Concrete
CCU for Decarbonising the Cement Industry
Published
4 years agoon
By
admin
Dr BN Mohapatra, Director General, National Council for Cement and Building Materials (NCCBM), expounds on the importance of carbon capture, utilisation and storage for achieving net zero goals for the industry.
Dr BN Mohapatra, Director General, National Council for Cement and Building Materials (NCCBM), expounds on the importance of carbon capture, utilisation and storage for achieving net zero goals for the industry.
Honourable Prime Minister of India Shri Narendra Modi has made the pledge to cut the CO2 emissions in the COP 26 summit at Glasgow in November. The new climate action targets ‘Panchamrit’ by India included:
- a net zero target for India by the year 2070;
- installing non-fossil fuel electricity capacity of 500 GW by 2030;
- sourcing 50 per cent of energy requirement from renewables by 2030;
- reducing 1 billion tonnes of projected emissions from now till 2030; and
- achieving carbon intensity reduction of 45 per cent over 2005 levels by 2030.
Globally, the cement sector generates about 7 per cent of the total anthropogenic emissions. The sources of CO2 emissions in cement manufacture are categorised as direct sources, which includes calcination (55 per cent to 60 per cent) and combustion (25 per cent to 30 per cent) and indirect sources of CO2 including electricity (8 per cent to 10 per cent) and transportation (2 per cent to 5 per cent).
In hard-to-abate sectors like cement, it is technologically very difficult to reduce the process related CO2 emissions. The Indian cement industry has been working on the issue of its GHG emissions and has brought down the CO2 emission factor from 1.12 t of CO2/t of cement in 1996 to 0.670 t of CO2/t of cement in 2017. In October 2021, Global Cement and Concrete Association (GCCA) published a Cement and Concrete Roadmap 2050 for the
Net Zero Concrete. The leading cement and concrete companies in India including major cement companies in India like UltraTech Cement Ltd., Holcim Group, Shree Cement Ltd., Dalmia Cement (B) Ltd.,
JK Cement Ltd., JSW Cement, Orient Cement Ltd. have accepted the goal to achieve Net Zero Concrete by 2050 and committed to fully contribute to building the sustainable world of tomorrow. Dalmia Cement (Bharat) Ltd., the fourth largest cement company in India has committed to become Carbon Negative by 2040 and working on its roadmap to use
100 per cent biomass and capturing the biogenic CO2 emissions.
The journey towards decarbonisation of Indian cement industry started in 2012 with preparation of a Low Carbon Technology Roadmap specifically for the Indian cement industry, when International Energy Agency (IEA) and Cement Sustainability Initiative (CSI), in collaboration with the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and the National Council for Cement and Building Materials (NCB) prepared this document.
The identified levers in the low carbon technology roadmap of Indian cement industry are:
i. Substitution of Clinker,
ii. Alternate Fuel and Raw Materials,
iii. Improving Energy Efficiency,
iv. Installation of Waste Heat Recovery and
v. Newer technologies like Renewable Energy, Novel Cements, Carbon Capture and Storage/Utilisation.
The first four levers have already been implemented by the Indian cement industry and the impact has already been reflected in the reduction of CO2 emission factor from cement industry. The specific direct CO2 emissions of major cement companies in the year 2020-21 is given in table below:

