise delivery planning and logistics in real time?
In simple terms, SiloConnect is a solution developed to help cement suppliers optimise their logistics by connecting RMC silos in real time, ensuring that the right cement is delivered at the right time and to the right location. The core objective is to provide real-time visibility of silo levels at RMC plants, allowing cement producers to better plan deliveries.
SiloConnect connects all the silos of RMC plants in real time and transmits this data remotely to the logistics teams of cement suppliers. With this information, they can decide when to dispatch trucks, how to prioritise customers, and how to optimise fleet utilisation. The biggest savings we see today are in logistics efficiency. Our customers are able to sell and ship more cement using the same fleet. This is achieved by increasing truck rotation, optimising delivery routes, and ultimately delivering the same volumes at a lower overall logistics cost.
Additionally, SiloConnect is designed as an open platform. It offers multiple connectors that allow data to be transmitted directly to third-party ERP systems. For example, it can integrate seamlessly with SAP or other major ERP platforms, enabling automatic order creation whenever replenishment is required.
How does your non-exclusive sensor design perform in the dusty, high-temperature, and harsh operating conditions typical of cement plants?
Harsh operating conditions such as high temperatures, heavy dust, extreme cold in some regions, and even heavy rainfall are all factored into the product design. These environmental challenges are considered from the very beginning of the development process.
Today, we have thousands of sensors operating reliably across a wide range of geographies, from northern Canada to Latin America, as well as in regions with heavy rainfall and extremely high temperatures, such as southern Europe. This extensive field experience demonstrates that, by design, the SiloConnect solution is highly robust and well-suited for demanding cement plant environments.
Have you initiated any pilot projects in India, and what outcomes do you expect from them?
We are at the very early stages of introducing SiloConnect in India. Recently, we installed our
first sensor at an RMC plant in collaboration with FDC Concrete, marking our initial entry into the Indian market.
In parallel, we are in discussions with a leading cement producer in India to potentially launch a pilot project within the next three months. The goal of these pilots is to demonstrate real-time visibility, logistics optimisation and measurable efficiency gains, paving the way for broader adoption across the industry.
What are your long-term plans and strategic approach for working with Indian cement manufacturers?
For India, our strategy is to establish strong and reliable local partnerships, which will allow us to scale the technology effectively. We believe that on-site service, local presence, and customer support are critical to delivering long-term value to cement producers.