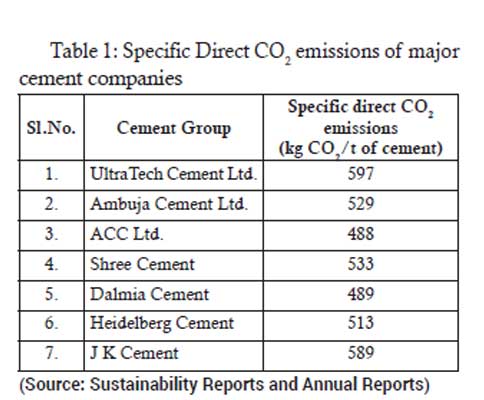
One of the important challenges for decarbonisation of the cement industry worldwide is to reduce the process emissions arising out of calcination of limestone. Therefore, to achieve the target of Net Zero cement industry, implementation of Carbon Capture and Utilisation is required. Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) or Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is the process of separating Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from flue gases of point sources such as stacks of cement plants, power plants etc., transporting it to a storage site or utilisation site, and depositing it or utilising it, thereby not letting CO2 enter the atmosphere for mitigation of global warming.
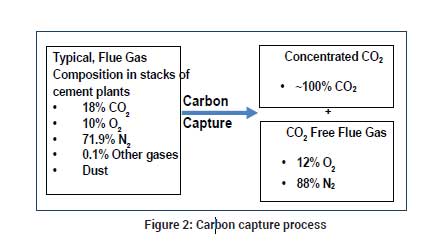
The first stage of CCU is CO2 capture i.e., separating CO2 from the flue gases coming out of the stacks of cement kilns. A typical composition of flue gas from stacks of cement plants contains 18 per cent CO2, 10 per cent O2, 71.9 per cent N2 and 0.1 per cent Other gases. In the carbon capture process, the CO2 is separated as concentrated CO2 for storage and transportation and remaining CO2 free flue gases are emitted to the atmosphere as shown in figure 2.
Carbon capture techniques can be classified in three categories:
- Post-combustion processes
- Pre-combustion process
- Oxy-fuel combustion process
Post-combustion carbon capture process involves extracting CO2 from the flue gas after combustion of fossil fuels. Out of the three capture techniques, post-combustion is well established and commercially available. The advantage of this technique is that it does not interfere with the plant process. The various methods of post-combustion carbon capture are:
- Chemical absorption: Monoethanolamine (MEA)
- Calcium looping
- Chilled ammonia process
- Solvent Based absorption
Oxy-fuel combustion involves supply of complete Oxygen to replace Air. Burner, calciner and clinker cooler have been successfully tested under oxyfuel conditions, and the technology is being brought forward. Also, thyssenkrupp has demonstrated a pilot scale oxyfuel retrofit and greenfield cement kilns.
Pre-combustion involves converting coal to hydrogen through gasification. This hydrogen is derived from fossil fuel and called Grey Hydrogen. A cement kiln at the British Ribblesdale plant, UK, by HeidelbergCement successfully tested use of Grey Hydrogen in its main burner.
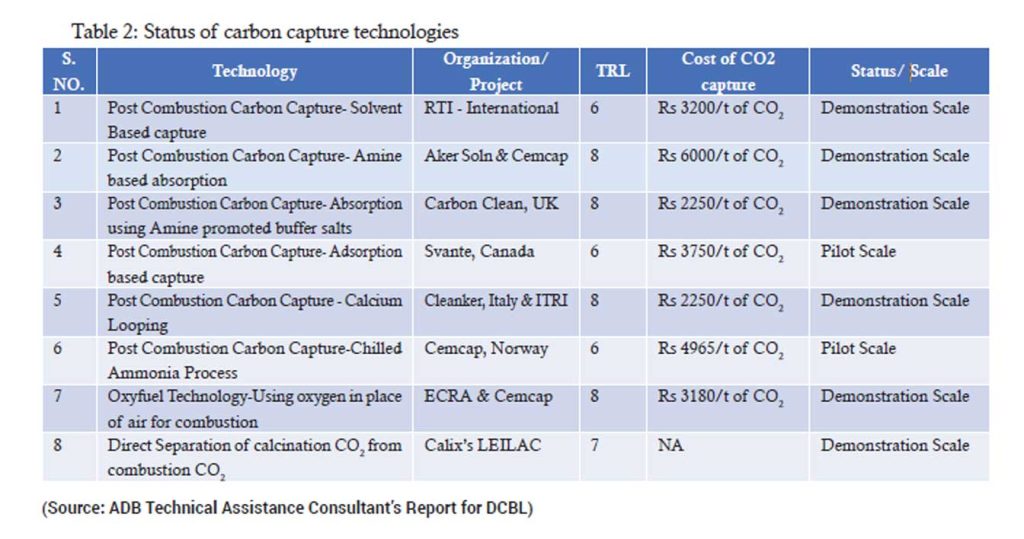
Several institutes and start-ups worldwide are working to find cost effective energy efficient ways to capture CO2 from flue gases. The status of carbon capture technologies all over the world is shown in table 2.
After capturing, the CO2 is transported to the utilisation/storage site. There are several utilisation pathways of captured CO2 like mineralisation, production of chemicals like urea, methanol, methane etc., as refrigerant, as inerting agent, for fire suppression, for enhanced fuel recovery, in production of plastics, for biological conversion to algae, for use in food products like beverages etc. as shown in Fig 3.