Ideally, our plan is to establish an Indian entity within the next 24 months. This will enable us to serve customers more closely, provide faster support and contribute meaningfully to the digital transformation of logistics and supply chain management in the Indian cement industry.
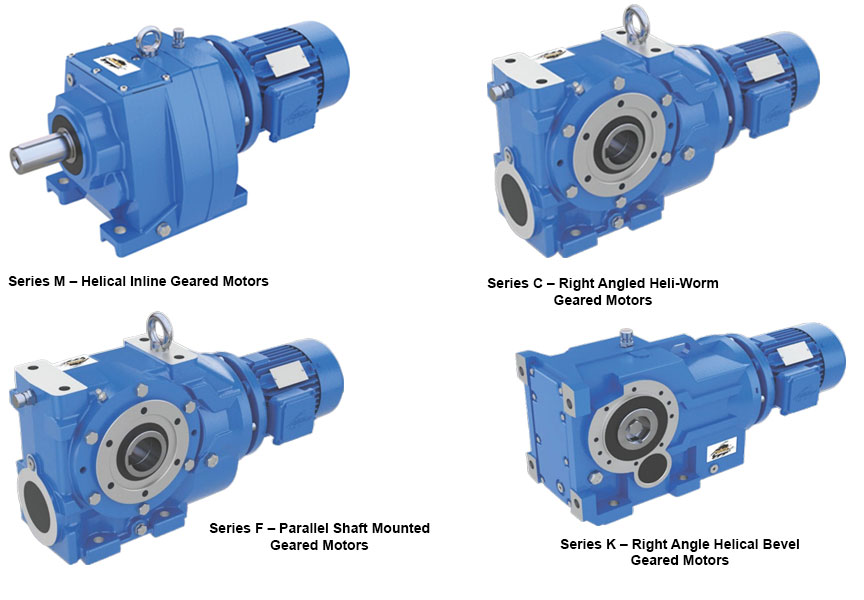
A deep dive into Core Gear Series of products M, C, F and K, by Power Build, and how they represent precision in motion.
At the heart of every high-performance industrial system lies the need for robust, reliable, and efficient power transmission. Power Build answers this need with its flagship geared motor series: M, C, F and K. Each series is meticulously engineered to serve specific operational demands while maintaining the universal promise of durability, efficiency, and performance.
Series M – Helical Inline Geared Motors
Compact and powerful, the Series M delivers exceptional drive solutions for a broad range of applications. With power handling up to 160kW and torque capacity reaching 20,000 Nm, it is the trusted solution for industries requiring quiet operation, high efficiency, and space-saving design. Series M is available with multiple mounting and motor options, making it a versatile choice for manufacturers and OEMs globally.
Series C – Right Angled Heli-Worm Geared Motors
Combining the benefits of helical and worm gearing, the Series C is designed for right-angled power transmission. With gear ratios of up to 16,000:1 and torque capacities of up to 10,000 Nm, this series is optimal for applications demanding precision in compact spaces. Industries looking for a smooth, low-noise operation with maximum torque efficiency rely on Series C for dependable performance.
Series F – Parallel Shaft Mounted Geared Motors
Built for endurance in the most demanding environments, Series F is widely adopted in steel plants, hoists, cranes and heavy-duty conveyors. Offering torque up to 10,000 Nm and high gear ratios up to 20,000:1, this product features an integral torque arm and diverse output configurations to meet industry-specific challenges head-on.
Series K – Right Angle Helical Bevel Geared Motors
For industries seeking high efficiency and torque-heavy performance, Series K is the answer. This right-angled geared motor series delivers torque up to 50,000 Nm, making it a preferred choice in core infrastructure sectors such as cement, power, mining and material handling. Its flexibility in mounting and broad motor options offer engineers the freedom in design and reliability in execution.
Together, these four series reflect Power Build’s commitment to excellence in mechanical power transmission. From compact inline designs to robust right-angle drives, each geared motor is a result of decades of engineering innovation, customer-focused design and field-tested reliability. Whether the requirement is speed control, torque multiplication or space efficiency, Radicon’s Series M, C, F and K stand as trusted powerhouses for global industries.
http://www.powerbuild.in
Call: +919727719344