Dalmia Cement (B) Ltd. in association with Asian Development Bank has carried out a Pre-feasibility study to assess the techno-economic pre-feasibility of the CCUS options in its Ariyalur cement plant. The study found urea and mineralization as the top-ranking options for CO2 utilisation but dropped Mineral carbonation as the CO2 derived cement will require longer time for technical approval. Urea production was selected as the best option for utilisation. Similar type of study at industry level is required to assess the potential utilisation when the carbon capture will be implemented in all cement plants. Other than utilisation of captured CO2, the long-term storage of CO2 in deep subsurface rock formations is the option which will not be financially viable.
LeadIT initiative
For promoting low-carbon transition especially in the hard-to-abate sectors like Iron & Steel, Aluminium, Cement and Concrete, petrochemicals, fertilisers, bricks, heavy-duty transport, etc. through active participation of private sector companies, Government of Sweden and India launched an initiative ‘Leadership for Industry Transition (LeadIT)’ at the UN Climate Action Summit in New York in 2019. Stockholm Environment Institute hosts the Secretariat of LeadIT. Under the LeadIT initiative, preparation of the sectoral roadmap for the cement and steel sector in India has been undertaken.

In May 2022, DG-NCCBM as part of Indian Delegation to Sweden visited Heidelberg Cement Ltd.’s Slite Cement Plant at Gotland, Sweden and SSAB Steel Plant and the pilot plant of the HYBRIT Project at Lulea, Sweden Under LeadIT initiative as shown in Fig 4 and 5.
The Slite cement plant is Sweden’s largest cement factory with a production capacity of 2.5 million tonnes per year and is currently the second-largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in Sweden, responsible for three per cent of all its CO2 emissions. HeidelbergCement is upgrading its Slite Cement plant to develop it into World’s first ‘Carbon-Neutral Cement Plant’, and it will be having facility to capture up to 1.8 million tonnes of CO2 annually, which corresponds to the plant’s 100 per cent CO2 emissions and store the same in an underground long storage facility. The pre-feasibility study for a Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) facility at the Slite Cement Plant has been completed recently and got promising results, which were presented during the visit. In the pre-feasibility study, amine capture was found to be the most suitable technology for Post-combustion Carbon Capture. It was informed that the implementation of the carbon capture facility will require some modification to the plant. As capturing CO2 is an energy intensive process, the power demand of the Slite Cement Plant is also expected to rise significantly. The pre-feasibility study has identified Geological sequestration, which involves the process of storing carbon dioxide by injecting the captured CO2 from a cement plant into deep subsurface rock formations for long-term storage. To store the captured CO2 from the Slite cement plant, the carbon dioxide will be buried under the North Sea in cavities created by the extraction of fossil fuels.
HYBRIT is a partnership between LKAB (Europe’s largest iron ore producer), Vattenfall (one of Europe’s largest energy companies) and SSAB (steel producer) formed to develop hydrogen-based production of fossil free sponge iron production, in order to reduce the negative climate effects of steel production. Using HYBRIT technology, SSAB aims to replace coking coal, traditionally needed for ore-based steelmaking, with fossil-free electricity and hydrogen, resulting in the world›s first fossil-free steelmaking technology. The pilot plant using fossil-free hydrogen at the SSAB site in Luleå, Sweden started in 2020. This facility demonstrates the feasibility and scalability of the new technology replacing coal by hydrogen in the steel production process and aims to produce 1.3 million tonnes of steel by the year 2026.
The slite cement carbon capture plant is targeted to start full scale operation by 2030 to capture the plant’s 100 per cent CO2 emissions. The plant officials informed the visiting delegation that a 400,000t/yr CCS system is being built by Norcem, a subsidiary of Heidelberg Cement, at its Brevik cement plant in Norway. The CSS facility at Brevik is presently under construction and will start operating by 2024. The Slite cement plant will have four times the capacity of that at the Brevik plant. Additionally, the use of bio-based fuels in the cement production at Slite will be increased.
For implementation of CCU in the Indian cement industry, such demonstration projects need to be implemented in a few plants, which will help in creating expertise in the cement industry to run CCU facilities and will also encourage other cement companies to move in this direction. There is a need to assess the impact due to implementation of CCU in all the integrated plants in terms of increase in cost of product due to high capture cost, avenues for utilisation of captured CO2, integration in existing plants and funding required for implementation at plant level.
About the author:
Dr BN Mohapatra is the Director General of National Council for Cement and Building Materials (NCCBM). He is a PhD in Cement Mineral Chemistry and the chairman of the Cement Sectoral Committee of the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE). He is also a member of various technical committees of Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), member of Research Committee of CSIR-National Physical Laboratory (NPL) and member of Research Advisory Committee of DISIR and AKS University.
Concrete
Merlin Prime Spaces Acquires 13,185 Sq M Land Parcel In Pune
Rs 273 crore purchase broadens the developer’s Pune presence
Published
12 hours agoon
March 6, 2026By
admin
Merlin Prime Spaces (MPS) has acquired a 13,185 sq m land parcel in Pune for Rs 273 crore, marking a notable expansion of its footprint in the city.
The transaction value converts to Rs 2,730 mn or Rs 2.73 bn.
The parcel is located in a strategic area of Pune and the firm described the acquisition as aligned with its growth objectives.
The deal follows recent activity in the region and will be watched by investors and developers.
MPS said the acquisition will support its planned development pipeline and enable delivery of commercial and residential space to meet local demand.
The company expects the site to provide flexibility in product design and phased development to respond to market conditions.
The move reflects an emphasis on land ownership in key suburban markets.
The emphasis on land acquisition reflects a strategy to secure inventory ahead of demand cycles.
The purchase follows a period of sustained investor interest in Pune real estate, driven by expanding office ecosystems and residential demand from professionals.
MPS will integrate the new holding into its existing portfolio and plans to engage with local authorities and stakeholders to progress approvals and infrastructure readiness.
No financial partners were disclosed in the announcement.
The firm indicated that timelines will depend on approvals and prevailing market conditions.
Analysts note that strategic land acquisitions at scale can help developers manage costs and timelines while preserving optionality for future projects.
MPS will now hold an enlarged land bank in the region as it pursues growth, and the acquisition underlines continued corporate appetite for measured expansion in second tier cities.
The company intends to move forward with detailed planning in the coming months.
Stakeholders will assess how the site is positioned relative to existing infrastructure and connectivity.
Concrete
Adani Cement and Naredco Partner to Promote Sustainable Construction
Collaboration to focus on skills, technology and greener practices
Published
12 hours agoon
March 6, 2026By
admin
Adani Cement has entered a strategic partnership with the National Real Estate Development Council (Naredco) to support India’s construction needs with a focus on sustainability, workforce capability and modern building technologies. The collaboration brings together Adani Cement’s building materials portfolio, research and development strengths and technical expertise with Naredco’s nationwide network of more than 15,000 member organisations. The agreement aims to address evolving demand across housing, commercial and infrastructure sectors.
Under the partnership, the organisations will roll out skill development and certification programmes for masons, contractors and site supervisors, with training to emphasise contemporary construction techniques, safety practices and quality standards. The programmes are intended to improve project execution and on-site efficiency and to raise labour productivity through standardised competencies. Emphasis will be placed on practical training and certification pathways that can be scaled across regions.
The alliance will function as a platform for knowledge sharing and technology exchange, facilitating access to advanced concrete solutions, innovative construction practices and modern materials. The effort is intended to enhance structural durability, execution quality and environmental responsibility across developments while promoting adoption of low-carbon technologies and green cement alternatives. Companies expect these measures to contribute to longer term resilience of built assets.
Senior executives conveyed that the partnership reflects a shared commitment to strengthening quality and sustainability in construction and that closer engagement with developers will help integrate advanced materials and technical support throughout the project lifecycle. Leadership noted the need for responsible construction practices as urbanisation accelerates and indicated that the association should encourage wider adoption of green building norms and collaboration within the real estate and construction ecosystem.
The organisations said they will also explore integrated building solutions, including ready-mix concrete offerings, while supporting initiatives aligned with affordable and inclusive housing. The partnership will progress through engagements, conferences and joint training programmes targeting rapidly urbanising cities and growth centres where demand for efficient and environmentally responsible construction grows. Naredco, established under the aegis of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, will leverage its policy and advocacy role to support implementation.

Operational excellence in cement is no longer about producing more—it is about producing smarter, cleaner and more reliably, where cost per tonne meets carbon per tonne.
Operational excellence in cement has moved far beyond the old pursuit of ‘more tonne’. The new benchmark is smarter, cleaner, more reliable production—delivered with discipline across process, people and data. In an industry where energy can account for nearly 30 per cent of manufacturing cost, even marginal gains translate into meaningful value. As Dr SB Hegde, Professor, Jain College of Engineering & Technology, Hubli and Visiting Professor, Pennsylvania State University, USA, puts it, “Operational excellence… is no longer about producing more. It is about producing smarter, cleaner, more reliably, and more sustainably.” The shift is structural: carbon per tonne will increasingly matter as much as cost per tonne, and competitiveness will be defined by the ability to stabilise operations while steadily lowering emissions.
From control rooms to command centres
The modern cement plant is no longer a handful of loops watched by a few operators. Control rooms have evolved from a few hundred signals to thousands—today, up to 25,000 signals can compete for attention. Dr Rizwan Sabjan, Head – Global Sales and Proposals, Process Control and Optimization, Fuller Technologies, frames the core problem plainly: plants have added WHRS circuits, alternative fuels, higher line capacities and tighter quality expectations, but human attention remains finite. “It is very impossible for an operator to operate the plant with so many things being added,” he says. “We need somebody who can operate 24×7… without any tiredness, without any distraction… The software can do that for us better.”
This is where advanced process control shifts from ‘automation spend’ to a financial lever. Dr Hegde underlines the logic: “Automation is not a technology expense. It is a financial strategy.” In large kilns, a one per cent improvement is not incremental—it is compounding.
Stability is the new productivity
At the heart of operational excellence lies stability. Not because stability is comfortable, but because it is profitable—and increasingly, low-carbon. When setpoints drift and operators chase variability, costs hide in refractory damage, thermal shocks, stop-start losses and quality swings. Dr Sabjan argues that algorithmic control can absorb process disturbances faster than any operator, acting as ‘a co-pilot or an autopilot’, making changes ‘as quick as possible’ rather than waiting for manual intervention. The result is not just fuel saving—it is steadier operation that extends refractory life and reduces avoidable downtime.
The pay-off can be seen through the lens of variability: manual operation often amplifies swings, while closed-loop optimisation tightens control. As Dr Sabjan notes, “It’s not only about savings… there are many indirect benefits, like increasing the refractory life, because we are avoiding the thermal shocks.”
Quality control
If stability is the base, quality is the multiplier. A high-capacity plant can dispatch enormous volumes daily, and quality cannot be a periodic check—it must be continuous. Yet, as Dr Sabjan points out, the biggest error is not in analysis equipment but upstream: “80 per cent of the error is happening at the sampling level.” If sampling is inconsistent, even the best XRF and XRD become expensive spectators.
Automation closes the loop by standardising sample collection, transport, preparation, analysis and corrective action. “We do invest a lot of money on analytical equipment like XRD and XRF, but if it is not put on the closed loop then there’s no use of it,” he says, because results become person-dependent and slow.
Raju Ramachandran, Chief Manufacturing Officer (East), Nuvoco Vistas Corp, reinforces the operational impact from the plant floor: “There’s a stark difference in what a RoboLab does… ensuring that the consistent quality is there… starts right from the sample collection.” For him, automation is not about removing people; it is about making outcomes repeatable.