Pankaj Kejriwal, Whole Time Director and COO, Star Cement, on driving efficiency today and designing sustainability for tomorrow.
In an era where the cement industry is under growing pressure to decarbonise while scaling capacity, Star Cement is charting a pragmatic yet forward-looking path. In this conversation, Pankaj Kejriwal, Whole Time Director and COO, Star Cement, shares how the company is leveraging waste heat recovery, alternative fuels, low-carbon products and clean energy innovations to balance operational efficiency with long-term sustainability.
How has your Lumshnong plant implemented the 24.8 MW Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS), and what impact has it had on thermal substitution and energy costs?
Earlier, the cost of coal in the Northeast was quite reasonable, but over the past few years, global price increases have also impacted the region. We implemented the WHRS project about five years ago, and it has resulted in significant savings by reducing our overall power costs.
That is why we first installed WHRS in our older kilns, and now it has also been incorporated into our new projects. Going forward, WHRS will be essential for any cement plant. We are also working on utilising the waste gases exiting the WHRS, which are still at around 100 degrees Celsius. To harness this residual heat, we are exploring systems based on the Organic Rankine Cycle, which will allow us to extract additional power from the same process.
With the launch of Star Smart Building Solutions and AAC blocks, how are you positioning yourself in the low-carbon construction materials segment?
We are actively working on low-carbon cement products and are currently evaluating LC3 cement. The introduction of autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks provided us with an effective entry into the consumer-facing segment of the industry. Since we already share a strong dealer network across products, this segment fits well into our overall strategy.
This move is clearly supporting our transition towards products with lower carbon intensity and aligns with our broader sustainability roadmap.
With a diverse product portfolio, what are the key USPs that enable you to support India’s ongoing infrastructure projects across sectors?
Cement requirements vary depending on application. There is OPC, PPC and PSC cement, and each serves different infrastructure needs. We manufacture blended cements as well, which allows us to supply products according to specific project requirements.
For instance, hydroelectric projects, including those with NHPC, have their own technical norms, which we are able to meet. From individual home builders to road infrastructure, dam projects, and regions with heavy monsoon exposure, where weather-shield cement is required, we are equipped to serve all segments. Our ability to tailor cement solutions across diverse climatic and infrastructure conditions is a key strength.
How are you managing biomass usage, circularity, and waste reduction across
your operations?
The Northeast has been fortunate in terms of biomass availability, particularly bamboo. Earlier, much of this bamboo was supplied to paper plants, but many of those facilities have since shut down. As a result, large quantities of bamboo biomass are now available, which we utilise in our thermal power plants, achieving a Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) of nearly 60 per cent.
We have also started using bamboo as a fuel in our cement kilns, where the TSR is currently around 10 per cent to 12 per cent and is expected to increase further. From a circularity perspective, we extensively use fly ash, which allows us to reuse a major industrial waste product. Additionally, waste generated from HDPE bags is now being processed through our alternative fuel and raw material (AFR) systems. These initiatives collectively support our circular economy objectives.
As Star Cement expands, what are the key logistical and raw material challenges you face in scaling operations?
Fly ash availability in the Northeast is a constraint, as there are no major thermal power plants in the region. We currently source fly ash from Bihar and West Bengal, which adds significant logistics costs. However, supportive railway policies have helped us manage this challenge effectively.
Beyond the Northeast, we are also expanding into other regions, including the western region, to cater to northern markets. We have secured limestone mines through auctions and are now in the process of identifying and securing other critical raw material resources to support this expansion.
With increasing carbon regulations alongside capacity expansion, how do you balance compliance while sustaining growth?
Compliance and growth go hand in hand for us. On the product side, we are working on LC3 cement and other low-carbon formulations. Within our existing product portfolio, we are optimising operations by increasing the use of green fuels and improving energy efficiency to reduce our carbon footprint.
We are also optimising thermal energy consumption and reducing electrical power usage. Notably, we are the first cement company in the Northeast to deploy EV tippers at scale for limestone transportation from mines to plants. Additionally, we have installed belt conveyors for limestone transfer, which further reduces emissions. All these initiatives together help us achieve regulatory compliance while supporting expansion.
Looking ahead to 2030 and 2050, what are the key innovation and sustainability priorities for Star Cement?
Across the cement industry, carbon capture is emerging as a major focus area, and we are also planning to work actively in this space. In parallel, we see strong potential in green hydrogen and are investing in solar power plants to support this transition.
With the rapid adoption of solar energy, power costs have reduced dramatically – from 10–12 per unit to around2.5 per unit. This reduction will enable the production of green hydrogen at scale. Once available, green hydrogen can be used for electricity generation, to power EV fleets, and even as a fuel in cement kilns.
Burning green hydrogen produces only water and oxygen, eliminating carbon emissions from that part of the process. While process-related CO2 emissions from limestone calcination remain a challenge, carbon capture technologies will help address this. Ultimately, while becoming a carbon-negative industry is challenging, it is a goal we must continue to work towards.

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Compliance and growth go hand in h and

Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence

FORNNAX Appoints Dieter Jerschl as Sales Partner for Central Europe

Our strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships

Power Build’s Core Gear Series

Compliance and growth go hand in h and

Turning Downtime into Actionable Intelligence






