Human-centric automation
One of the biggest barriers to performance is not hardware—it is fear. Dr Sabjan describes a persistent concern that digital tools exist to replace operators. “That’s not the way,” he says. “The technology is here to help operator… not to replace them… but to complement them.” The plants that realise this early tend to sustain performance because adoption becomes collaborative rather than forced.
Dr Hegde adds an important caveat: tools can mislead without competence. “If you don’t have the knowledge about the data… this will mislead you… it is like… using ChatGPT… it may tell the garbage.” His point is not anti-technology; it is pro-capability. Operational excellence now requires multidisciplinary teams—process, chemistry, physics, automation and reliability—working as one.
GS Daga, Managing Director, SecMec Consultants, takes the argument further, warning that the technology curve can outpace human readiness: “Our technology movement AI will move fast, and our people will be lagging behind.” For him, the industry’s most urgent intervention is systematic skilling—paired with the environment to apply those skills. Without that, even high-end systems remain underutilised.
Digital energy management
Digital optimisation is no longer confined to pilots; its impact is increasingly quantifiable. Raghu Vokuda, Chief Digital Officer, JSW Cement, describes the outcomes in practical terms: reductions in specific power consumption ‘close to 3 per cent to 7 per cent’, improvements in process stability ‘10 per cent to 20 per cent’, and thermal energy reductions ‘2–5 per cent’. He also highlights value beyond the process line—demand optimisation through forecasting models can reduce peak charges, and optimisation of WHRS can deliver ‘1 per cent to 3 per cent’ efficiency gains.
What matters is the operating approach. Rather than patchwork point solutions, he advocates blueprinting a model digital plant across pillars—maintenance, quality, energy, process, people, safety and sustainability—and then scaling. The difference is governance: defined ownership of data, harmonised OT–IT integration, and dashboards designed for each decision layer—from shopfloor to plant head to network leadership.
Predictive maintenance
Reliability has become a boardroom priority because the cost of failure is blunt and immediate. Dr Hegde captures it crisply: “One day of kiln stoppage can cost several crores.” Predictive maintenance and condition monitoring change reliability from reaction to anticipation—provided plants invest in the right sensors and a holistic architecture.
Dr Sabjan stresses the need for ‘extra investment’ where existing instrumentation is insufficient—kiln shell monitoring, refractory monitoring and other critical measurements. The goal is early warning: “How to have those pre-warnings… where the failures are going to come… and then ensure that the plant availability is high, the downtime is low.”
Ramachandran adds that IoT sensors are increasingly enabling early intervention—temperature rise in bearings, vibration patterns, motor and gearbox signals—moving from prediction to prescription. The operational advantage is not only fewer failures, but planned shutdowns: “Once the shutdown is planned in advance… you have lesser… unpredictable downtimes… and overall… you gain on the productivity.”
Alternative fuels and raw materials
As decarbonisation tightens, AFR becomes central—but scaling it is not simply a procurement decision. Vimal Kumar Jain, Technical Director, Heidelberg Cement, frames AFR as a structured programme built on three foundations: strong pre-processing infrastructure, consistent AFR quality, and a stable pyro process. “Only with the fundamentals in place can AFR be scaled safely—without compromising clinker quality or production stability.”
He also flags a ground reality: India’s AFR streams are often seasonal and variable. “In one season to another season, there is major change… high variation in the quality,” he says, making preprocessing capacity and quality discipline mandatory.
Ramachandran argues the sector also needs ecosystem support: a framework for AFR preprocessing ‘hand-in-hand’ between government and private players, so fuels arrive in forms that can be used efficiently and consistently.
Design and execution discipline
Operational excellence is increasingly determined upstream—by the choices made in concept, layout, technology selection, operability and maintainability. Jain puts it unambiguously: “Long term performance is largely decided before the plant is commissioned.” A disciplined design avoids bottlenecks that are expensive to fix later; disciplined execution ensures safe, smooth start-up with fewer issues.
He highlights an often-missed factor: continuity between project and operations teams. “When knowledge transfer is strong and ownership carries beyond commissioning, the plant stabilises much faster… and lifecycle costs reduce significantly.”
What will define the next decade
Across the value chain, the future benchmark is clear: carbon intensity. “Carbon per ton will matter as much as cost per ton,” says Dr Hegde. Vokuda echoes it: the industry will shift from optimising cost per tonne to carbon per ton.
The pathway, however, is practical rather than idealistic—low-clinker and blended cements, higher thermal substitution, renewable power integration, WHRS scaling and tighter energy efficiency. Jain argues for policy realism: if blended cement can meet quality, why it shall not be allowed more widely, particularly in government projects, and why supplementary materials cannot be used more ambitiously where performance is proven.
At the same time, the sector must prepare for CCUS without waiting for it. Jain calls for CCUS readiness—designing plants so capture can be added later without disruptive retrofits—while acknowledging that large-scale rollout may take time as costs remain high.
Ultimately, operational excellence will belong to plants that integrate—not isolate—the levers: process stability, quality automation, structured AFR, predictive reliability, disciplined execution, secure digitalisation and continuous learning. As Dr Sabjan notes, success will not come from one department owning the change: “Everybody has to own it… then only… the results could be wonderful.”
And as Daga reminds the industry, the future will reward those who keep their feet on the ground while adopting the new: “I don’t buy technology for the sake of technology. It has to make a commercial sense.” In the next decade, that commercial sense will be written in two numbers—cost per tonne and carbon per tonne—delivered through stable, skilled and digitally disciplined operations.

Merlin Prime Spaces Acquires 13,185 Sq M Land Parcel In Pune

Adani Cement and Naredco Partner to Promote Sustainable Construction

Operational Excellence Redefined!

World Cement Association Annual Conference 2026 in Bangkok

Assam Chief Minister Opens Star Cement Plant In Cachar

Merlin Prime Spaces Acquires 13,185 Sq M Land Parcel In Pune

Adani Cement and Naredco Partner to Promote Sustainable Construction

Operational Excellence Redefined!

World Cement Association Annual Conference 2026 in Bangkok

Assam Chief Minister Opens Star Cement Plant In Cachar
Trending News
-

 Economy & Market4 weeks ago
Economy & Market4 weeks agoFORNNAX Appoints Dieter Jerschl as Sales Partner for Central Europe
-

 Concrete2 weeks ago
Concrete2 weeks agoRefractory demands in our kiln have changed
-

 Concrete2 weeks ago
Concrete2 weeks agoDigital supply chain visibility is critical
-

 Concrete2 weeks ago
Concrete2 weeks agoOur strategy is to establish reliable local partnerships















